Abstract
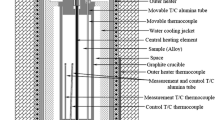
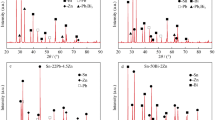
The variation of thermal conductivity of solid phase versus temperature for Sn-21 wt.% Bi, Sn-25 wt.% In and Sn-35 wt.% In-26 wt.% Bi alloys were measured with a radial heat flow apparatus. From the graphs of thermal conductivity versus temperature, the thermal conductivity of the solid phases at their melting temperatures and the thermal temperature coefficients for the same alloys were obtained. The ratios of thermal conductivity of liquid phase to solid phase for the same materials were measured with a Bridgman type directional solidification apparatus. The variations of electrical conductivity of solid phases versus temperature for the same alloys were determined from the Wiedemann-Franz law by using the measured values of thermal conductivity. From the graphs of electrical conductivity versus temperature, the electrical temperature coefficients for the same alloys were also determined. According to present experimental results it can be concluded that the thermal and electrical conductivity of Sn based alloys depend on the thermal and electrical conductivity of the alloying elements. If the thermal and electrical conductivity of the alloying elements are lower than the thermal conductivity of Sn, the thermal conductivity of Sn based alloys decreases, whereas, otherwise, it increases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. S. Touloukian, R. W. Powell, C. Y. Ho and P. G. Klemens, Thermal Conductivity Metallic Elements and Alloys, Vol 1, p. 17a, Plenum, New York (1970).
H. L. Callendar and J. T. Nicolson, Brt. Assoc. Adv. Sci., Rept. Ann. Meeting. 22, 418 (1897).
C. Niven, Proc. Roy. Soc. A76, 34 (1905).
R. W. Powell, Proc. Phys. Soc. 51, 407 (1939).
M. F. Angel, Phys. Rev. 33, 411 (1911).
D. L. McElroy and J. P. Moore, Academic Press, Vol. I, p.185, London (1969).
M. Gündüz and J. D. Hunt, Acta. mater. 33, 1651 (1985).
N. Mara ll and J. D. Hunt, Acta mater. 44, 1085 (1996).
M. Erol, K. Keşlioğlu, R. Şahingöz, and N. Maraşlı, Met. Mater. Int. 11, 421 (2005).
B. Saatçi, N. Maraşlı, and M. Gündüz, Therm. Acta. 454, 128 (2007).
N. Maraşlı, S. Akbulut, Y. Ocak, K. Keşlioğlu, U. Böyük, H. Kaya, and E. Çadırlı, J. Phys. Codens. Mat. 19, 506102 (2007).
Y. Terada, K. Ohkubo, T. Mohri, and T. Suzuki, J. Alloy. Compd. 285, 233 (1999).
C. Kittel, Introduction to Solid State Physics, 6th ed., p. 150–153, John Wiley and Sons, New York (1965).
J. Sigelko, S. Choi, K. N. Subramanian, J. P. Lucas, and T. R. Bieler, J. Electron Mater. 28, 1184 (1999).
J. Liang, N. Gollhardt, P. S. Lee, S. A. Schroeder, and W. L. Morris, Fatigue. Fract. Eng. M. 19, 1401 (1996).
P. T. Vianco, J. A. Rejent, and A. C. Kilgo, J. Electron. Mater. 33, 1373 (2004).
M. Kerr and N. Chawla, Acta. mater. 52, 4527 (2004).
J. Liang, S. Downes, N. Dariavach, D. Shangguan, and S. M. Heinrich, J. Electron. Mater. 33, 1507 (2004).
J. Liang, N. Dariavach, G. Barr, and Z. Fang, J. Electron. Mater. 35, 372 (2006).
M. L. Huang, L. Wang, and C. M. L. Wu, J. Mater. Res. 17, 2897 (2002).
M. Amagai, M. Watanabe, M. Omiya, K. Kishimoto and T. Shibuya, Microelectron. Reliab. 42, 951 (2002).
Y. S. Touloukian, R. W. Powell, C. Y. Ho, and P. G. Klemens, Thermal Conductivity Metallic Elements and Alloys, Vol. 1, p. 149, Plenum, New York (1970).
Y. S. Touloukian, R. W. Powell, C. Y. Ho, and P. G. Klemens, Thermal Conductivity Metallic Elements and Alloys, Vol. 1, p. 408, Plenum, New York (1970).
Y. S. Touloukian, R. W. Powell, C. Y. Ho and P. G. Klemens, Thermal Conductivity Metallic Elements and Alloys, Vol. 1, p. 39, Plenum, New York (1970).
D. A. Porter and K. E. Easterling, Phase Transformations in Metals and Alloys, p. 204, Van Nostrnad Reinhold Co. Ltd., UK (1991).
D. G. McCartney, Ph. D. Thesis, p.85–175, Oxford University, UK (1981).
Resistivities of Metallic Elements, http://www.kayelaby.npl.co.uk/general_physics.
S. Akbulut, Y. Ocak, K. Keşlioğlu, and N. Maraşlı J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 70, 72 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aksöz, S., Ocak, Y., Keşlioğlu, K. et al. Determination of thermo-electrical properties in Sn based alloys. Met. Mater. Int. 16, 507–515 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-010-0624-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-010-0624-4