Abstract
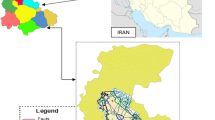
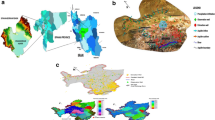
The severe discharge of aquifers is presenting many problems such as a drop in groundwater level and resulting in ground settlement and quality decline. To determine the groundwater system current conditions, the data of 15 piezometers and 11 sampling points concerning groundwater levels and quality were obtained from 1999 to 2014 in the study area of Jangal-Geysour, Razavi Khorasan Province, Iran. Concerning groundwater levels and quality data, two developed models of MODFLOW and MT3D were applied and calibrated from 1999 to 2010 and validated for the years 2010–2014. After substantial calibration and validation, four scenarios were presented. In scenario one (to balance the relative groundwater level drop condition in a five-year period) to achieve this target, the rate of withdrawals was decreased annually over 10%. To provide water demands of the public, the 10% reduction in the exploitation amount can be compensated by the groundwater sourced from the Jangal-Geysour groundwater resource field. In the second scenario, by applying the suggested addition withdrawals control method, the average moment withdrawal of 33.8 l/s was calculated for each well, and wells that exploit more than average should be controlled and the amount of overdraft subtracted from them. The third scenario studied wells used to supply the demand for agriculture, and tried to presented a suitable cropping pattern by considering allowed work hours to control and manage withdrawals. In the fourth scenario, the impact of irrigation of salty water on production decrease because of water level drop by continuing the current trend was evaluated.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad N (1974) Groundwater resources of Pakistan, 61-b/2. Gulberg III, Lahore, Pakistan
Alizadeh A (2009) Surface irrigation system design, 1rd edn. Astan Quds Razavi, Mashhad, pp 124–198
Amiri V, Berndtsson R (2020) Fluoride occurrence and human health risk from groundwater use at the west coast of Urmia Lake, Iran. Arab J Geosci 13(921):1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05905-7
Amiri V, Kamrani S, Ahmad A (2020) Groundwater quality evaluation using Shannon information theory and human health risk assessment in Yazd province, central plateau of Iran. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10362-6
Anderson MP, Woesner WW (1992) Applied groundwater modeling: simulation of flow and Advective transport. Academic, San Diego
Asghar MN, Prathapar SA, Shafique MS (2002) Extracting relatively-fresh groundwater from aquifers underlain by salty groundwater. Agric Water Manag 50(2):119–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-3774(01)00130-5
Ayenew T, Tilahun N (2008) Assessment of lake-groundwater interactions and anthropogenic stresses, using numerical groundwater flow model, for a rift lake catchment in Central Ethiopia. Lakes Reserv Res Manag 13(4):325–343. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1770.2008.00383.x
Bakalowicz M (2006) Importance of regional study site conditions in elaborating concepts and approaches in karst science. In: Harmon RS, Wicks CM, Ford DC, White WB (eds) Perspectives on karst geomorphology, hydrology, and geochemistry. GSA, Special Paper 404, pp 15–22
Basharat M (2012) Spatial and temporal appraisal of groundwater depth and quality in LBDC command-issues and options. Pakistan J Eng Appl Sci 11(14):14–29
Bense VF, Gleeson T, Loveless SE, Bour O, Scibek J (2013) Fault zone hydrogeology. Earth Sci Rev 127:171–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.09.008
Bredehoeft J (2003) From models performance assessment: the conceptualization problem. Ground Water 41(5):571–577. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2003.tb02395.x
Candela L, Elorza FJ, Tamoh K, Jiménez-Martínez J, Aureli A (2013) Groundwater modelling with limited data sets: the Chari-Logone area (Lake Chad Basin, Chad). Hydrol Process 28(11):3714–3727. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.9901
Carrera J, Neuman SP (1986) Estimation of aquifer parameters under transient and steady state conditions: 1. Maximum likelihood method incorporating prior information. Water Resour Res 22(2):199–210. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR022i002p00199
Chiang WH, Kinzelbach W (1998) Processing Modflow: a simulation system for modeling groundwater flow and pollution. User’s manual. U.S. Department of the interior, U.S. geological survey. https://ethz.ch/content/dam/ethz/special-interest/baug/ifu/ifu-dam/softwares/pmwin/pm5.pdf
CSIRO (2003) Investigation conjunctive water management options using a dynamic surface-groundwater modeling approach: a case study of Rechna doab. Commonwealth scientific and industrial research organization (CSIRO), land and water, Technical report 35/03, IWMI. http://www.clw.csiro.au/publications/technical2003/tr35-03.pdf
Doherty J (1998) PEST: model independent parameter estimation, user’s manual. Watermark, Brisbane
Domenico PA, Schwartz FW (1990) Physical and chemical hydrogeology, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 50–74
Engesgaard P, Jensen KH, Molson J, Frind EO, Olsen H (1996) Large-scale dispersion in a sandy aquifer: simulation of subsurface transport of environmental tritium. Water Resour Res 32(11):3253–3266. https://doi.org/10.1029/96WR02398
Fiori A (1996) Finite Peclet extensions of Dagan’s solutions to transport in anisotropic heterogeneous formations. Water Resour Res 32(1):193–198. https://doi.org/10.1029/95WR02768
Ganyaglo SY, Benoeng-Yakubo B, Osae S, Dampare SB, Fianko JR, Bhuiyan MAH (2010) Hydrochemical and isotopic characterisation of groundwaters in the eastern region of Ghana. J Water Resour Prot 2:199–208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-1085-7
Gebreyohannes T, De Smedt F, Walraevens K, Gebresilassie S, Hussien A, Hagos M, Amare K, Deckers J, Gebrehiwot K 2013. Application of a spatially distributed water balance model for assessing surface water and groundwater resources in the Geba basin, Tigray, Ethiopia. J Hydrol 499:110–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.06.026
Gelhar LW, Welty C, Rehfeldt KR (1992) A critical review of data on field-scale dispersion in aquifers. Water Resour Res 28(7):1955–1974. https://doi.org/10.1029/92WR00607
Girmay T, Teshome Z, Mahari M. Knowledge (2015) attitude and practices of peasants towards hyraxes in two selected church forests in Tigray. J Biodivers Conserv 7(5):299-307. https://doi.org/10.5897/IJBC2014.0793
Ghodrati M, Sabani A (2012) Groundwater numerical model. Danesh, Simay
Gillespie J, Nelson ST, Mayo AL, Tingey DG (2012) Why conceptual groundwater flow models matter: a trans boundary example from the arid Great Basin, western USA. Hydrogeol J 20(6):1133–1147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-012-0848-0
Hagos MA (2010) Groundwater flow modeling assisted by GIS and RS techniques (raya valley- ethiopia), M.Sc. Thesis, In: international institutes for geo-information science and earth observation Enschede. http://www.secheresse.info/spip.php?article72621
Harbaugh JW, Banta ER, Hill MC, McDonald MG (2000) MODFLOW2000, The US Geological Survey’s modular ground-water flow model: user guide to modularization concepts and the groundwater flow process. US Geol Surv Open-File Rep 00–92, p 121
He ML, Gibb D, McKinnon, J.J, McAllister, T.A (2013) Effect of high dietary levels of canola meal on growth performance, carcass quality and meat fatty acid profiles of feedlot cattle. Can J Anim Sci 93(2):269-280. https://doi.org/10.4141/cjas2012-090
Hernández JA, Talavera JM, Martínez-Gómez P, Dicenta F, Sevilla F (2001) Response of antioxidant enzymes to plum pox virus in two apricot cultivars. Physiol Plant. 111:313–321. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1399-3054.2001.1110308.x
Højberg A, Refsgaard J (2005) Model uncertainty—parameter uncertainty versus conceptual models. Water Sci Technol 52(6):177–186. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2005.0166
Huysmans M, Chew H, Ellwood R (2011) Clinical studies of dental erosion and erosive wear. Caries Res, 45(1):60–68. https://doi.org/10.1159/000325947
Huysmans M, Dassargues A (2005) Review of the use of P’eclet numbers to determine the relative importance of advection and diffusion in low permeability environments. Hydrogeol J 13(5-6):895–904. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-004-0387-4
Islam MB, Firoz ABM, Foglia L, Marandi A, Rahman Khan A, Schüth C, Ribbe L (2017) A regional groundwater-flow model for sustainable groundwater-resource management in the south Asian megacity of Dhaka, Bangladesh. Hydrogeol J 25(3):617–637. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-016-1526-4
Izady A, Davari K, Alizadeh A, Qahraman B, Haqaiqi Moqaddam SA (2007) Estimation of surface level using artificial neural network. Iranian J Irrigation Drainage 2:59–71
Izady A, Davary K, Alizadeh A, Moghaddam Nia A, Ziaei AN, Hasheminia SM (2013) Application of NN-ARX model to predict groundwater level in the Neishaboor plain, Iran. Water Resour Manag 27:4773–4794. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-013-0432-y
Izady A, Davary K, Alizadeh A, Ziaei AN, Alipoor A, Joodavi A, Brusseau ML (2014) A framework toward developing a groundwater conceptual model. Arab J Geosci 7:3611–3631. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-0971-9
Jerome M, Chantal GO (2002) Modeling flow and nitrate transport in groundwater for the prediction of water travel times and of consequences of land use evolution on water quality. Hydrol Process 16(2):479–492. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.328
Johnston R, Smakhtin V (2014) Hydrological modeling of large river basins: how much is enough? Water Resour Manag 28(10):2695–2730. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0637-8
Joodavi A, Zare M (2009) Groundwater resources planning in a "groundwater mining" condition; Feyz-Abad aquifer as a case study, International conferences on water resources, 2rd edn. Ahvaz, Iran, pp 411-417
Kardan H, Banihabib ME (2016) Analysis of interference of saltwater in desert aquifers (case study: South Khorasan, Sarayan Aquifer). J Water Soil 31(3):673–688. https://doi.org/10.22067/JSW.V31I3.48205
Khan S, Rana T, Gabriel HF, Ullah MK (2008) Hydrogeologic assessment of escalating groundwater exploitation in the Indus Basin, Pakistan. Hydrogeol J 16(8):1635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-008-0336-8-1654
Kim K (2002) Plagioclase weathering in the groundwater system of a sandy, silicate aquifer. Hydrol Process J 16(9):1793–1806. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.1081
King AC, Matthias R, Malcolm CE, Dioni IC (2017) Comparison of groundwater recharge estimation techniques in an alluvial aquifer system with an intermittent/ephemeral stream (Queensland, Australia). Hydrogeol J 25(6):1759–1777. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-017-1565-5
Klise KA, Tidwell VC, McKenna SA (2008), Comparison of laboratory-scale solute transport visualization experiments with numerical simulation using cross-bedded sandstone. Adv Water Resour 31(12):1731– 1741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2008.08.013
Kori SM, Qureshi AL, Lashari BK, Memon NA (2013) Optimum strategies of groundwater pumping regime under scavanger tubewells in lower indus basin, Sindh, Pakistan. Inter Water tech J (IWTJ) 3(3):138. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2041648
Le Page M, Berjamy B, Fakir Y, Bourgin F, Jarlan L, Abourida A, Benrhanem M, Jacob G, Huber M, Sghrer F, Simonneaux V, Chehbouni G (2012) An integrated DSS for groundwater management based on remote sensing. The case of a semi-arid aquifer in Morocco. Water Resour Manag 26(11):3209–3230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-012-0068-3
Mayo AL, Loucks MD (1995) Solute and isotopic geochemistry and ground water flow in the Central Wasatch range, Utah. J Hydrol 172(1–4):31–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(95)02748-E
Mekonnen D, Siddiqi A, Ringler C (2016) Drivers of groundwater use and technical efficiency of groundwater, canal water, and conjunctive use in Pakistan’s Indus Basin irrigation system. Intl J Water Resour Dev 32(3):459–476. https://doi.org/10.1080/07900627.2015.1133402
Meyer P, Ye M, Rockhold M, Neuman S, Cantrell K (2007) Combined estimation of hydrogeologic conceptual model parameter and scenario uncertainty with application to uranium transport at the Hanford site 300 area, Rep. NUREG/CR-6940 PNNL-16396, U.S. Nucl Regul Comm, Washington, D. C.
Meyer PD, Gee GW (1999) Groundwater conceptual models of dose assessment codes. Presented at U.S. NRC Workshop on GroundWater Modeling Related to Dose Assessment, Rockville, Maryland
Moriasi DN, Arnold JG, VanLiew MW, Bingner RL, Harmel RD, Veith TL (2007) Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Transe ASABE 50(3):885–900. https://doi.org/10.13031/trans.58.10715
Mokhtari Z, Nazemi A, Nadiri A (2012) The prediction of groundwater leveling using Shistar plain artificial neural network model. Geotech Geol (Appl Geol) 8(4):345–353
Nag SK (2009) Quality of groundwater in parts of ARSA block, Purulia District, West Bengal. Bhu-Jal 4(1):58–64
Narayan KA, Schleeberger C. Charlesworth PB, Bristow KL (2003) Effects of groundwater pumping on saltwater intrusion in the lower Burdekin Delta, North Queensland. In: Post DA (ed). International Congress on Modelling and Simulation. Modelling and Simulation Society of Australia and New Zealand
Neuman S, Wierenga P. (2003) A comprehensive strategy of hydrogeologic modeling and uncertainty analysis for nuclear facilities and sites, Rep. NUREG/CR-6805, U.S. Nucl Regu, Comm Washington, DC
Niazi A, Bentley LR, Hayashi M (2017) Estimation of spatial distribution of groundwater recharge from stream baseflow and groundwater chloride. J Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.01.032
Niazi A, Prasher S O, Adamowski J, Gleeson T P (2014) A system dynamics model to conserve arid region water resources through aquifer storage and recovery in conjunction with a dam. www.mdpi.com/journal/water. 6:2300–2321, https://doi.org/10.3390/w6082300
Omole D, Bamgbelu O, Tenebe I, Emenike P, Oniemayin B (2017) Analysis of groundwater quality in a Nigerian community. J Water Resour Hydraulic Eng 6(2):22–26. https://doi.org/10.5963/JWRHE0602001
P´erez-García JM, Sebastian-Gonz´alez´ E, Alexander KL, S´ anchez-Zapata JA, Botella F (2014) Effect of landscape configuration and habitat quality on the community structure of waterbirds using a man-made habit. Eur J Wildl Res 60:875–883. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10344-014-0854-8
Poeter E, Anderson D (2005) Multi model ranking and inference in ground water modeling. Ground Water 43(4):597–605. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2005.0061.x
Prinos, ST (2016) saltwater intrusion monitoring in Florida. Special Issue: Status of Florida’s Groundwater Resources, Florida Scientist, 79(4)
Refsgaard J, Van der Sluijs J, Brown J, Van der Keur P (2006) A framework for dealing with uncertainty due to model structure error. Adv Water Resour 29(11):1586–1597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2005.11.013
Rödiger T, Geyer S, Mallast U, Merz R, Krause P, Fischer C, Siebert C (2014) Multi-response calibration of a conceptual hydrological model in the semiarid catchment of Wadi al Arab, Jordan. J Hydrol 509:193–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.11.026
Rojas R, Feyen L, Batelaan O, Dassargues A (2010) On the value of conditioning data to reduce conceptual model uncertainty in groundwater modeling. Water Resour Res 46(8):520–540. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009WR008822
Rojas R, Feyen L, Dassargues A (2008) Conceptual model uncertainty in groundwater modeling: combining generalized likelihood uncertainty estimation and Bayesian model averaging. Water Resour Res 44(12):418–434. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008WR006908
Rooki R, Aryafar A, Adelinasab J (2017) Investigating the groundwater quality in aquifer of Gonabad basin, Khorasan Razavi, using multivariate statistical methods and artificial intelligence. J Resour Mineral Eng 2(1):49–61
Roth D, Guo W, Novick P (1998) Dominant-negative alleles of SEC10 reveal distinct domains involved in secretion and morphogenesis in yeast. Mol Biol Cell 9(7):1725-39. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.010188
Sabbaghi M, Shahnazari A, Ziaei AN (2017) Simulation and operation evaluation of Shahid Yaghoobi dam by using system dynamic (case study: dam Shahid Yaghoobi). J Watershed Manag Res 8(16):188–199
Shakoor A, Arshad M, Bakhsh A, Ahmed R (2015) Gisbased assessment and delineation of groundwater quality zones and its impact on agricultural productivity. Pakistan J Agri Sci 52(3):837–843
Shieh HY, Chen JS, Lin CN, Wang WK, Liu CW (2010) Development of an artificial neural network model for determination of longitudinal and transverse dispersivities in a convergent flow tracer test. J Hydrol 391(3-4):367–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-014-0089-y
Siadat Moghadam MJ (2004) Groundwater quality model of Mashad aquifer, M.Sc. Thesis, Civil Eng Dept, Khaje Nasir University
Sohrabi N, Chitsazan M, Amiri V, Moradi Nezhad T (2013) Evaluation of groundwater resources in alluvial aquifer based on MODFLOW program, case study: Evan plain (Iran). Agri Crop Sci 5(11):1164–1170
Sohrabi N, Kalantari N, Amiri V, Nakhaei M (2017) Assessing the chemical behavior and spatial distribution of yttrium and rare earth elements (YREEs) in a coastal aquifer adjacent to the Urmia hypersaline Lake, NW Iran. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24(25):20502–20520. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9644-7
Sun N Z (1994) Inverse problem in ground water modelling. Kluwer, Amsterdam, p 338
Tabios GQ, Salas JD (1985) A comparative analysis of techniques for spatial interpolation of precipitation. Water Resour Bull 21(3):365–380. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-21928-3-4
Trainor BC, Lin S, Finy MS, Rowland MR, Nelson RJ (2007) Photoperiod reverses the effects of estrogens on male aggression via genomic and non-genomic pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 104:9840–9845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2007.09.016
Tsou MS, Perkins SP, Zhan X, Whittemore DO, Zheng L (2006) Inverse approaches with lithologic information for a regional groundwater system in Southwest Kansas. J Hydrol 318(1–4):292–300. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2041648
Velayati S, Tavassloi S (1991) Resources and problems of water in Razavi Khorasan Province (in Persian). Mashhad, Iran
Wang R, Balkanski Y, Boucher O, Ciais P, Schuster GL, Chevallier F, Tao S, (2016) Estimation of global black carbon direct radiative forcing and its uncertainty constrained by observations. Journal of Geophysical Research 121(10):5948-5971. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JD024326
Wen Y, Rwegasira K, Bilderbeek J (2002). Corporate governance and capital structure decisions of the Chinese listed firms. Corporate Governance: An International Review 10(2):75-83. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8683.00271
World Health Organization (WHO) (2011) Guidelines for drinking-water quality (hardness in drinking-water), vol 1, 4th edn. WHO, Geneva
Ye M, Karl FP, Jenny BC, Greg MP, Donald MR (2010) A model - averaging method for assessing groundwater conceptual model uncertainty. Ground Water 48(5):716–728. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2009.00633.x
Zheng C (1990) MT3D-A modular three-dimensional transport model for simulation of advection, dispersion and chemical reactions of contaminants in groundwater systems. Report to the U.S. Environmental protection agency, ADA, OK
Zhou Y, Li W (2011) A review of regional groundwater flow modeling. Geosci Front 2:205–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2011.03.003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Broder J. Merkel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabbaghi, M., Shahnazari, A., Ziaei, A.N. et al. Regional groundwater qualitative and quantitative management through hydrogeological modeling in Jangal-Geysour, Razavi Khorasan Province, Iran. Arab J Geosci 14, 1902 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07643-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07643-w