Abstract
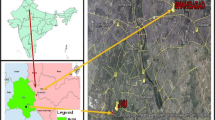
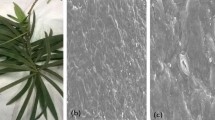
The tolerance against air pollution in plants depends on the nature of air particles and gases. This study was carried out to determine chemical composition of indoor dust and to assess its impact on the biochemical properties of foliage of Ficus elastica in two households with different characteristics of Delhi (India). The dustfall fluxe data of major cations and anions were analyzed to understand the spatial variations in the chemical composition and sources of the deposited particles onto the foliage. The fluxes of anionic species (SO42− + NO3−) were higher at MH (industrial) site as compared to the DH (residential) site. The physiological response of F. elastica was investigated by studying the biochemical constituents, i.e., ascorbic acid, soluble sugars, carotenoids, and chlorophyll a and b, in foliage and variations with respect to dustfall fluxes of anionic species (SO42− + NO3−) in the households. Higher (SO42− + NO3−) fluxes had noticeable impacts on biochemical constituents of F. elastica indicating indoor air pollution stress. Chemistry of dust particles showed influences from indoor and outdoor anthropogenic activities. The morphological effects of dustfall deposition on the foliage were also studied using SEM–EDX. Indoor plants can serve as a platform to capture dust particles and plant responses are influenced by the chemical composition of deposited dust.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data can be made available by authors on reasonable request.
References
Bates TS, Quinn PK, Coffman DJ et al (2004) Marine boundary layer dust and pollutant transport associated with the passage of a frontal system over eastern Asia. J Geophys Res D Atmos 109:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003JD004094
Beiderwieden E, Wrzesinsky T, Klemm O (2005) Chemical characterization of fog and rain water collected at the eastern Andes cordillera. Hydrol Earth Sys Sci Discuss 2:863–885
Brilli F, Fares S, Ghirardo A et al (2018) Plants for sustainable improvement of indoor air quality. Trends Plant Sci 23:507–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2018.03.004
Britto DT, Kronzucker HJ (2005) Nitrogen acquisition, PEP carboxylase, and cellular pH homeostasis: new views on old paradigms. Plant Cell Environ 28:1396–1409. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2005.01372.x
Buchner P, Takahashi H, Hawkesford MJ (2004) Plant sulphate transporters: co-ordination of uptake, intracellular and long-distance transport. J Exp Bot 55:1765–1773. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erh206
Cao Y, Li F, Wang Y et al (2019) Assisted deposition of PM2.5 from indoor air by ornamental potted plants. Sustain 11:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11092546
Cetin M, Sevik H (2016) Measuring the impact of selected plants on indoor CO2 concentrations. Polish J Environ Stud 25:973–979. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/61744
Chithra VS, Shiva Nagendra SM (2012) Indoor air quality investigations in a naturally ventilated school building located close to an urban roadway in Chennai, India. Build Environ 54:159–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2012.01.016
Cornejo JJ, Muñoz FG, Ma CY, Stewart AJ (1999) Studies on the decontamination of air by plants. Ecotoxicology 8:311–320. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008937417598
Debolt S, Melino V, Ford CM (2007) Ascorbate as a biosynthetic precursor in plants. Ann Bot 99:3–8
Dela Cruz M, Christensen JH, Thomsen JD, Müller R (2014) Can ornamental potted plants remove volatile organic compounds from indoor air? — a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:13909–13928. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3240-x
Farmer AM (1993) The effects of d u s t on vegetation. 79:63–75
Forni LG, Mora-Arellano VO, Packer JE, Willson RL (1986) Nitrogen dioxide and related free radicals: electron-transfer reactions with organic compounds in solutions containing nitrite or nitrate. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans 2:1–6
Fowler D, Cape JN, Unsworth MH (1989) Deposition of atmospheric pollutants on forests. Philos Trans - R Soc London, B 324:247–265. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.1989.0047
Gallie DR (2013) The role of L-ascorbic acid recycling in responding to environmental stress and in promoting plant growth. J Exp Bot 64:433–443
Gawrońska H, Bakera B (2015) Phytoremediation of particulate matter from indoor air by Chlorophytum comosum L. plants. Air Qual Atmos Heal 8:265–272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-014-0285-4
Gheorghe IF, Ion B (2011) The effects of air pollutants on vegetation and the role of vegetation in reducing atmospheric pollution. Impact Air Pollut Heal Econ Environ Agric sources 241–280
Gupta GP, Kumar B, Singh S, Kulshrestha UC (2015a) Urban climate and its effect on biochemical and morphological characteristics of Arjun (Terminalia arjuna) plant in National Capital Region Delhi. Chem Ecol 31:524–538. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2015.1043286
Gupta GP, Kumar B, Kulshrestha UC (2016a) Impact and pollution indices of urban dust on selected plant species for green belt development: mitigation of the air pollution in NCR Delhi, India. Arab J Geosci 9:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2226-4
Gupta GP, Kumar B, Singh S, Kulshrestha UC (2016b) Deposition and impact of urban atmospheric dust on two medicinal plants during different seasons in NCR delhi. Aerosol Air Qual Res 16:2920–2932. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2015.04.0272
Gupta GP, Singh S, Kumar B, Kulshrestha UC (2015b) Industrial dust sulphate and its effects on biochemical and morphological characteristics of Morus (Morus alba) plant in NCR Delhi. Environ Monit Assess 187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4301-4
Habil M, Massey DD, Taneja A (2015) Exposure from particle and ionic contamination to children in schools of India. Atmos Pollut Res 6:719–725. https://doi.org/10.5094/APR.2015.080
Hiscox JD, Israelstam GF (1979) Different methods of chlorophyll extraction. Can J Bot 57
Jain M, Kulshrestha UC, Parashar DC (1996) Characterization of dry deposition associated with fire in plastic scrap market of West Delhi. Chemosphere 32:2263–2268
Jain M, Kulshrestha UC, Sarkar AK, Parashar DC (2000) Influence of crustal aerosols on wet deposition at urban and rural sites in India. Atmos Environ 34:5129–5137
Jenkins PL, Phillips TJ, Mulberg EJ, Hui SP (1992) Activity patterns of Californians: use of and proximity to indoor pollutant sources. Atmos Environ Part A. Gen Top 26:2141–2148. https://doi.org/10.1016/0960-1686(92)90402-7
Jia M, Zhou D, Lu S, Yu J (2021) Assessment of foliar dust particle retention and toxic metal accumulation ability of fifteen roadside tree species: relationship and mechanism. Atmos Pollut Res 12:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2020.08.003
Katoch A, Kulshrestha UC (2020) Study of risk assessment of indoor NH3 in two urban households of NCR-Delhi. Curr World Environ 15:163–175. https://doi.org/10.12944/cwe.15.2.03
Katoch A, Kulshrestha UC (2021) Gaseous and particulate reactive nitrogen species in the indoor air of selected households in New Delhi. Environ Monit Assess 193:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-08991-6
Katoch A, Kulshrestha UC (2022) Assessment of indoor air pollution through fine particle capturing potential and accumulation on plant foliage in Delhi, India. Aerosol Air Qual Res 22:1–17. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.220014
Katoch A, Kulshrestha UC (2023) Seasonal variations of dustfall fluxes and biochemical parameters in the foliage of selected indoor plants in Delhi, India. Int J Phytoremediation 25:917–928. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2022.2122394
Keller T, Schwager H (1977) Air pollution and ascorbic acid. Eur J for Pathol 7:338–350. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0329.1977.tb00603.x
Kim KJ, Lim YW, Kim HH et al (2010) Variation in formaldehyde removal efficiency among indoor plant species. HortScience 45:1489–1495
Koziol MJ, Jordan CF (1978) Changes in carbohydrate levels in red kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) exposed to sulphur dioxide. J Exp Bot 29:1037–1043
Kulshrestha U (2013) Acid rain. In: Jorgensen E (ed) Encyclopedia of environmental management, vol 1. Taylor & Francis, New York, pp 8–22
Kulshrestha UC, Saxena A, Kumar N et al (1998) Chemical composition and association of size-differentiated aerosols at a suburban site in a semi-arid tract of India. J Atmos Chem 29:109–118. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005796400044
Kulshrestha UC, Kulshrestha MJ, Sekar R, Sastry GSR, Vairamani M (2003a) Chemical characteristics of rain water at an urban site of south-central India. Atmos Environ 37:3019–3302
Kulshrestha MJ, Kulshrestha UC, Parashar DC, Vairamani M (2003b) Estimation of SO4 contribution by dry deposition of SO2 onto the dust particles in India. Atmos Environ 37:3057–3063. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(03)00290-5
Kulshrestha UC, Granat L, Rodhe H (2003c) Precipitation chemistry studies in India- a search for regional patterns. Report CM-99, Stockholm University, Sweden
Kulshrestha UC, Granat L, Engardt M, Rodhe H (2005) Review of precipitation monitoring studies in India—a search for regional patterns. Atmos Environ 39(38):7403–7419
Leung DYC (2015) Outdoor-indoor air pollution in urban environment: challenges and opportunity. Front Environ Sci 2:1–7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2014.00069
Lin M, Gui H, Wang Y, Peng W (2017) Pollution characteristics, source apportionment, and health risk of heavy metals in street dust of Suzhou, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:1987–1998. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7934-0
Mandre M, Tuulmets L (1997) Pigment changes in Norway spruce induced by dust pollution. Water Air Soil Pollut 94:247–258
Miller CA, Davis DD (1981) Response of pinto bean plants exposed to O3, SO2, or mixtures at varying temperatures. HortScience 16:548–550
Mishra M, Kulshrestha U (2017) Chemical characteristics and deposition fluxes of dust-carbon mixed coarse aerosols at three sites of Delhi, NCR. J Atmos Chem 74:399–421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-016-9349-1
Mishra M, Kulshrestha UC (2021) A brief review on changes in air pollution scenario over South Asia during COVID-19 lockdown. Aerosol Air Qual Res 21:1–10. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.200541
Mishra M, Jawahar RVK, Horam C, Kulshrestha UC (2019) Morphological and elemental characteristics of indoor fine aerosols in urban households at three capital cities of India. J Indian Geophys Union 23:258–270
Nazaroff WW, Weschler CJ (2020) Indoor acids and bases. Indoor Air 30:559–644. https://doi.org/10.1111/ina.12670
Park S, Seo B, Lee G, Kahng S, Jang Y (2015) Chemical composition of water soluble inorganic species in precipitation at Shihwa Basin, Korea. Atmosphere 6(6):732–750. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6060732
Ramge P, Badeck F, Plöchl M, Kohlmaier GH (1993) Apoplastic antioxidants as decisive elimination factors within the uptake process of nitrogen dioxide into leaf tissues. New Phytol 125:771–785
Satsangi GS, Lakhani A, Khare P et al (2002) Measurements of major ion concentration in settled coarse particles and aerosols at a semiarid rural site in India. Environ Int 28:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(01)00122-2
Satyanarayana J, Reddy LAK, Kulshrestha MJ, Rao RN, Kulshrestha UC (2010) Chemical composition of rain water and influence of airmass trajectories at a rural site in an ecological sensitive area of Western Ghats (India). J Atmos Chem 66:101–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-011-9193-2
Shahid M, Dumat C, Khalid S et al (2017) Foliar heavy metal uptake, toxicity and detoxification in plants: a comparison of foliar and root metal uptake. J Hazard Mater 325:36–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.11.063
Shannigrahi AS, Fukushima T, Sharma RC (2004) Anticipated air pollution tolerance of some plant species considered for green belt development in and around an industrial/urban area in India: an overview. Int J Environ Stud 61:125–137. https://doi.org/10.1080/0020723032000163137
Sharma A, Singh S, Kulshrestha UC (2018) Aerosol-trace gases interactions and their role in air quality control of Delhi city (India). Arab J Geosci 11:358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3695-z
Sivakumaran S, Hall MA (1978) Effects of age and water stress on endogenous levels of plant growth regulators in Euphorbia lathyrus L. J Exp Bot 29:195–205. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/29.1.195
Smirnoff N (2000) Ascorbic acid: metabolism and functions of a multi-facetted molecule. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:229–235
Srivastava HS (1999) Biochemical defence mechanisms of plants to increased levels of ozone and other atmospheric pollutants. Curr Sci 76:525–533
Stabile L, Dell’Isola M, Russi A et al (2017) The effect of natural ventilation strategy on indoor air quality in schools. Sci Total Environ 595:894–902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.03.048
Teklemariam TA, Sparks JP (2006) Leaf fluxes of NO and NO2 in four herbaceous plant species: the role of ascorbic acid. Atmos Environ 40:2235–2244
Tian L, Zhang G, Zhang Q et al (2008) The impact of kitchen activities on indoor pollutant concentrations. Indoor Built Environ 17:377–383. https://doi.org/10.1177/1420326X08094626
Tiwari R, Gupta GP, Kulshrestha UC (2016) Summer time dustfall fluxes of reactive nitrogen and other inorganic species over the tropical megacity of indo-gangetic plains. Earth Interact 20:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1175/EI-D-15-0053.1
Topping D, Coe H, McFiggans G et al (2004) Aerosol chemical characteristics from sampling conducted on the Island of Jeju, Korea during ACE Asia. Atmos Environ 38:2111–2123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.01.022
Tripathi AK, Gautam M (2007) Biochemical parameters of plants as indicators of air pollution. J Environ Biol 28:127
TüneyKızılkaya İ, Unal D (2018) Effects of nitrate toxicity on free proline accumulation, chlorophyll degradation and photosynthetic efficiency in Chlorella vulgaris Beyerinck [Beijerinck]. Int J Second Metab 6:10–19. https://doi.org/10.21448/ijsm.471036
Turner A, Simmonds L (2006) Elemental concentrations and metal bioaccessibility in UK household dust. Sci Total Environ 371:74–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.08.011
Viecco M, Vera S, Jorquera H et al (2018) Potential of particle matter dry deposition on green roofs and living walls vegetation for mitigating urban atmospheric pollution in semiarid climates. Sustain 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10072431
Wang J, Huang Y, Li T et al (2020) Contamination, morphological status and sources of atmospheric dust in different land-using areas of a steel-industry city, China. Atmos Pollut Res 11:283–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2019.10.014
Weerakkody U, Dover JW, Mitchell P, Reiling K (2018) Evaluating the impact of individual leaf traits on atmospheric particulate matter accumulation using natural and synthetic leaves. Urban For Urban Green 30:98–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ufug.2018.01.001
Weerakkody U (2018) The impact of living walls in the reduction of atmospheric particulate matter pollution (Doctoral dissertation, Staffordshire University)
White KL, Hill AC, Bennett JH (1974) Synergistic inhibition of apparent photosynthesis rate of alfalfa by combinations of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide. Environ Sci Technol 8:574–576
WMO (1994) In: Mohnen V, Santroch J, Vet R (Eds.), Report of the workshop on precipitation chemistry laboratory techniques, Hradec Kralove, Czech Republic 17–21 October
Xin Xu, Hao L, Cao J (2007) Nitrogen dioxide-induced responses in Brassica campestris seedlings: the role of hydrogen peroxide in the modulation of antioxidative level and induced resistance. Agric Sci China 6:1193–1200
Yang S, Liu J, Bi X et al (2020) Risks related to heavy metal pollution in urban construction dust fall of fast-developing Chinese cities. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 197:110628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110628
Yaparla D, Nagendra SMS, Gummadi SN (2019) Characterization and health risk assessment of indoor dust in biomass and LPG-based households of rural Telangana, India. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 69:1438–1451. https://doi.org/10.1080/10962247.2019.1668874
Zhong JNM, Latif MT, Mohamad N et al (2014) Source apportionment of particulate matter (PM10) and indoor dust in a university building. Environ Forensics 15:8–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/15275922.2013.872712
Acknowledgements
This study is a part of DRS-Net (Deposition Research Network through students)—India. Sincere thanks is extended to technical staff of AIRF, JNU and CIF, SES (JNU) for their help.
Funding
Authors are grateful for financial support from CSIR-UGC, DST PURSE, and UKRI GCRF South Asian Nitrogen hub.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ankita Katoch—sample collection, chemical analysis, data analysis, visualization, manuscript preparation. U.C. Kulshrestha—conceptualization, editing, and content enrichment.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Amjad Kallel
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Katoch, A., Kulshrestha, U.C. Deposition of anthropogenic secondary anions through indoor dust on Ficus elastica plants in Delhi, India. Arab J Geosci 17, 112 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-024-11913-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-024-11913-8