Abstract
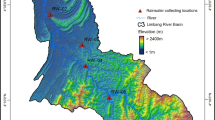
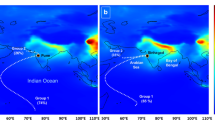
Samples of rain water were collected during monsoon season (June to September) of 2006 and 2007 at Hudegadde, a rural site located in an ecological sensitive area of Western Ghats. The collected samples were analyzed for pH, conductivity and major ions. At this site, rainwater pH varied from 4.20 to 7.39 with 5.65 as volume weighed mean. The observed mean was slightly lower than the average pH reported at most of the Indian continental sites. Monthly variation showed that average pH of rain water was the lowest during September (end of monsoon) and the highest during July (peak of monsoon). Overall, marine sources had dominating influence at this site. However, significant influence of anthropogenic and crustal sources from local as well as inter-continental regions was also noticed. As compared to NO −3 , higher concentration of SO 2−4 was noticed which might be due to contribution from industrial activities responsible for SO2 emission. At this site, influence of five types of airmass trajectories was noticed i.e. i) C.I.O. (Central part of Indian Ocean)-when air masses blown from Maldives and nearby region of central Indian ocean. These airmasses had higher concentrations of nss Ca2+ which did not show any adverse impact on the pH; ii) N.W.I.O.(North-West Indian Ocean)-when airmasses travelled from oceanic region close to north-east Africa. These airmassses had higher concentrations of nss sulphate and nitrate and gave rise to acid rain; iii) S.W.I.O. (South -West Indian Ocean)- when airmasses came from southern part of Indian ocean (close to Mauritius). During these airmasses, rain water samples had almost equal ratio of nss SO 2−4 and nss Ca2+ similar to N.W.I.O but very low NO −3 ; iv) Gulf-when airmasses were observed coming from Gulf region. Although these airmasses contributed only 2% of the total number of samples but carried high amount of nss SO 2−4 which gave rise to acid rain. The second lowest pH was observed during these airmasses which might be due to very high nssSO 2−4 /nssCa2+ ratios; v) N.W.I.O. + S.W.I.C. (North-West Indian Ocean+South-West Indian Continental)- when airmasses originated from north-west Indian Ocean travelling towards south continental part of India and then arriving to the site. During these airmasses, samples showed typical influence of urban activities having high concentrations of nss SO 2−4 and NO −3 leading to the lowest pH of rain water.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, K., Momin, G.A., Tiwari, S., Safai, P.D., Chate, D.M., Rao, P.S.P.: Fog and precipitation chemistry at Delhi, North India. Atmos. Environ. 38, 4215–4222 (2004)
Andreae, M., Merlot, P.: Emission of trace gases from biomass burning. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 15, 955–966 (2001)
Baba, M., Okazaki, M., Hashitani, T.: Effect of acid deposition on forested catchment in the western Tokyo, Japan. Water Air Soil Pollut. 85, 1215–1220 (1995)
Cowling, E.B.: Acid precipitation in historical perspective. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 110–123 (1982)
Das, R., Das, S.N., Mishra, V.N.: Chemical composition of rainwater and dustfall at Bhubaneswar in the east coast of India. Atmos. Environ. 39, 5908–5916 (2005)
Galloway, J.N., Likens, G.E., Edgerton, E.S.: Acid precipitation in the northeastern United States: pH and acidity. Science 194, 722–724 (1976)
Gillett, R., Ayers, G.: The use of thymol as a biocide in rainwater samples. Atmos. Environ. 24A, 2677–2681 (1991)
Granat, L.: Acid and alkaline rains in India- spatial distribution and measurements. In: Das, S.N., Tharkur, R.S. (eds.), IGBP Symposium on Changes in Global Climate Due to Natural and Human Activities. Allied Publishers Limited (1997)
Granat, L., Norman, M., Leck, K., Kulshrestha, U.C., Rodhe, H.: Wet scavenging of sulfur and other compounds during INDOEX. J. Geophys. Res. 107(19), 8025 (2002). doi:1011029/2001JD000499
Hicks, W.K., Kuylenstierna, J.C.I., Owen, A., Dentener, F., Seip, H.-M., Rodhe, H.: Soil sensitivity to acidification in Asia: Status and prospects. Ambio 37, 295–303 (2008)
Jain, M., Kulshrestha, U.C., Sarkar, A.K., Parashar, D.C.: Influence of crustal aerosols on wet deposition at urban and rural sites in India. Atmos. Environ. 34, 5129–5137 (2000)
Keene, W.C., Pszenny, A.P., Galloway, J.N., Hawley, M.E.: Sea salt corrections and interpretations of constituent ratios in marine precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. 91, 6647–6658 (1986)
Keene, W., Sander, R., Pszenny, A.P., Vogt, R., Crutzen, P.J., Galloway, J.N.: Aerosols pH in marine boundary layer. A review and model evaluation. J. Aerosol Science 29, 339–3356 (1998)
Khemani, L.T.: Physical and chemical characteristics of atmospheric aerosols. In: Cheremisionoff, P.N. (ed.) Air pollution control 2 Encyclopedia of Environmental control Techniques. Gulf publishing, USA (1989)
Kulshrestha, U. C., Rodhe, H.: Precipitation Chemistry Metadata from Asia. Presented in 2nd Steering Committee Meeting of CAD programme held at Bangkok, Thailand during November 26–27, (2007)
Kulshrestha, U.C., Sarkar, A.K., Srivastava, S.S., Parashar, D.C.: Investigation into atmospheric deposition through precipitation studies at New Delhi (India). Atmos. Environ. 30, 4149–4154 (1996)
Kulshrestha U. C., Jain M., Sarkar A. K., Kumar A., Parashar D. C.: Contribution of sulphate aerosols to the rain water at a urban site in India. In Proceedings of IGAC International Symposium on Atmospheric Chemistry and Future Global Environment, Naoya Congress Center, Nagoya, Japan, (1997)
Kulshrestha, U.C., Jain, M., Mandal, T.K., Gupta, P.K., Sarkar, A.K., Parashar, D.C.: Measurements of acid rain over Indian ocean and surface measurements of atmospheric aerosols at New Delhi during INDOEX pre-campaigns. Curr. Sci. 76, 968–972 (1999)
Kulshrestha, U.C., Sekar, R., Vairamani, M., Jain, M., Sarkar, A.K., Parashar, D.C., Mitra, A. P.: Signatures of biomass burning over Indian ocean during INDOEX IGAC Symposium, January 21–23, 2001, Bangkok, Thailand (2001)
Kulshrestha, U.C., Kulshrestha, M.J., Sekar, R., Sastry, G.S.R., Vairamani, M.: Chemical characteristics of rainwater at an urban site of south-central. India Atmos. Environ. 37, 3019–3026 (2003a)
Kulshrestha, M.J., Kulshrestha, U.C., Parasar, D.C., Vairamani, M.: Estimation of SO4 contribution by dry deposition of SO2 onto the dust particles in India. Atmos. Environ. 37, 3057–3063 (2003b)
Kulshrestha, U.C., Azhaguvel, S.N., Rao, T., Sekar, R.: Relationship of sulphate aerosols with natural and anthropogenic sources in south-central India Proceedings of 8th IGAC Conference, September 4–9, 2004. Christchurch, New Zealand (2004)
Kulshrestha, U.C., Granat, L., Engardt, M., Rodhe, H.: Review of precipitation monitoring studies in India a search for regional patterns. Atmos. Environ. 39, 7403–7419 (2005)
Kumar, N., Kulshrestha, U.C., Saxena, A., Khare, P., Kumari, K.M., Srivastava, S.S.: Effect of anthropogenic formate and acetate level in precipitation at four sites in Agra. Atmos. Environ. 27B, 87–91 (1993)
Kuylenstierna, J.C.I., Rodhe, H., Cinderby, S., Hicks, K.: Acidification in developing countries: Ecosystem sensitivity and the critical load approach on a Global scale. Ambio 30, 20–28 (2001)
Lorenz, M.: International co-operative programme on assessment and monitoring of air pollution effects on forests-ICP forest. Water Air Soil Pollut. 85, 1221–1226 (1995)
Mahadevan, T.N., Negi, B.S., Meenakshy, V.: Measurement of elemental composition of aerosol matter and precipitation from a remote continental sit in India. Atmos. Environ. 23, 869 (1989)
Manjappa, K., Kelaginamani, S.V.: Rainfall characteristics of Sirsi region of Karnataka and its effect on productivity of rice cropping system. Karnataka J. Agric. Sci. 18, 285–289 (2005)
Menz, F.C., Seip, H.M.: Acid rain in Europe and the United State: an update. Atmospheric Science 7, 253–265 (2004)
Momin, G.A., Ali, K., Rao, P.S.P., Safai, P.D., Chate, D.M., Praveen, P.S., Rodhe, H., Granat, L.: Study of chemical composition of rain water at an urban (pune) and a rural (Singhagad) location in India. J Geophys Res 110, D08302 (2005)
Norman M., Leck C., Rodhe H.: Interhemispehric differences in the chemical characteristics of the Indian Ocean aerosol during INDOEX. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Discussions, 2 (2002)
Norman M., Leck C.: Distribution of marine boundary layer ammonia over the Atlantic and Indian Oceans during the Aerosols99 cruise. In Chemical characteristics of atmospheric aerosols:The influence of natural and man-made sources and sinks. Ph D thesis of M Norman), Stockholm University, Sweden (2003)
Parashar, D.C., Granat, L., Kulshrestha, U.C., Pillai, A.G., Naik, M.S., Momin, G.A., Prakasarao, P.S., Safai, P.D., Khemani, L.T., Naqvi, S.W.A., Narvekar, P.V., Thapa, K.B., Rodhe, H.: Chemical composition of precipitation in India and Nepal-Apreliminary report on an Indo-Swedish project on Atmospheric chemistry. Report CM90, IMI. Stockholm University, Sweden (1996)
Rao, P.S.P., Momin, G.A., Naik, M.S., Safai, P.D., Pillai, A.G., Naik, A.G., Khemani, L.T.: Impact of Ca and SO4 on pH of rain water in rural environment in India. Indian J Environ Pollut 10, 941–943 (1990)
Rao, P.S.P., Momin, G.A., Safai, P.D., Pillai, A.G., Khemani, L.T.: Rain water and through fall chemistry in the silent valley forest in south India. Atmos. Environ. 36, 2025–2029 (1995)
Rastogi, N., Sarin, M.M.: Chemical Characteristics of individual rain events from a semi aride region in India, three year study. Atmos. Environ. 39, 3313–3323 (2005)
Rodhe, H., Langer, J., Gallardo, L., Kjellstrom, E.: Global scale transport of acidifying pollutants. Water Air Soil Pollut. 85, 37–50 (1995)
Safai, P.D., Rao, P.S.P., Momin, G.A., Ali, K., Chate, D.M., Praveen, P.S.: Chemical composition of precipitation during 1984–2002 at Pune, India. Atmos. Environ. 38, 1705–1714 (2004)
Satsangi, G.S., Lakhani, A., Khare, N., Kumari, K.M., Srivastawa, S.S.: Composition of rainwater at semiarid rural site in India. Atmos. Environ. 32, 3783–3793 (1998)
Satyanarayana, J., Reddy, L.A.K., Kulshrestha, M.J., Rao, R.N., Kulshrestha, U.C.: Influence of Crustal Sources and Necessity of Direct Measurements of Bicarbonate in Rain Water: An Indian Perspective. Accepted in AOGS 2010 held at Hyderabad during July 2010 (2010)
Saxena, A., Sharma, S., Kulshrestha, U.C., Srivastava, S.S.: Factors affecting alkaline nature of rainwater in Agra(India). Environ. Pollut. 74, 129–138 (1991)
Tiwari, S., Kulshrestha, U.C., Padmanabhamurty, B.: Monsoon rain chemistry and source apportionment using receptor modeling in and around National Capital Region (NCR) of Delhi, India. Atmos. Environ. 41, 5595–5604 (2007)
White, C., Dawod, A., Cruickshank, K., Gammack, A., Cresser, M.: Evidence of acidification of sensitive Scottish soils by atmospheric deposition. Water Air Soil Pollut. 85, 1203–1208 (1995)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Prof. H Rodhe and Dr L Granat, Stockholm University, Sweden for their valuable support and suggestions and Director, IICT for his encouragements. RAPIDC-CAD financial support from SIDA (Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency) through Stockholm University (IMI MISU) and Stockholm Environment Institute (SEI) is gratefully acknowledged. Our sincere thanks are due to Mr. K.C. Hegde for helping in sample collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Satyanarayana, J., Reddy, L.A.K., Kulshrestha, M.J. et al. Chemical composition of rain water and influence of airmass trajectories at a rural site in an ecological sensitive area of Western Ghats (India). J Atmos Chem 66, 101–116 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-011-9193-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-011-9193-2