Abstract
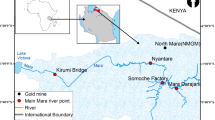
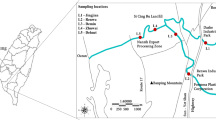
Kalpani River, Pakistan is an important stream that collects more than two third of the untreated domestic, commercial, industrial, and sewerage water, agricultural overflow, and other unwanted effluents of the surrounding area. These effluents have degraded the overall quality of this river water. The current study aims to examine the concentration of selected heavy metal (HM) contamination in Kalpani River sediments. The HMs studied were Pb, Cd, Zn, Ni, Fe, and Cu. Sediment samples were taken from nine selected locations (labeled as P1, P2, P3, … P9) and tested for HM contamination. The HMs contamination level in the sediment was computed using the contamination factor (CF), pollution load index (PLI), and geo-accumulation index (Igeo). All three indicators revealed that the Kalpani River in Mardan city is polluted with hazardous HMs such as Cd, Pb, and Zn. Pb, Ni, Fe, and Cu CF levels in sediment samples ranged from low (< 1) to moderate (1–3). However, the CF values for Cd and Zn indicated being highly polluted (> 6). The PLI values along the Kalpani River varied considerably and were observed lower upstream (P1 and P2, i.e., 0.821), highest (1.229) at the middle course, and lower (0.897) downstream. The Igeo for the studied HMs ranged from moderately to strongly polluted. The primary anthropogenic sources responsible for HM pollution in the Kalpani River were improper waste dumping, untreated sewage urban and industrial wastewater into the river, and excessive pesticide usage.







Similar content being viewed by others
Code availability
Not applicable.
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work. This manuscript is not under review elsewhere and its publication in the Arabian Journal of Geosciences is approved by all authors.
Data availability
Data availability statement is not applicable.
References
Acar O (2012) Evaluation of cadmium, lead, copper, iron and zinc in Turkish dietary vegetable oils and olives using electrothermal and flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Grasas Aceites 63(4):383–393. https://doi.org/10.3989/gya.047512
Ackah M (2019) Soil elemental concentrations, geoaccumulation index, non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic risks in functional areas of an informal e-waste recycling area in Accra, Ghana. Chemosphere 235:908–917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.07.014
Adebowale KO, Agunbide FO, Olu-Owolabi B (2009) Trace metal concentration, site variations and partitioning pattern in water and bottom sediments from coastal area: a case study of Ondo Coast, Nigeria. Environ Res J 3(2), 46–59. https://ir.unilag.edu.ng/handle/123456789/4856
Ahmad I, Jan MQ, DiPietro JA (2003) Age and tectonic implications of granitoid rocks from the Indian plate of Northern Pakistan. J. Virtual Explor.11(2)
Ashraf M, Dawood H (2010) Geology of acid and alkalic minor bodies associated with granitic and alkalic complexes of Malakand Division. Geol Bull Punjab Univ 45:49–68
Balkhair KS, Ashraf MA (2016) Field accumulation risks of heavy metals in soil and vegetable crop irrigated with sewage water in western region of Saudi Arabia. Saudi J of Biol Sci 23(1):S32–S44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.09.023
Banu Z, Chowdhury MSA, Hossain MD, Nakagami KI (2013) Contamination and ecological risk assessment of heavy metal in the sediment of Turag River, Bangladesh: an index analysis approach. J Water Resource Prot. https://doi.org/10.4236/jwarp.2013.52024
Barakat A, El Baghdadi M, Rais J, Nadem S (2012) Assessment of heavy metal in surface sediments of Day River at Beni-Mellal region Morocco. Res J Environ Earth Sci 4(8):797–806
Briffa J, Sinagra E, Blundell R (2020) Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 6(9):e04691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04691
Chakravarty M, Patgiri AD (2009) Metal pollution assessment in sediments of the Dikrong River NE India. J Hum Ecol 27(1):63–67. https://doi.org/10.1080/09709274.2009.11906193
Chatterjee S, Dutta A, Gupta RK, Sinha UK (2022) Genesis, evolution, speciation and fluid-mineral equilibrium study of an unexplored geothermal area in Northeast Himalaya India. Geothermics 105:102483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2022.102483
Dragović S, Mihailović N, Gajić B (2008) Heavy metals in soils: distribution, relationship with soil characteristics and radionuclides and multivariate assessment of contamination sources. Chemosphere 72(3):491–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.02.063
Fagbote EO, Olanipekun EO (2010) Evaluation of the status of heavy metal pollution of soil and plant (Chromolaena odorata) of Agbabu Bitumen Deposit Area Nigeria. Am-Euras J Sci Res 5(4):241–248
Fang T, Yang K, Lu W, Cui K, Li J, Liang Y, Li H (2019) An overview of heavy metal pollution in Chaohu Lake, China: enrichment, distribution, speciation, and associated risk under natural and anthropogenic changes. Environ Sci Pol Res 1–12. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06210-x
Fawzy EM, Ahmed MM, Soltan ME, Gamal TA (2012) Spatial and seasonal variations in depth profile of metals in some sediments from Red Sea Islands and the effect of grain size. Toxicol Environ Chem 94(6):1053–1074. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772248.2012.691506
Forsythe KW, Marvin CH, Valancius CJ, Watt JP, Swales SJ, Aversa JM, Jakubek DJ (2016) Using geo-visualization to assess lead sediment contamination in Lake St. Clair Can Geogr 60(1):149–158. https://doi.org/10.1111/cag.12253
Garcia-Sanchez A, Alonso-Rojo P, Santos-Frances F (2010) Distribution and mobility of arsenic in soils of a mining area (Western Spain). Sci Total Environ 408(19):4194–4201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.05.032
Goudie AS, Viles HA (2013) The earth transformed: an introduction to human impacts on the environment. John Wiley and Sons
Green AJ, Planchart A (2018) The neurological toxicity of heavy metals: a fish perspective. Comp Biochem Physiol Part - C: Toxicol Pharmacol 208:12-19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2017.11.008
Gupta N, Yadav KK, Kumar V, Kumar S, Chadd RP, Kumar A (2019) Trace elements in soil-vegetables interface: translocation, bioaccumulation, toxicity and amelioration-a review. Sci Total Environ 651:2927–2942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.047
Harguinteguy CA, Cirelli AF, Pignata ML (2014) Heavy metal accumulation in leaves of aquatic plant Stuckenia filiformis and its relationship with sediment and water in the Suquía river (Argentina). Microchem J 114:111–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2013.12.010
Harikumar PS, Jisha TS (2010) Distribution pattern of trace metal pollutants in the sediments of an urban wetland in the southwest coast of India. Int J Eng Sci Technol 2(5):840–850
Harikumar PS, Nasir UP, Rahman MM (2009) Distribution of heavy metals in the core sediments of a tropical wetland system. Int J Environ Sci Technol 6(2):225–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03327626
Huang P, Li TG, Li AC, Yu XK, Hu NJ (2014) Distribution, enrichment and sources of heavy metals in surface sediments of the North Yellow Sea. Cont Shelf Res 73:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2013.11.014
Ipeaiyeda AR, Ayoade AR (2017) Flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination of heavy metals in aqueous solution and surface water preceded by co-precipitation procedure with copper (II) 8-hydroxyquinoline. Appl Water Sci 7(8):4449–4459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-017-0590-9
Javed M (2004) Comparison of selected heavy metals toxicity in the planktonic biota of the river Ravi. Indian J Biol Sci 1:59–62
Khaliq A, Ahmad J, Shah Z (2003) New geological investigations regarding MCT along southwestern part of Malakand granite gneiss, Malakand agency, kpk. Pakistan Geol Bull Univ Peshawar 36:23–30
Khan S, Rehman S, Khan AZ, Khan MA, Shah MT (2010) Soil and vegetables enrichment with heavy metals from geological sources in Gilgit, northern Pakistan. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73(7):1820–1827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.08.016
Kumar A, Maroju S, Bhat A (2007) Application of ArcGIS geostatistical analyst for interpolating environmental data from observations. Environ Prog 26(3):220–225. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.10223
Legorburu I, Rodríguez JG, Borja Á, Menchaca I, Solaun O, Valencia V, Larreta J (2013) Source characterization and spatio–temporal evolution of the metal pollution in the sediments of the Basque estuaries (Bay of Biscay). Mar Pollut Bull 66(1–2):25–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.11.016
Luo XS, Xue Y, Wang YL, Cang L, Xu B, Ding J (2015) Source identification and apportionment of heavy metals in urban soil profiles. Chemosphere 127:152–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.01.048
Martin JM, Meybeck M (1979) Elemental mass-balance of material carried by major world rivers. Mar Chem 7(3):173–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4203(79)90039-2
Matschullat J, Ottenstein R, Reimann C (2000) Geochemical background–can we calculate it? Environ Geol 39(9):990–1000. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002549900084
Mingbiao L, Jianqiang L, Weipeng CAO, Maolan W (2008) Study of heavy metal speciation in branch sediments of Poyang Lake. J Environ Sci 20(2):161–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1001-0742(08)60025-x
Mishra S, Bharagava RN, More N, Yadav A, Zainith S, Mani S, Chowdhary P (2019) Heavy metal contamination: an alarming threat to environment and human health. In Environmental biotechnology: For sustainable future (pp. 103–125). Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-7284-0_5
Mohammed AS, Kapri A, Goel R (2011) Heavy metal pollution: source, impact, and remedies. In Biomanagement of metal-contaminated soils (pp. 1–28). Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-1914-9_1
Muhammad S, Shah MT, Khan S (2011) Health risk assessment of heavy metals and their source apportionment in drinking water of Kohistan region, northern Pakistan. Microchem J 98(2):334–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2011.03.003
Muller G (1969) Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 2:108–118
Nazir A, Khan MA, Ghosh P (2022) Assessment of variations in metal concentrations of the Ganges River water by using multivariate statistical techniques. Limnologica 125989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.limno.2022.125989
Pigneret M, Mermillod-Blondin F, Volatier L, Romestaing C, Maire E, Adrien J, Hervant F (2016) Urban pollution of sediments: impact on the physiology and burrowing activity of tubificid worms and consequences on biogeochemical processes. Sci Total Environ 568:196–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.05.174
Rabee AM, Al-Fatlawy YF, Nameer M (2011) Using pollution load index (PLI) and geoaccumulation index (I-Geo) for the assessment of heavy metals pollution in Tigris river sediment in Baghdad Region. Al-Nahrain J Sci 14(4), 108–114. https://anjs.edu.iq/index.php/anjs/article/view/772/691
Raju KV, Somashekar RK, Prakash KL (2012) Heavy metal status of sediment in river Cauvery Karnataka. Environ Monit Assess 184(1):361–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-1973-2
Rashid A, Farooqi A, Gao X, Zahir S, Noor S, Khattak JA (2020) Geochemical modeling, source apportionment, health risk exposure and control of higher fluoride in groundwater of sub-district Dargai. Pakistan Chemosphere 243:125409
Rawat KS, Tripathi VK, Singh SK (2018) Groundwater quality evaluation using numerical indices: a case study (Delhi, India). Sustain Water Resour Manag 4(4):875–885. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-017-0181-9
Rezende HC, Nascentes CC, Coelho NM (2011) Cloud point extraction for determination of cadmium in soft drinks by thermospray flame furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchem J 97(2):118–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2010.08.006
Sabo R, Jin L, Stark N, Ibach RE (2013) Effect of environmental conditions on the mechanical properties and fungal degradation of polycaprolactone/microcrystalline cellulose/wood flour composites. BioResources 8, (3), 3322–3335; 3322–3335. DOI: https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.8.3.3322-3335
Sajid M, Andersen J, Rocholl A, Wiedenbeck M (2018) U-Pb geochronology and petrogenesis of peraluminous granitoids from northern Indian plate in NW Pakistan: Andean type orogenic signatures from the early Paleozoic along the northern Gondwana. Lithos 318:340–356
Salah EAM, Zaidan TA, Al-Rawi AS (2012) Assessment of heavy metals pollution in the sediments of Euphrates River Iraq. J Water Resour Prot 4(12):1009. https://doi.org/10.4236/jwarp.2012.412117
Salehi F, Abdoli MA, Baghdadi M (2014) Sources of Cu, V, Cd, Cr, Mn, Zn Co, Ni, Pb, Ca and Fe in soil of Aradkooh landfill. Int J Environ Res 8(3):543–550. https://doi.org/10.22059/IJER.2014.748
Sharley DJ, Sharp SM, Bourgues S, Pettigrove VJ (2016) Detecting long-term temporal trends in sediment-bound trace metals from urbanised catchments. Environ Pol 219:705–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.06.072
Singh SK, Srivastava PK, Singh D, Han D, Gautam SK, Pandey AC (2015) Modeling groundwater quality over a humid subtropical region using numerical indices, earth observation datasets, and X-ray diffraction technique: a case study of Allahabad district India. Environ Geochem Health 37(1):157–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-014-9638-z
Sodrzeieski PA, Andrade LCD, Tiecher T, Camargo FADO (2019) Physico-chemical variability and heavy metal pollution of surface sediment in a non-channeled section of Dilúvio Stream (Southern Brazil) and the influence of channeled section in sediment pollution. Rev Ambiente and Água 14(1). DOI: https://doi.org/10.4136/ambi-agua.2285
Soliman NF, Nasr SM, Okbah MA, El Haddad HS (2015) Assessment of metals contamination in sediments from the Mediterranean Sea (Libya) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. Global J Adv Res 1:120–136
Sthanadar AA, Sthanadar IA, Muhammad A, Ali PA, Shah M, Zahid M, Yousaf M (2013) Bioaccumulation profile of heavy metals in the liver tissues of Wallago attu (MULLEY) from Kalpani River Mardan, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Pakistan. Int J Biosci 3(11):92–103. http://www.innspub.net. Accessed 13 Oct 2021
Sthanadar IA, Sthanadar AA, Begum B, Nair MJ, Ahmad I, Muhammad A, Ullah S (2015) Aquatic pollution assessment using skin tissues of mulley (Wallago attu, Bloch and Schneider, 1801) as a bio-indicator in Kalpani River at District Mardan Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. J Biodivers Env Sci 6(02):57–66
Suja F, Pramanik BK, Zain SM (2009) Contamination, bioaccumulation and toxic effects of perfluorinated chemicals (PFCs) in the water environment: a review paper. Water Sci Technol 60(6):1533–1544. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2009.504
Sulaiman FR, Bakri NIF, Nazmi N, Latif MT (2017) Assessment of heavy metals in indoor dust of a university in a tropical environment. Environ Foren 18(1):74–82. https://doi.org/10.1080/15275922.2016.1263903
Taher MM, Saleh SM, Alberkani AA (2021) Assessment of metal contamination in deposited dust of the industrial area and some streets-Aden city, Yemen. Univ Aden J Natl Appl Sci 25(1):111–129. https://doi.org/10.47372/uajnas.2021.n1.a10
Tareen AK, Sultan IN, Parakulsuksatid P, Shafi M, Khan A, Khan MW, Hussain S (2014) Detection of heavy metals (Pb, Sb, Al, As) through atomic absorption spectroscopy from drinking water of District Pishin, Balochistan, Pakistan. Intl J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 3(1):299–308
Taylor MP, Mackay AK, Hudson-Edwards KA, Holz E (2010) Soil Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn contaminants around Mount Isa city, Queensland, Australia: potential sources and risks to human health. Appl Geochem 25(6):841–855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2010.03.003
Tian L, Zhu X, Wang L, Peng F, Pang Q, He F, Xu B (2021) Distribution, occurrence mechanisms, and management of high fluoride levels in the water, sediment, and soil of Shahu Lake China. Appl Geochem 126:104869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2021.104869
Tomlinson DL, Wilson JG, Harris CR, Jeffrey DW (1980) Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen 33(1):566. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02414780
Turekian KK, Wedepohl KH (1961) Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. Geol Soc Am Bull 72(2):175–192. https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(1961)72[175:DOTEIS]2.0.CO;2
Upadhyay AK, Gupta KK, Sircar JK, Deb MK, Mundhara GL (2006) Heavy metals in freshly deposited sediments of the river Subernarekha, India: an example of lithogenic and anthropogenic effects. Environ Geol 50(3):397–403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0218-0
Varol M, Şen B (2012) Assessment of nutrient and heavy metal contamination in surface water and sediments of the upper Tigris River, Turkey. CATENA 92:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2011.11.011
Wilson J (1987) Evaluation of estuarine quality status at system level with the biological quality index and the pollution load index (PLI). Biol Environ 103:47–59
Xu F, Liu Z, Cao Y, Qiu L, Feng J, Xu F, Tian X (2017) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in urban river sediments in the Jiaozhou Bay catchment, Qingdao, China. CATENA 150:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.11.004
Yang Z, Wang Y, Shen Z, Niu J, Tang Z (2009) Distribution and speciation of heavy metals in sediments from the mainstream, tributaries, and lakes of the Yangtze River catchment of Wuhan China. J Hazard Mater 166(2–3):1186–1194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.12.034
Zahoor M, Mabood F, Ullah F (2014) Comparative study of different metals in rocks of Heroshah Malakand Pakistan. J Chem Soc Pak 36(5)
Zare Khosheghbal M, Esmaeilzadeh M, Ghazban F, Charmsazi ME (2020) Heavy metal pollution status in surface sediments of The Khajeh Kory River North of Iran. Water Sci Technol 81(6):1148–1158. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2020.202
Zhang XY, Lin FF, Wong MT, Feng XL, Wang K (2009) Identification of soil heavy metal sources from anthropogenic activities and pollution assessment of Fuyang County China. Environ Monit Assess 154(1–4):439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0410-7
Zhong WS, Ren T, Zhao LJ (2016) Determination of Pb (lead), Cd (cadmium), Cr (chromium), Cu (copper), and Ni (nickel) in Chinese tea with high-resolution continuum source graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. J Food Drug Anal 24(1):46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2015.04.010
Funding
The University of Peshawar (UoP), Peshawar, Pakistan, and the Higher Education Commission (HEC), Islamabad, Pakistan, provided financial support for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Muhammad Jamal Nasir: conceptualization, writing—original draft, software, visualization, methodology, supervision, and reviewing. Abdul Wahab: data collection, draft preparation, software, and data curation. Tehreem Ayaz: writing, software, visualization, reviewing, editing, and formatting. Sardar Khan: supervision and reviewing. Amir Zeb Khan: reviewing and editing. Ming Lei: reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Amjad Kallel
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nasir, M.J., Wahab, A., Ayaz, T. et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution using contamination factor, pollution load index, and geoaccumulation index in Kalpani River sediments, Pakistan. Arab J Geosci 16, 143 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11231-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11231-5