Abstract
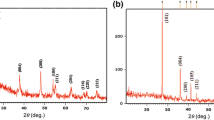
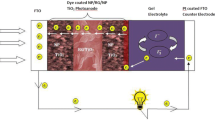
Dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) are composed of a dye-adsorbed nanoporous TiO2 layer on a fluorinedoped tin oxide (FTO) glass substrate, redox electrolytes, and a counter electrode. DSSCs are constructed through the application of nano-metals and TiO2 nanoparticle/TiO2 nanotube (TNT) composite particles with various compositions. The use of oxide semiconductors in the form of nanorods, nanowires, and nanotubes is an interesting approach to improve electron transport through the film. In addition, a suitable amount of TNT in the film could provide a large surface area for the adsorption of the dye. A nano-metal is proposed, wherein the conduction band (CB) prohibits the trapping effects of electrons within the TiO2 conduction band. This result is attributed to the prevention of electron recombination between the electrons in the TiO2 conduction band with dye or electrolytes. A TiO2 composite layer was coated onto FTO glass using a screen-printing method. The dye-sensitized solar cells were fabricated using N719 ruthenium (II) dye and I3/I3 − electrolyte. The impedance results indicate improved electron transport at the TiO2/dye/electrolyte interface. The DSSC based on the Fe2O3/TiO2/TNT composite particle hybrids exhibits better photovoltaic performance than the cell made from only TiO2 nanoparticles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Grätzel, Inorg. Chem. 44, 6841 (2005).
T. W. Hamann, R. A. Jensen, A. B. F. Martinson, H. V. Ryswyk, and J. T. Hupp, Energ. Environ. Sci. 1, 66 (2008).
F. T. Kong, S. Y. Dai, and K. J. Wang, Adv. Opto. Elect. 2007, 13 (2007).
T. Prakash, Electron. Mater. Lett. 8, 231 (2012).
P. Huh and S. C. Kim, Electron. Mater. Lett. 8, 131 (2012).
J. B. Xia, N. Masaki, K. J. Jiang, Y. Wada, and S. Yanagida, Chem. Lett. 35, 252 (2006).
M. Ni, M. K. H. Leung, D. Y. C. Leung, and K. Sumathy, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 90, 1331 (2006).
C. S. Chou, R. Y. Yang, C. K. Yeh, and Y. J. Lin, Powder Technol. 194, 95 (2009).
S. H. Kang, J. Y. Kim, Y. Kim, H. S. Kim, and Y. E. Sung, J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 9614 (2007).
M. Paulose, K. Shankar, O. K. Varghese, G. K. Mor, B. Hardin, and C. A. Grimes, Nanotechnology 17, 1446 (2006).
G. K. Mor, O. K. Varghese, M. Paulose, K. Shankar, and C. A. Grimes, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 90, 2011 (2006).
T. Kasuga, M. Hiramatsu, A. Hoson, T. Sekino, and K. Niihara, Langmuir 14, 3160 (1998).
T. Kasuga, M. Hiramatsu, A. Hoson, T. Sekino, and K. Niihara, Adv. Mater. 11, 1307 (1999).
J. S. Im, S. K. Lee, and Y. S. Lee, Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 2164 (2011).
Y. S. Jin, K. H. Kim, S. J. Park, H. H. Yoon, and H. W. Choi, J. Nanosci Nanotechnology. 11, 10971 (2011).
Y. S. Jin and H. W. Choi, J. Nanosci Nanotechnology. 12, 662 (2012).
C. H. Lee, K. H. Kim, K. U. Jang, S. J. Park, and H. W. Choi, Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 539, 125 (2011).
S. Ito, P. Chen, P. Comte, M. K. Nazeeruddin, P. Liska, P. Pechy, and M. Grätzel, Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 15, 603 (2007).
S. Gagliardi, L. Giorgi, R. Giorgi, N. Lisi, T. D. Makris, E. Salernitano, and A. Rufoloni, Superlattices Microstruct. 46, 205 (2009).
Q. Qin, J. Tao, and Y. Yang, Synth. Met. 160, 1167 (2010).
K. D. Becker, M. Schrader, H. S. Kwon, and H. I. Yoo, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11, 3082 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, CH., Kim, K.H., Bark, C.W. et al. Preparation of doping metal TiO2 particle/nanotube composite layer and their applications in dye-sensitized solar cells. Met. Mater. Int. 19, 1355–1359 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-013-0640-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-013-0640-2