Abstract
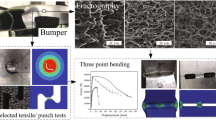
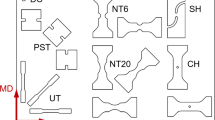
The fracture criterion was characterized for an AZ31 Mg alloy plate with the 3.0 mm thickness at the elevated temperature of 250 °C in this work. In order to properly characterize the fracture criterion, its mechanical properties were also characterized. As for mechanical properties, simple tension tests were performed to calibrate the Hill1948 yield function. Also, in order to account for the hardening deterioration (softening) behavior beyond the uniform deformation limit, the flow curves of the Mg alloy plate were numerically obtained based on the inverse calibration method, in which strain rate sensitivity was also considered. As for the fracture criterion, effective fracture strains, which are dependent on stress triaxiality and deformation paths, were numerically characterized utilizing experimental data based on specimens with four different shapes newly developed. For comparison purposes, empirical fracture criteria such as the Cockcroft-Latham, Brozzo, Ayada and Clift models were also calibrated. For validation purposes, the five fracture criteria were applied for a real part (an EL-cover) drawing case and the result confirmed that the fracture criterion developed in this work performed best among the five models tried out.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Lee, Y.-H. Chen, and J.-Y. Wang, J. Mater. Process. Tech. 124, 19 (2002).
E. Doege and K. Droder, J. Mater. Process. Tech. 115, 14 (2001).
F.-K. Chen and T.-B. Huang, J. Mater. Process. Tech. 142, 643 (2003).
H. Palaniswamy, G. Ngaile, and T. Altan, J. Mater. Process. Tech. 146, 52 (2004).
S. H. Zhang, K. Zhang, Y. C. Xu, Z. T. Wang, Y. Xu, and Z. G. Wang, J. Mater. Process. Tech. 185, 147 (2007).
S. Yoshihara, K.-I. Manabe, and H. Nishimura, J. Mater. Process. Tech, 170, 579 (2005).
H. J. Kim, S. C. Choi, K. T. Lee, and H. Y. Kim, Mater Trans. 49, 1112 (2008).
Y. Lee, Y. Kwon, S. Kang, S. Kim, and J. Lee, J. Mater. Process. Tech. 201, 431 (2008).
S. C. Choi, H. Y. Kim, S. M. Hong, Y. S. Shin, G. H. Lee, and H. J. Kim, Met. Mater. Int. 15, 575 (2009).
M. Cockcroft and D. Latham, J Inst Metals. 96, 33 (1968).
P. Brozzo, B. Deluca, and R. Rendina, Proc. 7th biennal Conf. IDDR, Amsterdam (1972).
M. Ayada, T. Higashino, and K. Mori, Advanced Technology of Plasticity 1987, 1, 553–558 (1987).
S.-W. Kim and Y.-S. Lee, Metall Mater Trans. B. 1(2013).
I. C. Jung, Y. K. Kim, T. H. Cho, S. H. Oh, T. E. Kim, S. W. Shon, W. T. Kim, and D. H. Kim, Met. Mater. Int. 20, 99 (2014).
S. H. Park, H. S. Kim, and B. S. You, Met. Mater. Int. 20, 291 (2014).
C. W. Ha and N. J. Park, Korean J. Met. Mater. 52, 589 (2014).
K. Iwanaga, H. Tashiro, H. Okamoto, and K. Shimizu, J. Mater. Process. Tech. 155–156, 1313 (2004).
Y. Chino, H. Iwasaki, and M. Mabuchi, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 466, 90 (2007).
J. Deng, Y. Lin, S.-S. Li, J. Chen, and Y. Ding, Materials. Design. 49, 209 (2013).
K. Chung, N. Ma, T. Park, D. Kim, D. Yoo, and C. Kim, Int. J. Plasticity. 27, 1485 (2011).
N. Ma, T. Park, D. Kim, C. Kim, and K. Chung, Met. Mater. Int. 16, 427 (2010).
K. Chung, H. Kim, and C. Lee, Int. J. Plasticity. 58, 3 (2014).
K. Chung, C. Lee, and H. Kim, Int. J. Plasticity. 58, 35 (2014).
T. Al-Samman and G. Gottstein, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 490, 411 (2008).
J. Koike, R. Ohyama, T. Kobayashi, M. Suzuki, and K. Maruyama, Mater. Trans. 44, 445 (2003).
S. E. Clift, P. Hartley, C. Sturgess, and G. Rowe, Int. J. Mech. Sci. 32, 1 (1990).
R. Hill, Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series A. Mathematical and Physical Sciences, pp. 281–297(1948).
Y. Bao and T. Wierzbicki, Int. J. Mech. Sci. 46, 81 (2004).
M. Luo, M. Dunand, and D. Mohr, Int. J. Plasticity. 32–33, 36 (2012).
R. Hill, The Mathematical Theory of Plasticity, pp.318–321, Oxford University Press, Oxford (1950).
V. Tvergaard and A. Needleman, Acta metallurgica. 32, 157 (1984).
A. L. Gurson, J. Eng. Mater-T. Asme. 99, 2 (1977).
J. Lemaitre, J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 107, 83 (1985).
Y. Bai and T. Wierzbicki, Int. J. Fracture. 161, 1 (2010).
Y. Bai and T. Wierzbicki, Int. J. Plasticity. 24, 1071 (2008).
M. Dunand and D. Mohr, Int J Solids Struct. 47, 1130 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seok, DY., Kim, D., Kim, SW. et al. Fracture criterion for AZ31 Mg alloy plate at elevated temperature. Met. Mater. Int. 21, 54–71 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-015-1007-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-015-1007-7