Abstract
Background
Asthma is a significant chronic health problem worldwide. Management aims at disease control by reducing functional impairment and exacerbations and improving quality of life (QoL). We report a multi-center study to survey asthma control and QoL in four cities in the Pearl River Delta.
Methods
The conjoint survey involved ten Hong Kong pediatric hospitals/units, two Shenzhen hospitals, two Macau hospitals, and two Guangzhou hospitals on asthma control (using Asthma Control Test) and QoL (Pediatric Allergic Disease Quality of Life Questionnaire, PADQLQ). Acceptability of a treatment is graded as very good/good/fair/poor.
Results
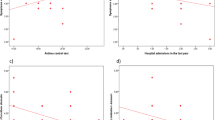
Good asthma control was only reported in 80% subjects in Hong Kong, but higher in sister cities (85–94%, P < 0.001). Allergic rhinitis, “incense burning”, and “smoker in family” were prevalent among the four cities. Logistic regression showed better control of asthma was associated with better PADQLQ (B = − 0.029, P < 0.001), better acceptability of bronchodilator (B = − 1.488, P = 0.025), negatively with “smoker in family” (B = − 0.83, P = 0.015) and various PADQLQ domains. Conversely, worse PADQLQ was associated with allergic rhinitis severity (B = 4.77, P < 0.001), poor control of asthma (B = 7.56, P < 0.001), increased frequency of traditional Chinese medicine use (B = 1.7, P < 0.05), increased frequency of bronchodilator usage (B = 1.05, P < 0.05), “smoker in family” (B = 4.05, P < 0.05), and incense burning at home (B = 3.9, P < 0.05).
Conclusions
There are some clinical and cultural differences among the four southern Chinese cities within the Guangdong province. This study identifies potentially modifiable environmental and treatment factors associated with poor asthma control and QoL for health-care interventions. Having a smoker in the family is independently associated with poor asthma control and QoL.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hon KL, Leung TF, Leung AK. Clinical effectiveness and safety of montelukast in asthma. What are the conclusions from clinical trials and meta-analyses? Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014;8:839–50.
Cannon E. Aligning patient care and asthma treatment guidelines. Am J Manag Care. 2005;11:S416–21.
Masoli M, Fabian D, Holt S, Beasley R, Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) Program. The global burden of asthma: executive summary of the GINA Dissemination Committee report. Allergy. 2004;59:469–78.
Ober C, Yao TC. The genetics of asthma and allergic disease: a 21st century perspective. Immunol Rev. 2011;242:10–30.
Worldwide variation in prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and atopic eczema: ISAAC. The International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) Steering Committee. Lancet. 1998;351:1225–32.
Li F, Zhou Y, Li S, Jiang F, Jin X, Yan C, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of childhood allergic diseases in eight metropolitan cities in China: a multicenter study. BMC Public Health. 2011;11:437.
Hon KL, Nelson EA. Gender disparity in paediatric hospital admissions. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2006;35:882–8.
Papi A, Brightling C, Pedersen SE, Reddel HK. Asthma. Lancet. 2018;391:783–800.
Lai CK, Beasley R, Crane J, Foliaki S, Shah J, Weiland S, et al. Global variation in the prevalence and severity of asthma symptoms: phase three of the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC). Thorax. 2009;64:476–83.
Lai CK, Ko FW, Bhome A, De Guia TS, Wong GW, Zainudin BM, et al. Relationship between asthma control status, the Asthma Control Test™ and urgent health-care utilization in Asia. Respirology. 2011;16:688–97.
Hon KL, Wang SS, Leung TF. The atopic march: from skin to the airways. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2012;11:73–7.
Leung TF, Ko FW, Sy HY, Wong E, Li CY, Yung E, et al. Identifying uncontrolled asthma in young children: clinical scores or objective variables? J Asthma. 2009;46:130–5.
Ip KI, Hon KL, Tsang KYC, Leung TNH. Steroid phobia, Chinese medicine and asthma control. Clin Respir J. 2018;12:1559–64.
Wong GW, Kwon N, Hong JG, Hsu JY, Gunasekera KD. Pediatric asthma control in Asia: phase 2 of the Asthma Insights and Reality in Asia-Pacific (AIRIAP 2) survey. Allergy. 2013;68:524–30.
Nathan RA, Sorkness CA, Kosinski M, Schatz M, Li JT, Marcus P, et al. Development of the asthma control test: a survey for assessing asthma control. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;113:59–65.
Kiotseridis H, Cilio CM, Bjermer L, Aurivillius M, Jacobsson H, Dahl A, et al. Quality of life in children and adolescents with respiratory allergy, assessed with a generic and disease-specific instrument. Clin Respir J. 2013;7:168–75.
Roberts G, Hurley C, Lack G. Development of a quality-of-life assessment for the allergic child or teenager with multisystem allergic disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;11:491–7.
Ng DK, Wong KC, Chan CH, Ng EP. Development of the Chinese version of the Paediatric Allergic Disease Quality of Life Questionnaire: reliability and validity. Hong Kong Med J. 2011;17:460–4.
Hon KL, Tsang S, Wong CY, Tse PM, Wong C, To WH, et al. Atopy in children with eczema. Indian J Pediatr. 2010;77:519–22.
Hon K, Leung T. X-ray quiz. J Paediatr Respir Crit Care. 2013;9:11.
Hon KLE, Leung T. Killing many birds with one stone. Hong Kong J Paediatr. 2008;13:135–8.
Patterson R, Walker CL, Greenberger PA, Sheridan EP. Prednisonephobia. Allergy Proc. 1989;10:423–8.
Tuft L. “Steroid-phobia” in asthma management. Ann Allergy. 1979;42:152–9.
Zedan MM, Ezz El Regal M, A Osman E, E Fouda A. Steroid phobia among parents of asthmatic children: myths and truth. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010;9:163–8.
Skoner JD, Schaffner TJ, Schad CA, Kwon AY, Skoner DP. Addressing steroid phobia: improving the risk-benefit ratio with new agents. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2008;29:358–64.
Hon KL, Tang WS, Leung TF, Cheung KL, Ng PC. Outcome of children with life-threatening asthma necessitating pediatric intensive care. Ital J Pediatr. 2010;36:47.
Hon KL, Kam WY, Leung TF, Lam MC, Wong KY, Lee KC, et al. Steroid fears in children with eczema. Acta Paediatr. 2006;95:1451–5.
Chen HY, Lin YH, Thien PF, Chang SC, Chen YC, Lo SS, et al. Identifying core herbal treatments for children with asthma: implication from a chinese herbal medicine database in Taiwan. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:125943.
Hon KL, Lee VW. Challenges for drug discovery and development in China. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2017;12:105–13.
Liu AH, Zeiger R, Sorkness C, Mahr T, Ostrom N, Burgess S, et al. Development and cross-sectional validation of the Childhood Asthma Control Test. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119:817–25.
Leung CM, Leung AK, Hon KL, Kong AY. Fighting tobacco smoking–a difficult but not impossible battle. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2009;6:69–83.
Bellin MH, Newsome A, Land C, Kub J, Mudd SS, Bollinger ME, et al. Asthma Home Management in the Inner-City: What can the Children Teach us? J Pediatr Health Care. 2017;31:362–71.
Brand PL, Mäkelä MJ, Szefler SJ, Frischer T, Price D, ERS Task Force Monitoring Asthma in Children. Monitoring asthma in childhood: symptoms, exacerbations and quality of life. Eur Respir Rev. 2015;24:187–93.
Vidal GA. Pediatric asthma control and quality of life questionnaires. Rev Chil Pediatr. 2014;85:359–66 (in Spanish).
Boulet LP, FitzGerald JM, Reddel HK. The revised 2014 GINA strategy report: opportunities for change. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2015;21:1–7.
Hon KLE, Leung AKC. Medications and recent patents for status asthmaticus in children. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2017;11:12–21.
Leung AK. Sunburn from the treatment of neonatal jaundice. Burns Incl Therm Inj. 1986;12:291–2.
Barnes PJ, Pedersen S, Busse WW. Efficacy and safety of inhaled corticosteroids. New developments. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157:S1–53.
Camargo CA Jr, Rachelefsky G, Schatz M. Managing asthma exacerbations in the emergency department: summary of the National Asthma Education And Prevention Program Expert Panel Report 3 guidelines for the management of asthma exacerbations. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2009;6:357–66.
National Asthma Education and Prevention Program. National Asthma Education and Prevention Program. Expert Panel Report: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Update on Selected Topics–2002. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;110:S141–219.
Main C, Shepherd J, Anderson R, Rogers G, Thompson-Coon J, Liu Z, et al. Systematic review and economic analysis of the comparative effectiveness of different inhaled corticosteroids and their usage with long-acting beta2 agonists for the treatment of chronic asthma in children under the age of 12 years. Health Technol Assess. 2008;12:1–174, iii-iv.
Foresi A, Morelli MC, Catena E. Low-dose budesonide with the addition of an increased dose during exacerbations is effective in long-term asthma control. On behalf of the Italian Study Group. Chest. 2000;117:440–6.
Tan WC, Koh TH, Hay CS, Taylor E. The effect of inhaled budesonide on the diurnal variation in airway mechanics, airway responsiveness and serum neutrophil chemotactic activity in Asian patients with predominant nocturnal asthma. Respirology. 1998;3:13–20.
Hon KL, Tsang YC, Pong NH, Luk DC, Lee VW, Woo WM, et al. Correlations among steroid fear, acceptability, usage frequency, quality of life and disease severity in childhood eczema. J Dermatolog Treat. 2015;26:418–25.
Martin J, Donaldson AN, Villarroel R, Parmar MK, Ernst E, Higginson IJ. Efficacy of acupuncture in asthma: systematic review and meta-analysis of published data from 11 randomised controlled trials. Eur Respir J. 2002;20:846–52.
Posadzki P, Ernst E. Yoga for asthma? A systematic review of randomized clinical trials. J Asthma. 2011;48:632–9.
Barnes PM, Bloom B, Nahin RL. Complementary and alternative medicine use among adults and children: United States, 2007. Natl Health Stat Report. 2008;12:1–23.
Hon KL, Fung CK, Leung AK, Leung TN, Ng DK. Complementary and alternative medicine for childhood asthma: an overview of evidence and patents. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2015;9:66–79.
Chang C, Gershwin ME. Integrative medicine in allergy and immunology. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2013;44:208–28.
Fisher P, Ward A. Complementary medicine in Europe. BMJ. 1994;309:107–11.
Ernst E. Complementary therapies for asthma: what patients use. J Asthma. 1998;35:667–71.
Schafer T, Riehle A, Wichmann HE, Ring J. Alternative medicine in allergies–prevalence, patterns of use, and costs. Allergy. 2002;57:694–700.
Blanc PD, Trupin L, Earnest G, Katz PP, Yelin EH, Eisner MD. Alternative therapies among adults with a reported diagnosis of asthma or rhinosinusitis: data from a population-based survey. Chest. 2001;120:1461–7.
Chen FP, Chen TJ, Kung YY, Chen YC, Chou LF, Chen FJ, et al. Use frequency of traditional Chinese medicine in Taiwan. BMC Health Serv Res. 2007;7:26.
Ock SM, Choi JY, Cha YS, Lee J, Chun MS, Huh CH, et al. The use of complementary and alternative medicine in a general population in South Korea: results from a national survey in 2006. J Korean Med Sci. 2009;24:1–6.
Yamashita H, Tsukayama H, Sugishita C. Popularity of complementary and alternative medicine in Japan: a telephone survey. Complement Ther Med. 2002;10:84–93.
Lim MK, Sadarangani P, Chan HL, Heng JY. Complementary and alternative medicine use in multiracial Singapore. Complement Ther Med. 2005;13:16–24.
McClafferty H. An overview of integrative therapies in asthma treatment. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2014;14:464–6.
Hon KL, Leung AKC, Leung TNH, Lee VWY. Complementary, alternative and integrative medicine for childhood atopic dermatitis. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2017;11:114–24.
Hon KL, Lee VW, Leung TF. Stop tarnishing steroid and Chinese medicine. World J Pediatr. 2015;12:133–4.
Braido F. Failure in asthma control: reasons and consequences. Scientifica (Cairo). 2013;2013:549252.
Funding
A small research grant was provided by Hong Kong Society of Pediatric Respirology and Allergy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KLH is the principal author who coordinated this survey. All co-authors obtained ethical approval from their respective centers and collected and contributed data to this survey. JSCK and MHW were involved in statistical analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was obtained from NTEC CREC for the principal author and the respective ethics committees of all participating centers.
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hon, K.L., Bao, Y.M., Chan, K.C. et al. Determinants for asthma control, quality of life and use of complementary and alternative medicine in asthmatic pediatric patients in four cities. World J Pediatr 14, 482–491 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-018-0167-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-018-0167-1