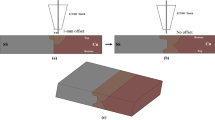
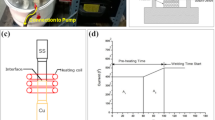
Abstract
The Cu–SS welded structures are widely used in nuclear and power generation industries. Various solid state and fusion welding techniques have been experimented for welding Cu–SS with resultant phenomena of low joining strength in solid state and generation of crack in fusion. Of late application of induction heating as a joining technique is gaining momentum in view of its low maintenance, high production rate and cost effectiveness. In consideration of the above facts, in this study, induction heating for welding Cu–SS is experimented in ambient condition under varied settings of load and current. Although few micro-cracks were observed in SEM images, successful joining between copper and stainless steel was achieved. Some compounds like FeCu4, Cr3Fe, Cu(Fe2O4) and CrO were detected by XRD near the weld interface. The microhardness increased near the interface in comparison to the base metals. The interface microhardness was increased with current and load. Similarly, the tensile strength was also increased for higher values of process parameters. Highest strength of 220 MPa was obtained at 2 kg load and 650 A current. Failure of welded joint under tension took place by ductile–brittle fracture mode.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yilmaz, O., & Çelik, H. (2003). Electrical and thermal properties of the interface at diffusion-bonded and soldered 304 stainless steel and copper bimetal. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,141, 67–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(03)00029-3.
Durgutlu, A., Gülenç, B., & Findik, F. (2005). Examination of copper/stainless steel joints formed by explosive welding. Materials and Design,26, 497–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2004.07.021.
He, J., Sirois, D., Li, S., Sullivan, M., Wikle, C., & Chin, B. A. (2016). Ballistic impact welding of copper to low carbon steel. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,232, 165–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.01.029.
Luo, J., Xiang, J., Liu, D., Li, F., & Xue, K. (2012). Radial friction welding interface between brass and high carbon steel. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,212, 385–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2011.10.001.
Kim, Y. G., Jo, B. J., Kim, J. S., & Kim, I. J. (2017). A study on dissimilar welding of aluminum alloy and advanced high strength steel by spot welding process. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing,18, 121–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-017-0015-6.
Liang, X., Yuan, X., Wang, H., Li, X., Li, C., & Pan, X. (2016). Microstructure, mechanical properties and failure mechanisms of resistance spot welding joints between ultra high strength steel 22MnB5 and galvanized steel HSLA350. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing,17, 1659–1664. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-016-0192-8.
Cheng, Z., Huang, J., Ye, Z., Chen, Y., Yang, J., & Chen, S. (2019). Microstructures and mechanical properties of copper–stainless steel butt-welded joints by MIG-TIG double-sided arc welding. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,265, 87–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.10.007.
Wang, Y. Q., Md, A., & Afsar, J. I. S. (2009). Optimization of brazing conditions for OFHC Cu and ASTM A501 low carbon steel by Taguchi method. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing,10, 97–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-009-0053-9.
Magnabosco, I., Ferro, P., Bonollo, F., & Arnberg, L. (2006). An investigation of fusion zone microstructures in electron beam welding of copper–stainless steel. Materials Science and Engineering A,424, 163–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.03.096.
Chen, S., Huang, J., Xia, J., Zhao, X., & Lin, S. (2015). Influence of processing parameters on the characteristics of stainless steel/copper laser welding. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,222, 43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2015.03.003.
Mai, T. A., & Spowage, A. C. (2004). Characterisation of dissimilar joints in laser welding of steel–kovar, copper–steel and copper–aluminium. Materials Science and Engineering A,374, 224–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2004.02.025.
Yao, C., Xu, B., Zhang, X., Huang, J., Fu, J., & Wu, Y. (2009). Interface microstructure and mechanical properties of laser welding copper–steel dissimilar joint. Optics and Lasers in Engineering,47, 807–814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2009.02.004.
Saranarayanan, R., Lakshminarayanan, A. K., & Venkatraman, B. (2019). A combined full-field imaging and metallography approach to assess the local properties of gas tungsten arc welded copper–stainless steel joints. Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering,19, 251–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acme.2018.08.009.
Shiri, S. G., Nazarzadeh, M., Sharifitabar, M., & Afarani, M. S. (2012). Gas tungsten arc welding of CP-copper to 304 stainless steel using different filler materials. Transactions of the Nonferrous Metals Society of China,22, 2937–2942. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61553-7.
Yan, P., Guüngör, Ö. E., Thibaux, P., & Bhadeshia, H. K. D. H. (2010). Induction welding and heat treatment of steel pipes: Evolution of crystallographic texture detrimental to toughness. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining,15, 137–141. https://doi.org/10.1179/136217109X12568132624163.
Noda, T., Shimizu, T., Okabe, M., & Iikubo, T. (1997). Joining of TiAl and steels by induction brazing. Materials Science and Engineering A,239–240, 613–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(97)00638-2.
Jiang, C., Chen, H., Wang, Q., & Li, Y. (2016). Effect of brazing temperature and holding time on joint properties of induction brazed WC-Co/carbon steel using Ag-based alloy. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,229, 562–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2015.09.044.
Li, F., Ning, J., & Liang, S. Y. (2019). Analytical modeling of the temperature using uniform moving heat source in planar induction heating process. Applied Sciences,9, 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9071445.
Li, F., Li, X., Zhu, T., & Rong, Y. K. (2013). Numerical simulation of the moving induction heating process with magnetic flux concentrator. Advances in Mechanical Engineering,5, 907295. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/907295.
Li, F., Li, X., Qin, X., & Rong, Y. K. (2018). Study on the plane induction heating process strengthened by magnetic flux concentrator based on response surface methodology. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology,32(5), 2347–2356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-018-0446-8.
Di Luozzo, N., Fontana, M., & Arcondo, B. (2012). Modelling of induction heating of carbon steel tubes: Mathematical analysis, numerical simulation and validation. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,536, 564–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.12.084.
Khazaal, M. H., Abdulbaqi, I. M., & Thejel, R. H. (2016). Modeling, design and analysis of an induction heating coil for brazing process using FEM. In Proceedings of the 2016 Al-Sadey international conference on multidisciplinary in IT and communication science and applications, Baghdad, Iraq, 9–10 May 2016.
Barka, N. (2017). Study of the machine parameters effects on the case depths of 4340 spur gear heated by induction-2D model. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,93, 1173–1181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0586-5.
Nguyen, T. T., Yang, Y. S., & Kim, J. W. (2014). An artificial neural network system for heating-path prediction in induction heating process for concave curved surface forming. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing,15, 259–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-014-0333-x.
Park, H. S., & Dang, X. P. (2012). Optimization of the in-line induction heating process for hot forging in terms of saving operating energy. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing,13, 1085–1093. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-012-0142-z.
Nguyen, T. T., Yang, Y. S., Kim, K. S., & Hyun, C. M. (2011). Prediction of heating-line paths in induction heating process using the artificial neural network. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing,12, 105–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-011-0013-z.
Choi, J. K., Park, K. S., & Lee, S. S. (2018). Prediction of high-frequency induction hardening depth of an AISI 1045 specimen by finite element analysis and experiments. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing,19, 1821–1827. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-018-0210-0.
Bhogendro Meitei, R. K., Maji, P., Samadhiya, A., Ghosh, S. K., Roy, B. S., Das, A. K., et al. (2018). A study on induction welding of mild steel and copper with flux under applied load condition. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,34, 435–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.06.029.
Butrymowicz, D. B., Manning, J. R., & Read, M. E. (1976). Diffusion in copper and copper alloys part IV. Diffusion in systems involving elements of group VIII. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data,5, 103–200. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.555528.
Huang, K., & Logé, R. E. (2016). A review of dynamic recrystallization phenomena in metallic materials. Materials and Design,111, 548–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.09.012.
Ji, X., Mirkoohi, E., Ning, J., & Liang, S. Y. (2020). Analytical modeling of post-printing grain size in metal additive manufacturing. Optics and Lasers in Engineering,124, 105805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2019.105805.
Thangarasu, A., Murugan, N., & Dinaharan, I. (2014). Production and wear characterization of AA6082–TiC surface composites by friction stir processing. Procedia Engineering,97, 590–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2014.12.287.
Bahrami, M., Dehghani, K., & Besharati Givi, M. K. (2014). A novel approach to develop aluminum matrix nano-composite employing friction stir welding technique. Materials & Design,53, 217–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.07.006.
Sharifitabar, M., Sarani, A., Khorshahian, S., & Afarani, M. S. (5052Al). Fabrication of 5052Al/Al2O3 nanoceramic particle reinforced composite via friction stir processing route. Materials and Design,32(8–9), 4164–4172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2011.04.048.
Moeser, M. (2016). Fractography with the SEM (failure analysis), https://martinmoeser.de/2016. Accessed on 01 May 2016.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhogendro Meitei, R.K., Maji, P., Samadhiya, A. et al. An Experimental Investigation on Joining of Copper and Stainless Steel by Induction Welding Technique. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 21, 613–621 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-019-00284-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-019-00284-w