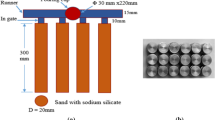
Abstract
This research demonstrates the application of machine learning models and statistics methods in predicting and analyzing dry sliding wear rates on novel copper-based surface composites. Boron nitride particles of varying fractions was deposited experimentally over the copper surface through friction stir processing. Experimental and statistical analysis proved that the presence of BN particles can reduce wear rate considerably. Analysis of worn-out surface revealed a mild adhesive wear during low load condition and an abrasive mode of wear during higher load conditions. Artificial neural network based feed forward back propagation model with topology 4-7-1 was modeled and prediction profiles displayed good agreement with experimental outcomes.
Graphic Abstract















Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.C. Tjong, K.C. Lau, Tribological behaviour of SiC particle-reinforced copper matrix composites. Mater. Lett. 43, 274–280 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-577X(99)00273-6
K. Song, X. Guo, S. Liang, P. Zhao, Y. Zhang, Relationship between interfacial stress and thermal expansion coefficient of copper–matrix composites with different reinforced phases. Mater. Sci. Technol. 30, 171–175 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1179/1743284713Y.0000000332
V. Rajkovic, D. Bozic, J. Stasic, H. Wang, M.T. Jovanovic, Processing, characterization and properties of copper-based composites strengthened by low amount of alumina particles. Powder Technol. 268, 392–400 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2014.08.051
B. Chen, J. Yang, Q. Zhang, H. Huang, H. Li, H. Tang et al., Tribological properties of copper-based composites with copper coated NbSe2 and CNT. Mater. Des. 75, 24–31 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.03.012
G.A. Bagheri, The effect of reinforcement percentages on properties of copper matrix composites reinforced with TiC particles. J. Alloys Compd. 676, 120–126 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.03.085
M. Kestursatya, J.K. Kim, P.K. Rohatgi, Wear performance of copper-graphite composite and a leaded copper alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 339, 150–158 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(02)00114-4
D. Nayak, M. Debata, Effect of composition and milling time on mechanical and wear performance of copper-graphite composites processed by powder metallurgy route. Powder Metall. 000, 1–9 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1179/1743290113Y.0000000080
J. Wang, R. Zhang, J. Xu, C. Wu, P. Chen, Effect of the content of ball-milled expanded graphite on the bending and tribological properties of copper-graphite composites. Mater. Des. 47, 667–671 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.01.008
B. Chen, Q. Bi, J. Yang, Y. Xia, J. Hao, Tribological properties of solid lubricants (graphite, h-BN) for Cu-based P/M friction composites. Tribol. Int. 41, 1145–1152 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2008.02.014
O.A.M. Elkady, A. Abu-Oqail, E.M.M. Ewais, M. El-Sheikh, Physico-mechanical and tribological properties of Cu/h-BN nanocomposites synthesized by PM route. J. Alloys Compd. 625, 309–317 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.10.171
S. Huang, Y. Feng, H. Liu, K. Ding, G. Qian, Electrical sliding friction and wear properties of Cu–MoS2–graphite–WS2 nanotubes composites in air and vacuum conditions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 560, 685–692 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.10.014
M.M.H. Bastwros, A.M.K. Esawi, A. Wifi, Friction and wear behavior of Al-CNT composites. Wear 307, 164–173 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2013.08.021
C. Guiderdoni, E. Pavlenko, V. Turq, A. Weibel, P. Puech, C. Estournès et al., The preparation of carbon nanotube (CNT)/copper composites and the effect of the number of CNT walls on their hardness, friction and wear properties. Carbon N Y 58, 185–197 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2013.02.049
E.R.I. Mahmoud, M. Takahashi, T. Shibayanagi, K. Ikeuchi, Wear characteristics of surface-hybrid-MMCs layer fabricated on aluminum plate by friction stir processing. Wear 268, 1111–1121 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2010.01.005
A. Shafiei-Zarghani, S.F. Kashani-Bozorg, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, Microstructures and mechanical properties of Al/Al2O3 surface nano-composite layer produced by friction stir processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 500, 84–91 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2008.09.064
P. Liu, Q.Y. Shi, Zhang Y. Bin, Microstructural evaluation and corrosion properties of aluminium matrix surface composite adding Al-based amorphous fabricated by friction stir processing. Compos. Part B Eng. 52, 137–143 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.04.019
C.N. Shyam Kumar, R. Bauri, D. Yadav, Wear properties of 5083 Al-W surface composite fabricated by friction stir processing. Tribol. Int. 101, 284–290 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2016.04.033
T. Thankachan, K.S. Prakash, Microstructural, mechanical and tribological behavior of aluminum nitride reinforced copper surface composites fabricated through friction stir processing route. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 688, 301–308 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.02.010
T. Thankachan, K.S. Prakash, V. Kavimani, Investigations on the effect of friction stir processing on Cu–BN surface composites. Mater Manuf Process 33, 299–307 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2017.1291952
T. Thankachan, K. Soorya Prakash, M. Loganathan, WEDM process parameter optimization of FSPed copper–BN composites. Mater Manuf Process 33, 350–358 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2017.1339311
T. Thankachan, K. Soorya Prakash, M. Kamarthin, Optimizing the tribological behavior of hybrid copper surface composites using statistical and machine learning techniques. J. Tribol. 140, 031610 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4038688
C. Zishan, L. Hejun, F. Qiangang, Q. Xinfa, Tribological behaviors of SiC/h-BN composite coating at elevated temperatures. Tribiol. Int. 56, 58–65 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2012.06.026
B. Podgornik, T. Kosec, A. Kocijan, Č. Donik, Tribological behaviour and lubrication performance of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) as a replacement for graphite in aluminium forming. Tribol. Int. 81, 267–275 (2015)
G. Kranthi, A. Satapathy, Evaluation and prediction of wear response of pine wood dust filled epoxy composites using neural computation. Comput. Mater. Sci. 49, 609–614 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2010.06.001
T. Thankachan, K. Sooryaprakash, Artificial neural network-based modeling for impact energy of cast duplex stainless steel. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2880-9
T. Thankachan, K.S. Prakash, C. David Pleass, D. Rammasamy, B. Prabakaran, S. Jothi, Artificial neural network to predict the degraded mechanical properties of metallic materials due to the presence of hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 42, 28612–28621 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.09.149
K.S. Prakash, T. Thankachan, R. Radhakrishnan, Parametric optimization of dry sliding wear loss of copper–MWCNT composites. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 27, 627–637 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60070-0
L.A. Gyurova, K. Friedrich, Artificial neural networks for predicting sliding friction and wear properties of polyphenylene sulfide composites. Tribol. Int. 44, 603–609 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2010.12.011
M.E. Haque, K.V. Sudhakar, Prediction of corrosion–fatigue behavior of DP steel through artificial neural network. Int. J. Fatigue 23, 1–4 (2001)
H. Mirzadeh, A. Najafizadeh, Correlation between processing parameters and strain-induced martensitic transformation in cold worked AISI 301 stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 59, 1650–1654 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2008.03.004
K. Hornik, M. Stinchcombe, H. White, Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators. Neural Netw. (1989). https://doi.org/10.1016/0893-6080(89)90020-8
T. Thankachan, K. Sooryaprakash, Artificial neural network-based modeling for impact energy of cast duplex stainless steel. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 43(3), 1335–1343 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2880-9
T. Thankachan, K.S. Prakash, V. Kavimani, Effect of friction stir processing and hybrid reinforcements on copper. Mater. Manuf. Process. 33, 1681–1692 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2018.1453149
M.I. Abd El Aal, H.S. Kim, Effect of the fabrication method on the wear properties of copper silicon carbide composites. Tribol. Int. 128, 140–154 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2018.07.024
Y. Xiao, Z. Zhang, P. Yao, K. Fan, H. Zhou, T. Gong et al., Mechanical and tribological behaviors of copper metal matrix composites for brake pads used in high-speed trains. Tribol. Int. 119, 585–592 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2017.11.038
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thankachan, T., Soorya Prakash, K., Kavimani, V. et al. Machine Learning and Statistical Approach to Predict and Analyze Wear Rates in Copper Surface Composites. Met. Mater. Int. 27, 220–234 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00809-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00809-3