Abstract
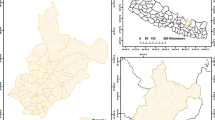
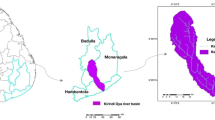
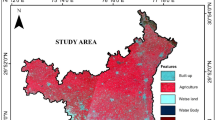
Soil erosion and consequent sedimentation are natural processes that are enhanced by human activities. Soil erosion and related land degradation are major issues, particularly in subtropical monsoon-dominated parts of the world. Soil erosion not only endangers soil fertility and food availability but also harms aquatic ecosystems and water supplies. The purpose of this research is to quantify and map the yearly soil loss in the Panjkora river basin, Pakistan. The Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) model is used in the geospatial environment to achieve the study objectives. The results reveal that the Panjkora basin is moderate to highly susceptible to soil erosion. The estimated annual soil loss from the basin is 5.94 million tons or 10.25 tons per hectare/year. Though the high and very high soil erosion is experienced only in 2.18% of the overall study area, is responsible for 78.52% of the entire soil loss from the Panjkora basin. The study suggests that the K factor (soil type), R factor (rainfall intensity), and LS factor (topography) have the most significant impact on soil erosion in the study area. This study emphasizes the need for proper land and water resource management with viable rehabilitation measures. The soil risk map aids in identifying soil erosion hotspots where efforts should be concentrated to prevent future soil loss. Terraced agricultural and arboriculture methods should be implemented in the Panjkora river basin to prevent additional soil loss.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali A, Khan TA, Ahmad S (2018) Analysis of climate data of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Pakistan. Int Res J Eng Technol 5:4266–4282
Ali K, Khan N, Ullah R, Shah M, Khan MEH, Jones DA, Dewidar M (2022, 1801) Spatial Pattern and Key Environmental Determinants of Vegetation in Sand Mining and Non-Mining Sites along the Panjkora River Basin. Land 11(10)
Amit BERA (2017) Estimation of soil loss by USLE model using GIS and remote sensing techniques: a case study of Muhuri River Basin, Tripura India. Eurasian J Soil Sci 6(3):206–215
Arunrat N, Pumijumnong N (2014) Evaluation of Erosion Productivity Impact Calculator (EPIC) model for nitrogen losses in rice paddy of Thailand. Asian J Agric Res 8(2):70–83
Ashraf A, Abuzar MK, Ahmad B, Ahmad MM, Hussain Q (2017) Modeling risk of soil erosion in high and medium rainfall zones of Pothwar region, Pakistan. Proc Pak Acad Sci: B Life Environ Sci 54(2):67–77
Aster G (2011) Readme. Advanced spaceborne thermal emission and reflection radiometer (ASTER) global digital elevation model (GDEM). Version 2
Avakoudjo J, Kouelo FA, Kindomihou VM, Akponikpe PI, Azontonde AH, Sinsin BA, Agonvinon MS (2020) Water Erosion in the Donga Soils in Subhumid Zone in West Africa. J Environ Prot 11:1073–1088
Azizian A, Koohi S (2021) The effects of applying different DEM resolutions, DEM sources and flow tracing algorithms on LS factor and sediment yield estimation using USLE in Barajin river basin (BRB). Iran. Paddy Water Environ 19:453–468
Babu R, Dhyani BL, Kumar N (2004) Assessment of erodibility status and refined Iso-Erodent Map of India. Indian J Soil Conserv 32(2):171–177
Bajirao TS, Kumar P (2021) Geospatial technology for prioritization of Koyna River basin of India based on soil erosion rates using different approaches. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:35242–35265
Balabathina V, Raju RP, Mulualem W (2019) Integrated remote sensing and gis-based universal soil loss equation for soil erosion estimation in the Megech River Catchment, Tana Lake Sub-basin North-western Ethiopia. Am J Geogr 8(4):141–157
Basson GR (2008) Reservoir sedimentation- An overview of global sedimentation rates and predicted sediment deposition
Batool S, Shirazi SA, Mahmood SA (2021) Appraisal of soil erosion through RUSLE model and hypsometry in Chakwal Watershed (Potwar-Pakistan). Sarhad J Agric 37(2):594–606
Bekele B, Gemi Y (2021) Soil erosion risk and sediment yield assessment with universal soil loss equation and GIS: in Dijo watershed, Rift valley Basin of Ethiopia. Model Earth Syst Environ 7(1):273–291
Benchettouh A, Kouri L, Jebari S (2017) Spatial estimation of soil erosion risk using RUSLE/GIS techniques and practices conservation suggested for reducing soil erosion in Wadi Mina watershed (northwest, Algeria). Arab J Geosci 10(4):79
Bera A (2017) Assessment of soil loss by universal soil loss equation (USLE) model using GIS techniques: a case study of Gumti River Basin, Tripura India. Model Earth Syst Environ 3(1):29
Berberoglu S, Cilek A, Kirkby M, Irvine B, Donmez C (2020) Spatial and temporal evaluation of soil erosion in Turkey under climate change scenarios using the Pan-European Soil Erosion Risk Assessment (PESERA) model. Environ Monit Assess 192(8):1–22
Bhat SA, Hamid I, Dar MUD, Rasool D, Pandit BA, Khan S (2017) Soil erosion modeling using RUSLE & GIS on micro watershed of J&K. J Pharmacogn Phytochem 6(5):838–842
Boakye E, Anyemedu FOK, Donkor EA, Quaye-Ballard JA (2020) Spatial distribution of soil erosion and sediment yield in the Pra River Basin. SN Appl Sci 2(3):1–12
Borrelli P, Märker M, Panagos P, Schütt B (2014) Modeling soil erosion and river sediment yield for an intermountain drainage basin of the Central Apennines, Italy. Catena 114:45–58
Borrelli P, Robinson DA, Panagos P, Lugato E, Yang JE, Alewell C, Ballabio C (2020) Land use and climate change impacts on global soil erosion by water (2015-2070). Proc Natl Acad Sci 117(36):21994–22001
Chuenchum P, Xu M, Tang W (2020) Estimation of soil erosion and sediment yield in the Lancang–Mekong river using the modified revised universal soil loss equation and GIS techniques. Water 12(1):135
Coward MP, Rex DC, Asif Khan M, Windley BF, Broughton RD, Luff IW, Pudsey CJ (1986) Collision tectonics in the NW Himalayas. Geol Soc Spec Publ 19(1):203–219
Danishwar S, Stern RJ, Khan MA (2001) Field relations and structural constraints for the Teru volcanic formation, northern Kohistan Terrane Pakistani Himalayas. J Asian Earth Sci 19(5):683–695
Das GK, Guchait R (2016) Modeling of risk of soil erosion in Kharkai Watershed using RUSLE and TRMM Data: A geospatial approach. Int J Sci Res 5:1–10
Das S, Bora PK, Das R (2021) Estimation of slope length gradient (LS) factor for the sub-watershed areas of Juri River in Tripura. Model Earth Syst Environ 8:1171–1177
Desmet PJJ, Govers G (1996) A GIS procedure for automatically calculating the USLE LS factor on topographically complex landscape units. J Soil Water Conserv 51(5):427–433
Dewangan CL, Ahmad I (2019) Assessment of Reservoir Sedimentation and Identification of Critical Soil Erosion Zone in Kodar Reservoir Watershed. Appl Geomatics Civil Eng: Proc ICGCE 33:203
Dewangan CL, Ahmad I (2020) Assessment of Reservoir Sedimentation and Identification of Critical Soil Erosion Zone in Kodar Reservoir Watershed of Chhattisgarh State, India. In: Applications of Geomatics in Civil Engineering. Springer, Singapore, pp 203–214
Diodato N (2004) Estimating RUSLE’s rainfall factor in the part of Italy with a Mediterranean rainfall regime. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 8(1):103–107
Duarte A (2019) Hopper system design using CFD–Warsak HPS Water-intake (Pakistan). Conference Paper: Bend and straight open-channel experimental research Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/335919808_hopper_system_design_using_cfd_warsak_hpp_water-intake-aduarte
Dutta D, Das S, Kundu A, Taj A (2015) Soil erosion risk assessment in Sanjal watershed, Jharkhand (India) using geo-informatics, RUSLE model and TRMM data. Modeling Earth systems and environment 1:1–9
El-Swaify SA, Dangler EW (1976) Erodibilities of selected tropical soils in relation to structural and hydrologic parameters. In: Foster G (ed) Soil Erosion Prediction and Control. Soil and Water Conservation Society, Ankeny, pp 105–114
Erdogan EH, Erpul G, Bayramin İ (2007) Use of USLE/GIS methodology for predicting soil loss in a semiarid agricultural watershed. Environ Monit Assess 131(1):153–161
Esmaeili Gholzom H, Ahmadi H, Moeini A, Motamed Vaziri B (2021) Water erosion risk assessment in the Kasilian watershed with ICONA model and GIS/RS techniques. Res Earth Sci 12(3):144–163
Eswaran H, Lal R, Reich PF (2019) Land degradation: an overview. In: Response to land degradation, 1st edn. CRC Press, pp 20–35
Farhan Y, Anaba O (2016) A Remote Sensing and GIS Approach for Prioritization of Wadi Shueib Mini-Watersheds (Central Jordan) Based on Morphometric and Soil Erosion Susceptibility Analysis. J Geogr Inf Syst 8:1–19
Flabouris K (2008) Study of rainfall factor R on the RUSLE law (Doctoral dissertation, Doctoral dissertation). Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece
Foster GR (1986) Understanding ephemeral gully erosion. In: Assessing the National Research Inventory. National Research Council, Board on Agriculture, Soil Conservation, vol 2. National Academy Press, Washington DC, pp 90–118
Ganasri BP, Ramesh H (2016) Assessment of soil erosion by RUSLE model using remote sensing and GIS-A case study of Nethravathi Basin. Geosci Front 7(6):953–961
Ghosal K, Bhattacharya SD (2020) A Review of RUSLE Model. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 48(4):689–707
Gilani H, Ahmad A, Younes I, Abbas S (2021) Estimation of annual soil erosion dynamics (2005-2015) in Pakistan using Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). Authorea Preprints. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.4138
Helldén U (1987) An assessment of woody biomass, community forests, land use and soil erosion in Ethiopia. A feasibility study on the use of remote sensing and GIS [geographical information system]-analysis for planning purposes in developing countries. Lund University Press
Hurni H (1985) Soil conservation manual for Ethiopia. First draft. In: Ministry of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation and Development Department, Community Forests and Soil Conservation Development Department. Addis Ababa
ICONA (1988) Agresividad de la lluvia en Espan˜a. Servicio de Publicaciones del Ministerio de Agricultura, Pescay Alimentacion, Madrid, Espan˜a, p 39
Jiang Q, Zhou P, Liao C, Liu Y, Liu F (2020) Spatial pattern of soil erodibility factor (K) as affected by ecological restoration in a typical degraded watershed of central China. Sci Total Environ 749:141609
Kalita N, Borgohain A, Sahariah D, Sarma S (2018) Estimation of soil loss sensitivity in the Jinari river basin using the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Natl Geogr J India 64(1-2):118–127
Kaur B, Sur K, Verma VK, Pateriya B (2022) Implications of Watershed Management Programs for Sustainable Development in Rural Scenario—A Case Study from Foothills of Punjab State, India. Water Conserv Sci Eng 7:647–655
Kayet N, Pathak K, Chakrabarty A, Sahoo S (2018) Evaluation of soil loss estimation using the RUSLE model and SCS-CN method in hillslope mining areas. Int Soil Water Conserv Res 6(1):31–42
Koirala P, Thakuri S, Joshi S, Chauhan R (2019) Estimation of soil erosion in Nepal using a RUSLE modeling andgeospatial tool. Geosciences 9(4):147
Kolli MK, Opp C, Groll M (2021) Estimation of soil erosion and sediment yield concentration across the Kolleru Lake catchment using GIS. Environ Earth Sci 80(4):1–14
Kumar S, Kushwaha SPS (2013) Modelling soil erosion risk based on RUSLE-3D using GIS in a Shivalik sub-watershed. J Earth Sys Sci 122(2):389–398
Kuok KK, Mah DY, Chiu PC (2013) Evaluation of C and P factors in universal soil loss equation on trapping sediment: case study of Santubong River. J Water Resource Prot 5(12):1149–1154
Li C, Pan C (2020) Overland runoff erosion dynamics on steep slopes with forages under field simulated rainfall and inflow. Hydrol Process 34(8):1794–1809
Liu G, Zheng F, Wilson GV, Xu X, Liu C (2021) Three decades of ephemeral gully erosion studies. Soil Tillage Res 212:105046
Luvai A, Obiero J, Omuto C (2022) Soil Loss Assessment Using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) Model. Appl Environ Soil Sci 2022. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2122554
Mahmood S, A ul H K, Ullah S (2016) Assessment of 2010 flash flood causes and associated damages in Dir Valley, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Pakistan. Int J Disaster Risk Reduct 16:215–223
Maqsoom A, Aslam B, Hassan U, Kazmi ZA, Sodangi M, Tufail RF, Farooq D (2020) Geospatial assessment of soil erosion intensity and sediment yield using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) model. ISPRS Int J Geo-inf 9(6):356
McCool DK, Brown LC, Foster GR, Mutchler CK, Meyer LD (1987) Revised slope steepness factor for the Universal Soil Loss Equation. T ASAE 30(5):1387–1396
Meliho M, Nouira A, Benmansour M, Boulmane M, Khattabi A, Mhammdi N, Benkdad A (2019) Assessment of soil erosion rates in a Mediterranean cultivated and uncultivated soils using fallout 137Cs. J Environ Radioactiv 208:106021
Mohammed S, Alsafadi K, Talukdar S, Kiwan S, Hennawi S, Alshihabi O, Harsanyie E (2020) Estimation of soil erosion risk in southern part of Syria by using RUSLE integrating geo informatics approach. Remote Sens Appl Soc Environ 20:100375
Moore ID, Burch GJ (1986) Physical basis of the length-slope factor in the universal soil loss equation. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50(5):1294–1298
Morgan RPC, McIntyre K, Vickers AW, Quinton JN, Rickson RJ (1997) A rainfall simulation study of soil erosion on rangeland in Swaziland. Soil technol 11(3):291–299
Morris G (2020) Classification of management alternatives to combat reservoir sedimentation. Water 12(3):861
Mosavi A, Sajedi-Hosseini F, Choubin B, Taromideh F, Rahi G, Dineva AA (2020, 1995) Susceptibility mapping of soil water erosion using machine learning models. Water 12(7)
Munoth P, Goyal R (2020) Impacts of land use land cover change on runoff and sediment yield of Upper Tapi River Sub-Basin India. Int J River Basin Manag 18(2):177–189
Nampak H, Pradhan B, Mojaddadi Rizeei H, Park HJ (2018) Assessment of land cover and land use change impact on soil loss in a tropical catchment by using multitemporal SPOT-5 satellite images and Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation model. Land Degrad Dev 29(10):3440–3455
Ostovari Y, Moosavi AA, Mozaffari H, Pourghasemi HR (2021) RUSLE model coupled with RS-GIS for soil erosion evaluation compared with T value in Southwest Iran. Arab J Geosci 14(2):1–15
Pal SC, Chakrabortty R (2019) Simulating the impact of climate change on soil erosion in sub-tropical monsoon dominated watershed based on RUSLE, SCS runoff and MIROC5 climatic model. Adv Space Res 64(2):352–377
Panagos P, Borrelli P, Meusburger K (2015a) A new European slope length and steepness factor (LS-Factor) for modeling soil erosion by water. Geosci 5(2):117–126
Panagos P, Borrelli P, Meusburger K, van der Zanden EH, Poesen J, Alewell C (2015b) Modelling the effect of support practices (P-factor) on the reduction of soil erosion by water at European scale. Environ Sci Policy 51:23–34
Paszkowski A, JrS G, Borgomeo E, Khan MSA, Hall JW (2021) Geomorphic change in the Ganges–Brahmaputra–Meghna delta. Nat Rev Earth Environ 2(11):763–780
PEDO (2014) Executive Summary for Shigo Kas Hydropower Project. Pakhtunkhwa Energy Development Organization
Pham TG, Degener J, Kappas M (2018) Integrated universal soil loss equation (USLE) and Geographical Information System (GIS) for soil erosion estimation in A Sap basin: Central Vietnam. Int Soil Water Conserv Res 6(2):99–110
Phinzi K, Ngetar NS, Ebhuoma O (2021) Soil erosion risk assessment in the Umzintlava catchment (T32E), Eastern Cape, South Africa, using RUSLE and random forest algorithm. S Afr Geogr J 103(2):139–162
Prasannakumar V, Vijith H, Abinod S, Geetha NJGF (2012) Estimation of soil erosion risk within a small mountainous sub-watershed in Kerala, India, using Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) and geo-information technology. Geosci Front 3(2):209–215
Rajbanshi J, Bhattacharya S (2020) Assessment of soil erosion, sediment yield and basin specific controlling factors using RUSLE-SDR and PLSR approach in Konar river basin India. J Hydrol 587:124935
Ram Babu VV, Tejwani KG, Agarwal MC, Bhushan LS (1979) Rainfall Intensity Duration-Return Equation and Nomographs of India. In: Proceeding of International Conference on Statistical Climatology, Tokyo Japan, Nov 29, 1979. In Statistical Climatology Development in Atmospheric Science. Elsevier Scientific Publication Co, p 13
Renard KG, Foster GR, Weesies GA, McCool DK, Yoder DC (1996) Predicting soil erosion by water: A guide to conservation planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). Agric Handb 703:25–28
Rashid MU, Shakir AS, Khan NM (2014) Evaluation of sediment management options and minimum operation levels for Tarbela Reservoir, Pakistan. Arab J Sci Eng 39:2655–2668
Riquetti NB, Mello CR, Beskow S, Viola MR (2020) Rainfall erosivity in South America: Current patterns and future perspectives. Sci Total Environ 724:138315
Rozos D, Skilodimou HD, Loupasakis C, Bathrellos GD (2013) Application of the revised universal soil loss equation model on landslide prevention. An example from N. Euboea (Evia) Island, Greece. Environ Earth Sci 70(7):3255–3266
Sabir MA, Shafiq-Ur-Rehman S, Umar M, Waseem A, Farooq M, Khan AR (2013) The Impact of Suspended Sediment Load on Reservoir Siltation and Energy Production: a Case Study of the Indus River and Its Tributaries. Pol J Environ Stud 22(1):219–225
Saha A, Ghosh M, Pal SC (2020) Understanding the morphology and development of a rill-gully: An Empirical study of Khoai Badland, West Bengal, India. In: Gully Erosion Studies from India and Surrounding Regions. Springer Nature, pp 147–161
Schwab GO, Frevert RK, Edminster TW, Barnes KK (1981) Chapter 14-Subsurface Drainage Design. Soil and Water Conservation Engineering, 3rd edn. John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp 314–347
Searle M, Cox J (1999) Tectonic setting, origin, and obduction of the Oman ophiolite. Geol Soc Am Bull 111(1):104–122
Senanayake S, Pradhan B, Alamri A, Park HJ (2022) A new application of deep neural network (LSTM) and RUSLE models in soil erosion prediction. Sci Total Environ 845:157220
Shah MT, Shervais JW (1999) The Dir-Utror metavolcanic sequence, Kohistan arc terrane, northern Pakistan. J Asian Earth Sci 17(4):459–475
Sharpley AN, Williams JR (1990) EPIC. Erosion/Productivity impact calculator: 1. Model documentation. 2. User manual. U.S. Department of Agriculture Technical Bulletin, p 235
Shin GJ (1999a) The analysis of soil erosion analysis in watershed using GIS. Dissertation. Gang-won National University, Gangwon-Do, South Korea
Shin KJ (1999b) The soil loss analysis using GSIS in watershed. Dissertation. Kangwon National University, Kangwon-Do, South Korea
Shit PK, Pourghasemi HR, Bhunia GS (eds) (2019) Gully erosion studies from India and surrounding regions. Springer Nature
Singh G, Rambabu VV, Chandra S (1981) Soil Loss Prediction Research in India. ICAR Bull. Dehradun, CSWCTRI
Singh R, Phadke VS (2006) Assessing soil loss by water erosion in Jamni River Basin, Bundelkhand region, India, adopting universal soil loss equation using GIS. Curr Sci 90(10):1431–1435
Sullivan MA, Windley BF, Saunders AD, Haynes JR, Rex DC (1993) A palaeogeographic reconstruction of the Dir Group: evidence for magmatic arc migration within Kohistan N. Pakistan. Geol Soc Spec Publ 74(1):139–160
Sur K, Chauhan P (2019a) Dynamic trend of land degradation/restoration along Indira Gandhi Canal command area in Jaisalmer District, Rajasthan, India: a case study. Environ Earth Sci 78:1–11
Sur K, Chauhan P (2019b) Imaging spectroscopic approach for land degradation studies: a case study from the arid land of India. Geomat Nat Haz Risk 10(1):898–911
Syvitski JP, Vörösmarty CJ, Kettner AJ, Green P (2005) Impact of humans on the flux of terrestrial sediment to the global coastal ocean. Science 308(5720):376–380
Tachikawa T, Hato M, Kaku M, Iwasaki A (2011) Characteristics of ASTER GDEM version 2. In: 2011 IEEE international geoscience and remote sensing symposium. IEEE, pp 3657–3660
Tamene L, Le QB (2015) Estimating soil erosion in sub-Saharan Africa based on landscape similarity mapping and using the revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE). Nutr Cycl Agroecosystems 102:17–31
Teng H, Liang Z, Chen S, Liu Y, Rossel RAV, Chappell A, Shi Z (2018) Current and future assessments of soil erosion by water on the Tibetan Plateau based on RUSLE and CMIP5 climate models. Sci Total Environ 635:673–686
Terranova O, Antronico L, Coscarelli R, Iaquinta P (2009) Soil erosion risk scenarios in the Mediterranean environment using RUSLE and GIS: an application model for Calabria (southern Italy). Geomorphology 112(3-4):228–245
Teshome A, Halefom A, Teshome M, Ahmad I, Taddele Y, Dananto M, Szucs P (2021) Soil erosion modelling using GIS and revised universal soil loss equation approach: a case study of Guna-Tana landscape Northern Ethiopia. Model Earth Syst Environ 7(1):125–134
Tirkey AS, Pandey AC, Nathawat MS (2013) Use of satellite data, GIS and RUSLE for estimation of average annual soil loss in Daltonganj watershed of Jharkhand (India). J Remote Sens Technol 1(1):20–30
Tiruneh G, Ayalew M (2015) Soil loss estimation using geographic information system in enfraz watershed for soil conservation planning in highlands of Ethiopia. Int J Agric Innov Technol 5(2):21–30
Tundu C, Tumbare MJ, Kileshye Onema JM (2018) Sedimentation and its impacts/effects on river system and reservoir water quality: case study of Mazowe catchment, Zimbabwe. Proc Int Assoc Hydrol Sci 377:57–66
Ullah K, Zhang J (2020) GIS-based flood hazard mapping using relative frequency ratio method: A case study of Panjkora River Basin, eastern Hindu Kush Pakistan. Plos One 15(3):e0229153
Ullah S, Ali A, Iqbal M, Javid M, Imran M (2018) Geospatial assessment of soil erosion intensity and sediment yield: a case study of Potohar Region Pakistan. Environ Earth Sci 77(19):1–13
Walling DE (2011) Human impact on the sediment loads of Asian rivers. In: Sediment problems and sediment management in Asian river basins–Proceedings of the workshop held at Hyderabad, India, pp 37–51
Williams JR, Jones CA, Dyke PT (1984) The EPIC model and its application. In: Proc. Int. Symp. on minimum data sets for agrotechnology transfer, India, Patancheru, pp 111–121
Wilson MJ (2004) Weathering of the primary rock-forming minerals: processes, products and rates. Clay Miner 39(3):233–266
Wischmeier WH, Smith DD (1978) Predicting rainfall erosion losses: a guide to conservation planning (No. 537). Department of Agriculture, Science and Education Administration
Zhao G, Xue H, Ling F (2010) Assessment of ASTER GDEM performance by comparing with SRTM and ICESat/GLAS data in Central China. In: 2010 18th International Conference on Geoinformatics. IEEE, pp 1–5
Zheng F, Zhang XJ, Wang J, Flanagan DC (2020) Assessing applicability of the WEPP hillslope model to steep landscapes in the northern Loess Plateau of China. Soil Tillage Res 197:104492
Acknowledgements
We are very thankful to “Lukasz Pawlik” for his cooperation during the writing/review process.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Biswajeet Pradhan
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nasir, M.J., Alam, S., Ahmad, W. et al. Geospatial soil loss risk assessment using RUSLE model: a study of Panjkora River Basin, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Arab J Geosci 16, 440 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11555-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11555-2