Abstract
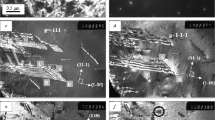
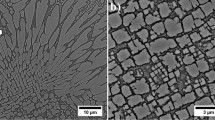
Structural studies have been performed on precipitation hardening found in Ni3Al-base ordered alloys using transmission electron microscopy. The γ′ phase hardens appreciably by the fine precipitation of disordered γ. The strength of γ′ increases over the temperature range of experiment by the precipitation of fine γ particles. The peak temperature where a maximum strength was obtained shifted to higher temperature. Superlattice dislocations dissociate into fourfold Shockley partial dislocations in a uniform supersaturated solid solution of the γ′ phase. Dislocations are attracted into the disordered γ phase and dissociate further in the particles. At any stage of aging, dislocations cut through the particles and the Orowan bypassing process does not occur even in the overaged stage of this alloy system. When the applied stress is removed, the dislocations make cross slip into (010) plane, while those in γ precipitates remain on the (111) primary slip plane. The increase of high temperature strength in γ′ containing γ precipitates is due to the restraint of cross slip of dislocations from (111) to (010) by the dispersion of disordered γ particles. The orientation dependence of strength is decreased by the fine precipitation of a disordered γ phase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. H. Chun, M. C. Kim, M. H. Oh, D. M. Wee, Y. Xu, M. Demura, K. Kishida and T. Hirano, J. Kor. Inst. Met. & Mater. 43, 801 (2005).
I. S. Kim, J. G. Kang, C. Y. Jo, H. U. Hong, N. H. Kang, and B. G. Choi, Korean J. Met. Mater. 49, 112 (2011).
C. S. Han, Korean J. Met. Mater. 49, 137 (2011).
T. Khan, P. Caron, and D. Blavette, Scripta Metall. 20, 1395 (1986).
S. H. Song, S. H. Kim, Y. H. Hong, M. H. Oh and D. M. Wee, Met. Mater. Int. 10, 307 (2004).
I. S. Kim, B. G.. Choi, H. U. Hong, and C. Y. Jo, Korean J. Met. Mater. 49, 535 (2011).
A. J. Ardell, Metall. Trans. A 16, 2131 (1985).
P. B. Hirsch and A. Kelly, Philos. Mag. 12, 881 (1965).
L. M. Brown, R. K. Ham, and R. H. Cook, Scripta Metall. 7, 815 (1973).
J. Friedel, Philos. Mag. A 45, 271 (1982).
U. F. Kocks, Philos. Mag. 13, 541 (1966).
A. J. E. Forman and M. J. Makin, Philos. Mag. 14, 911 (1966).
A. E. Staton-Bevan and R. D. Rawlings, Phys. Status Solidi A 29, 613 (1975).
P. Veyssiere, D. L. Guan and J. Rabier, Philos. Mag. A 49, 45 (1984).
P. Veyssiere, J. A. Horton, M. H. Yoo and C. T. Liu, Philos. Mag. Letters 57, 17 (1988).
N. Baluc, H. P. Karnthaler and M. J. Mills, Inst. Phys. Conf. Ser. 98, 463 (1988).
E. Arzt and J. Rosler, Acta Metall. 36, 1053 (1988).
S. S. Ezz, D. P. Pope and V. Vitek, Acta Metall. 35, 1879 (1987).
S. S. Ezz, D. P. Pope and V. Paidar, Acta Metall. 30, 921 (1982).
F. E. Heredia and D. P. Pope, Acta Metall. 34, 279 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12540-015-2134-x.
The editorial board of Metals and Materials International has decided to retract this article for reasons of plagiarism and redundant (duplicate) publication.
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, CS., Han, CS. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Microstructure and strengthening mechanism of Ni3Al intermetallic compound. Met. Mater. Int. 19, 941–948 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-013-5006-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-013-5006-2