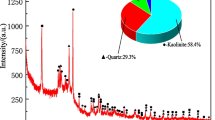
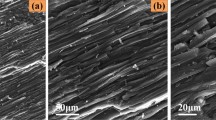
Abstract
Ascertaining the change of fracture conductivity caused by coal fines with different particle sizes displaced by single-phase water can provide a theoretical basis for studying the migration characteristics of coal fines in coal fractures. A single-phase water displacement device was used to measure the effects of changes in parameters such as the displacement time, the mass concentration of coal fines in the output fluid and the cumulative water yield when the coal fines were driven by single-phase water with six different particle sizes. The changes of permeability and fracture conductivity of resin–coal core samples caused by mixtures of water and coal fines with different particle sizes were calculated and analyzed. The results demonstrated that, with the decrease of the particle size of coal fines, the required time for the fracture to be completely sealed in the resin–coal core sample and the mass concentration of coal fines in the output fluid are increasing; the grinding effect of coal fines with particle size < 80 mesh on the crack wall surface is obvious, and coal fines with particle size > 200 mesh can pass through the cracks, and the cumulative water yield is higher when these two kinds of coal fines are displaced. The fracture conductivity of resin–coal core sample caused by coal fines with different particle sizes displaced by single-phase water shows the same characteristics of “slowly rising–rapidly rising–reaching a peak and starting to decrease–reducing to zero”. In the displacement process of fines at < 80 mesh and > 200 mesh, the fracture conductivity increases rapidly in the early stage and decreases slowly in the later stage. In the displacement process of 80–100 mesh coal fines, the fracture conductivity increases slowly in the early stage and decreases rapidly in the later stage.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai TH, Chen ZW, Aminossadati SM et al (2017) Experimental investigation on the impact of coal fines generation and migration on coal permeability. J Pet Sci Eng 159:257–266
Cao DY, Yao Z, Li XM et al (2013) Rules of coal powder output under physical simulation experiments of single-phase water flow displacement. J China Coal Soc 38(04):624–628 [In Chinese]
Chen ZH, Wang YB, Sun P (2009) Destructive influences and effectively treatments of coal powder to high rank coalbed methane production. J China Coal Soc 34(2):229–232 [In Chinese]
Chen WW, Wang SW, Qin Y et al (2014) Migration and control of coal powder in CBM well. J China Coal Soc 39(S2):416–421 [In Chinese]
Gao DP, Liu YW, Wang TJ et al (2018) Experimental Investigation of the Impact of Coal Fines Migration on Coal Core Water Flooding. Sustainability 10(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/su10114102
Guo ZH, Hussain F, Cinar Y (2015) Permeability variation associated with fines production from anthracite coal during water injection. Int J Coal Geol:45–57
Guo ZH, Vu PNH, Hussain F (2018) A laboratory study of the effect of creep and fines migration on coal permeability during single-phase flow. Int J Coal Geol 200:61–76
Lan WJ, Wang HX, Yang SY et al (2017) Study on the migration of pulverized coal in CBM wellbore. J Pet Sci Eng 156:740–747
Li XM, Cao DY, Yao Z, et al. (2015) Study on mechanism of pulverized coal discharge based on flow-state physical simulation. Coal Sci Technol 43(02):76-79+83 [In Chinese].
Liu CH, Liu XF, Zhou C (2015) Migration patterns of coal powder in coal reservoirs during the well drainage. Coal Geol Explor 43(05):23–26 [In Chinese]
Massarotto P, Iyer RS, Elma M et al (2014) An experimental study on characterizing coal bed methane (CBM) fines production and migration of mineral matter in coal beds. Energy Fuel 28(2):766–773
Qi YG, Zhang FN, Liu B et al (2013) Calculation on discharge flow of pulverized coal in gas production channel for coalbed methane well. J China Coal Soc 38(09):1627–1633 [In Chinese]
Shi QM, Qin Y, Zhou BY et al (2018) An experimental study of the agglomeration of coal fines in suspensions: inspiration for controlling fines in coal reservoirs. Fuel 211:110–120
Tao S, Tang DZ, Hao X et al (2017) The influence of flow velocity on coal fines output and coal permeability in the Fukang Block, southern Junggar Basin, China. Sci Report 7(2):551–556
Wei YC, Cao DY, Yuan Y et al (2013a) Characteristics of pulverized coal during coalbed methane drainage in Hancheng block, Shaanxi Province, China. Energy Explor Exploit 31(5):745–757
Wei YC, Cao DY, Yuan Y, et al. (2013b) Characteristics and controlling factors of pulverized coal during coalbed methane drainage in Hancheng area. J China Coal Soc 38(8):1424-1429 [In Chinese].
Wei YC, Zhang AX, Cao DY et al (2016) Characteristics of pulverized coal during coalbed methane drainage in Linfen block. Coal Geol Explor 44(3):30–35 [In Chinese]
Yao Z, Cao DY, Wei YC et al (2016) Experimental analysis on the effect of tectonically deformed coal types on fines generation characteristics. J Pet Sci Eng 146:350–359
You R, Peddieson J, Gadiyaram J et al (2010) Simulation of particle/fluid flows in vertical circular pipes. Int J Non-Lin Mech 45(5):490–506
Zhao Z, Ni XM, Liu ZD, et al. (2020) Experimental study on the attenuation characteristics of coal fissure induced by gas-water two-phase drive. J China Coal Soc: 1-12 [2020-04-19] [In Chinese]. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2019.1299.
Funding
This study was supported by National Major Science and Technology Projects of China (2017ZX05064-003-001), National Natural Science Foundation of China (41872174), and Program for Innovative Research Team in University of Ministry of Education of China (IRT_16R22).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Santanu Banerjee
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, X., Li, Q., Zhao, Z. et al. The change of fracture conductivity caused by coal fines with different particle sizes displaced by single-phase water. Arab J Geosci 13, 1268 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-06270-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-06270-1