Abstract
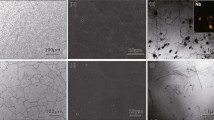
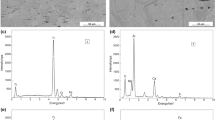
Effects of deformation-induced martensite and grain size on ductile-to-brittle transition behavior of austenitic 18Cr-10Mn-(0.3∼0.6)N stainless steels with different alloying elements were investigated by means of Charpy impact tests and microstructural analyses. The steels all exhibited ductile-to-brittle transition behavior due to unusual brittle fracture at low temperatures despite having a face-centered cubic structure. The ductileto-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) obtained from Chapry impact tests did not coincide with that predicted by an empirical equation depending on N content in austenitic Cr-Mn-N stainless steels. Furthermore, a decrease of grain size was not effective in terms of lowering DBTT. Electron back-scattered diffraction and transmission electron microscopy analyses of the cross-sectional area of the fracture surface showed that some austenites with lower stability could be transformed to α’-martensite by localized plastic deformation near the fracture surface. Based on these results, it was suggested that when austenitic 18Cr-10Mn-N stainless steels have limited Ni, Mo, and N content, the deterioration of austenite stability promotes the formation of deformation-induced martensite and thus increases DBTT by substantially decreasing low-temperature toughness.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. G. Gavriljuk, H. Berns, High Nitrogen Steels, Spriner-Verlag, Berlin (1999).
N. Akdut, B. C. De Cooman, and J. Foct, Proc. of the 7th International Conference on High Nitrogen Steels, Ostend, Belgium (2004).
J. D. Defilippi, K. G. Brickner, E. M. Gilbert, Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 245, 2141 (1969).
P. Müllner, C. Solenthaler, P. J. Uggowitzer, and M. O. Speidel, Acta mater. 42, 2211 (1994).
Y. Tomota and S. Endo, ISIJ Int. 30, 656 (1990).
Y. Tomota, Y. Xia, and K. Inoue, Acta mater. 46, 1577 (1998).
P. J. Uggowitzer, N. Paulus, and M. O. Speidel, Proc. Application of Stainless Steels’ 92, Vol. 1, p. 62, Jernkontoret, Stockholm (1992).
P. J. Uggowitzer, R. Magdowski, and M. O. Speidel, ISIJ Int. 36, 901 (1996).
G. Balachandran, M. L. Bhatia, N. B. Ballal, and P. Krishna RAO, ISIJ Int. 41, 1018 (2001).
Y. Kim, N. Kang, Y. Park, I. Choi, G. Kim, S. Kim, and K. Cho, J. Kor. Inst. Met. & Mater. 46, 780 (2008).
J. Talonen and H. Hänninen, Acta mater. 55, 333 (2002).
L. P. Karjalinen, T. Taulavuori, M. Sellman, and A. Kyröläinen A, Steel Res. Int. 79, 404 (2008).
B. Hwang, T.-H. Lee, C.-S. Oh, and S-J. Kim, Proc. of the 23rd Conference on Advanced Structural Materials, p. 117, The Korean Insititute of Metals and Materials, Daejeon, Korea (2009).
S. Wang, K. Yang, Y. Shan, and L. Li, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 490, 95 (2008).
B. Hwang, Y. G. Kim, S. Lee, N. J. Kim, and J. Y. Yoo, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 36, 371 (2005).
T.-H. Lee, E. Shin, C.-S. Oh, H.-Y. Ha, and S.-J. Kim, Acta mater. 58, 3173 (2010).
T.-H. Lee, C.-S. Oh, and S.-J. Kim, Scripta mater. 58, 110 (2008).
M.-X. Zhang and P. M. Kelly, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 32, 2695 (2001).
J. Bernauer, G. Saller, M. O. Speidel, Proc. of the 7th International Conference on High Nitrogen Steels, p. 529, Ostend, Belgium (2004).
M. Milititsky, D. K. Matlock, A. Regully, N. Dewispelaere, J. Penning, and H. Hänninen, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 496, 189 (2008).
R. W. Hertzberg, Deformation and Fracture Mechanics of Engineering Materials, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York (1996).
A. Gilber, G. T. Hahn, C. N. Reid, and R. A. Wilcox, Acta metall. 12, 754 (1964).
N. J. Petch, Phil. Mag. 3, 1089 (1958).
F. B. Fickering, Physical Metallurgy and the Design of Steels, Applied Science Publishers Ltd., London (1978).
S. Yamamoto, N. Yamagami, and C. Ouchi, Adv. Cryog. Eng. 32, 57 (1986).
M. Harzenmoser, R. P. Reed, P. J. Uggowitzer, M. O. Speidel, Proc. 2nd Int. Conf. High Nitrogen Steels, p. 197, Stahl & Eisen, Aachen (1990).
R. E. Schramm and R. P. Reed, Metall. Trans. A 6, 1345 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, B., Lee, TH. & Kim, SJ. Effects of deformation-induced martensite and grain size on ductile-to-brittle transition behavior of austenitic 18Cr-10Mn-N stainless steels. Met. Mater. Int. 16, 905–911 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-010-1208-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-010-1208-z