Abstract
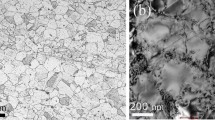
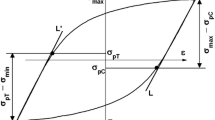
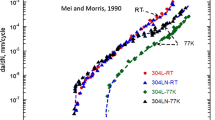
Effect of aging and oxidation on strain hardening behaviour of a nickel-free high nitrogen austenitic stainless steel has been investigated using room temperature tensile tests and TEM. The alloy in both oxidised and unoxidised conditions exhibits a transition in flow behaviour that can be described best by the Ludwigson flow relationship as evident from the lowest values of the sum of residual squares, χ 2, of the fit. The transition in macroscopic flow behaviour with strain has been correlated to change in deformation mechanism from planar slip in the low strain regime (LSR) to deformation twinning and slip in the high strain regime (HSR) in solution treated (ST) condition of the alloy. However, the LSR of the alloy aged for longer times (>100 h) is characterized by the formation of dislocation tangles, while the HSR is marked by the formation of well-defined finer dislocation cell structure. This difference in deformation sub-structures in low and high strain regimes between ST and long term aged samples has been correlated to the change in stacking fault energy due to the precipitation of Cr2N and σ-phases. Further, the alloy in ST condition exhibits the highest strain hardening rate, which then progressively decreases with aging time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. H. Holloman and L. D. Jafee, Trans AMIE 162, 223 (1945).
P. Ludwik, Elemente der Technologischen Mechanik, p. 32, Springer Verlag OHG, Berlin (1909).
E. Voce, J. Inst. Met. 74, 537 (1948).
H. Swift, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1, 1 (1952).
D. C. Ludwigson, Metall. Trans. 2, 2825 (1971).
J. R. Low and F. Garofalo, Proc. Soc. Exp. Stress Anal. 44, 16 (1947).
D. T. Llewellyn, Mater. Sci. Technol. 13, 389 (1997).
I. Karaman, H. Sehitoglu, Y. I. Chumlyakov, and H. J. Maier, JOM 54, 31 (2002).
A. Soussan, S. Degallaix, and T. Magnin, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 142, 169 (1991).
P. Müllner, C. Solenthaler, P. Uggowitzer, and M. O. Speidel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 164, 164 (1993).
S. Asgari, E. El-Danaf, S. R. Kalidindi, and R. D. Doherty, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 28, 1781 (1997).
D. V. V. Satyanarayana, G. Malakondaiah, and D. S. Sarma, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 452, 244 (2007).
J. S. Chou and C. G. Chao, Scr. Metall. Mater. 26, 261 (1992).
S. Mahajan and G. Y. Chin, Acta Metall. 21, 1353 (1973).
V. G. Gavriljuk and H. Berns, High Nitrogen Steels: Structure, Properties, Manufacture, Applications, pp. 169–188, Springer Science & Business Media (1999).
J. Li, H. Liu, and P. Huang, J. Cent. South Univ. 19, 1189 (2012).
Z. Jiang, Z. Zhang, H. Li, Z. Li, and M. Qi-Feng, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 17, 729 (2010).
H.-B. LI, Z.-H. Jiang, H. Feng, Q.-F. Ma, and D.-P. Zhan, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 19, 43 (2012).
A. Rokanopoulou and G. D. Papadimitriou, Mater. Sci. Technol. 27, 1391 (2011).
K. Yang and Y. Ren, Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 11, 014105 (2010).
M. O. Speidel, High Nitrogen Steels-HNS 88, 92 (1988).
J. Menzel, G. Stein, and P. Dahlmann, in Proc. 1st Int. Conf. High Nitrogen Steels, p. 147, Lille, France (1988).
P. J. Uggowitzer and M. Harzenmoser, in Proc. 1st Int. Conf. High Nitrogen Steels, p. 174, Lille, France (1988).
M. O. Speidel, in Proc. 2nd Int. Conf. High Nitrogen Steels, pp. 128–131, Stahl Und Eisen, Dusseldorf, Germany (1990).
F. Vanderschaeve, R. Taillard, and J. Foct, J. Mater. Sci. 30, 6035 (1995).
J. W. Simmons, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 207, 159 (1996).
H. Baba, T. Kodama, and Y. Katada, Corros. Sci. 44, 2393 (2002).
H. Hänninen, J. Romu, R. Ilola, J. Tervo, and A. Laitinen, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 117, 424 (2001).
T.-H. Lee, C.-S. Oh, S.-J. Kim, and S. Takaki, Acta Mater. 55, 3649 (2007).
T.-H. Lee, C.-S. Oh, and S.-J. Kim, Scr. Mater. 58, 110 (2008).
M. Pozuelo, J. E. Wittig, J. A. Jiménez, and G. Frommeyer, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 40, 1826 (2009).
S. Degallaix, J. Foct, and A. Hendry, Mater. Sci. Technol. 2, 946 (1986).
B. Kartik, R. Veerababu, M. Sundararaman, and D. V. V. Satyanarayana, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 642, 288 (2015).
Y. Sun, X. Li, and T. Bell, Mater. Sci. Technol. 15, 1171 (1999).
R. E. Stoltz and J. B. Vander Sande, Metall. Trans. A 11, 1033 (1980).
V. G. Gavriljuk and S. P. Jephimenko, in Proc. 2nd Int. Conf. High Nitrogen Steels HNS 90, p. 11, Stahleisen, Dussldorf, Germany (1990).
V. Gerold and H. P. Karnthaler, Acta Metall. 37, 2177 (1989).
M. Grujicic, J.-O. Nilson, W. S. Owen, and T. Thorcaldsson, in HNS 88 Conf. Proc., p. 151, Institute of Metals, London (1989).
J. Sassen, A. J. Garrat-Reed, and W. S. Owen, in HNS 88 Conf. Proc., p. 159, the Institute of Metals, London (1989).
C. Crussard and B. Jaoul, Rev. Met. Paris XLVII, 589 (1950).
R. E. Reed-Hill, W. R. Cribb, and S. N. Monteiro, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 4, 2665 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karthik, B., Veerababu, R. & Satyanarayana, D.V.V. Effect of aging and oxidation on strain hardening behaviour of a nickel-free high nitrogen austenitic stainless steel. Met. Mater. Int. 22, 413–423 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-016-5611-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-016-5611-y