Abstract
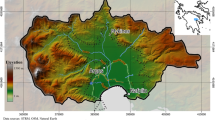
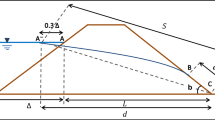
The main objective of the construction of the Kord-Oliya earth dam is to reserve surplus water for consumption and artificial recharge in the area. The effect of such dams on the basin is to alter the hydrological regime of its adjacent areas to somehow prevent drought. By considering the existence of such dams and the costs of their construction, operation, and maintenance, it is necessary to study their effect on surrounding groundwater. The objective of this study is to combine a geotechnical model for the subject earth dam through SEEP 3D software and its output in hydrogeological model through GMS software in a 3D mode for surface and groundwater management in a simultaneous manner. It is necessary to estimate the groundwater level of the area, to determine the hydrogeological and geotechnical conditions of the aquifer through mathematical models for optimal exploitation of the Karvan Plain. Excessive water harvesting for agriculture consumption from the Karvan aquifer has been and is on an increase which has led to a decrease in groundwater level in the area and introduced many environmental risks. This modeling is calibrated and validated for 121 months on this aquifer in both the steady and unsteady states in two scenarios with and without this earth dam. The obtained results indicate that existence of this dam does not increase the groundwater level in a gradual manner in the area in the consecutive years, while the mean groundwater level is on an increase by 14 m. By considering scenario one, the total volume of alluvial aquifer reserves increase 83.4 Mm3.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldassarre G (2018) An international team of drought scientists, Unintended consequences of dams and reservoirs, Uppsala University
Bayat M, Eslamian S, Shams GH, Hajiannia A (2019) The 3D analysis and estimation of transient seepage in earth dams through PLAXIS 3D Software - neural network : case Study: Kord–Oliya Dam, Isfahan province, Iran, Environmental earth science
Bayat M, Eslamian S, Shams GH, Hajiannia A (2020) Groundwater level prediction through GMS software: Case study: Karvan area. Questions Geographicae 39(3):139–145
Çelik R (2018) Impact of Dams on Groundwater Static Water Level Changes: a Case Study Kralkızı and Dicle Dam Watershed, International Journal of Engineering Research and Development
Djuma H, Bruggeman A, Camera C, Eliades M, Kostarelos K (2017) The impact of a Check dam on groundwater, recharge and sedimentation in an ephemeral stream. Water 9:813
Heidarian Z, Hafezi Moghadas N, Nedaie S (2011) Effect of Alghadir dam on quantity groundwater resources of Saveh plain, the 7th Iranian conference of engineering geology and environment
Kim W, Lee J, Kim Kim S (2019) Assessment of water supply stability for drought-vulnerable Boryeong multipurpose dam in South Korea using future dry climate change scenarios, Water
Mohammadi S, Bozari SH (2017) Impact assessment of dam construction on quantity and quality of groundwater, 4th International conference on environmental planning and management
Ranjbar M, Amini N (2014) Evaluating of dams on groundwater resources, 2014, International of geographical society of Iran, No 40
Sokolov A, Aleksandrovich A, Chapman D, Grandin T (1974) Methods for water balance computations: an international guide for research and practice, Studies and reports in hydrology
Zaman Asik T (2018) 'RMSE' or 'NRMSE' Which is better to assess numerical model performance evaluation and why?, Bangladesh Army International University of Science and Technology
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Amjad Kallel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bayat, M., Eslamian, S., Shams, G. et al. Assessing the earth dams’ effect on the groundwater of its location case study: Kord-Oliya dam. Arab J Geosci 13, 1199 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-06195-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-06195-9