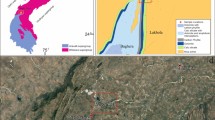
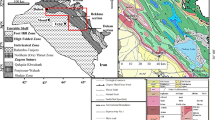
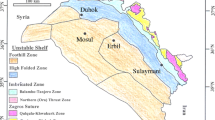
Abstract
Major, trace, rare earth elements (REE), and stable isotopic compositions in carbonate rocks of Pila Spi Formation were measured to constrain the source of rare earth elements and depositional environment. The low ΣREE content (average = 6.53 ppm, n = 14) indicates that the carbonates seawater-like REE patterns with (1) LREE depletion (average (Nd/Yb)n = 0.81), (2) HREE enrichment, (3) negative Ce anomaly (average = 0.91), and (4) superchondritic Y/Ho ratio (average = 30.07); slightly lower average value of Y/Ho ratio than the typical seawater value (~ 44–74) suggests modification of the seawater by input of fresh water. The (Nd/Yb)n and (Dy/Yb)n ratios of the Pila Spi carbonates have similarity with that of the Arabian sea carbonate. The low concentrations of U (0.35–1.0 ppm) suggest the deposition under oxygen-rich environment. This study indicates that the carbonates still preserve their original seawater-like REE pattern, provided that the contamination with terrigenous materials was small, and they serve as a seawater proxy. The Pila Spi carbonates have δ13C values ranged from − 6.17 to 0.76‰ PDB, and the δ18O values range between − 3.85 and 0.46‰ PDB. The positive correlation between δ13C and δ18O (r = 0.949, n = 14) values indicates the alteration of original isotopic compositions due to diagenesis. Finally, it is conceived that the Pila Spi carbonate was deposited in the lagoon environment with seawater invading and mixing of the continental (terrigenous) materials to the basin is viable.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander BW, Bau M, Andersson P, Dulski P (2008) Continentally-derived solutes in shallow Archean seawater: rare earth element and Nd isotope evidence in iron formation from the 2.9 Ga Pongola Supergroup, South Africa. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 72:378–394
Al-Mashaikie SZ, Latif RM (2017) Sedimentology and lithostratigraphy of the Pila Spi Formation in Koi Sanjaq area, NE Iraq: new insight for depositional environment and basin configuration. Iraqi J Sci 58:669–686
Al-Qayim B, Al-Shaibani S (1997) Lithostratigraphy of Cretaceous–Tertiary transect Bekhme Gorge, NE Iraq. Iraqi Geol J 28(2):127–136
Al-Qayim B, Al-Shaibani S, Nisan B (1988) Stratigraphic evolution of Paleogene sequence Haibat Sultan, Northeastern Iraq. J Geol Soc Iraq 21(2):51–61
Al-Qayim B, Al-Shaibani S, Nissan B (1994) A bimodal tidal depositional system of the Gercus Formation, Shaqlawa area, Northern Iraq. Iraqi Geol J 27(2):75–95
Al-Sakry SI (1999) Stratigraphy and facies of Paleogene carbonate formations of selected sections, Northeastern Iraq. M Sc Thesis, University of Baghdad
Armstrong-Altrin JS, Verma SP, Madhavaraju J, Lee YI, Ramasamy S (2003) Geochemistry of Late Miocene Kudankulam Limestones, South India. Int Geol Rev 45:16–26
Armstrong-Altrin JS, Madhavaraju J, Sial AN, Kasper-Zubillaga JJ, Nagarajan R, Flores-Castro K, Rodríguez JL (2011) Petrography and stable isotope geochemistry of the Cretaceous El Abra Limestones (Actopan), Mexico: implication on diagenesis. J Geol Soc India 77:349–359
Armstrong-Altrin JS, Machain-Castillo ML, Rosales-Hoz L, Carranza-Edwards A, Sanchez-Cabeza JA, Ruíz-Fernández AC (2015) Provenance and depositional history of continental slope sediments in the Southwestern Gulf of Mexico unraveled by geochemical analysis. Cont Shelf Res 95:15–26
Banner JL, Hanson GN, Meyers WJ (1988) Water-rock interaction history of regionally extensive dolomites of the Burlington- Keokuk Formation (Mississippian): isotopic evidence. In: Shukla V, Baker P (eds) Sedimentology and geochemistry of dolostones. SEPM Special Publication 43. SEPM, Tulsa, pp 97–114
Bau M (1991) Rare-earth element mobility during hydrothermal and metamorphic fluid-rock interaction and the significance of the oxidation state of europium. Chem Geol 93:219–230
Bau M, Dulski P (1996a) Anthropogenic origin of positive gadolinium anomalies in river waters. Earth Planet Sci Lett 143:245–255
Bau M, Dulski P (1996b) Distribution of Y and rare-earth elements in the Penge and Kuruman Iron Formations, Traansvaal Supergroup, South Africa. Precambrian Res 79:37–55
Bellen RC, Dunnington HV, Wetzel R, Morton D (1959) Lexique Stratigraphic International. Asie, Fasc. 10a, Iraq, Paris
Choquette PW, Pray LC (1970) Geologic nomenclature and classification of porosity in sedimentary carbonates. Bull Am Assoc Pet Geol 54:207–250
Condie KC (1991) Another look at rare earth elements in shales. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 55:2527–2531
Cuna S, Pop D, Hosu A (2001) Carbon and oxygen isotope ratios in Rona limestone, Romania. Studia Universitatis Babeş-Bolyai, Geologia, XLVI, 1
De Baar HJW, German CR, Elderfield H, Van Gaans P (1988) Rare earth element distributions in anoxic waters of the Cariaco Trench. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 52:1203–1219
Deepulal PM, Kumar TR, Sujatha CH (2012) Behavior of REEs in a tropical estuary and adjacent continental shelf of southwest coast of India: evidence from anomalies. J Earth Syst Sci 121:1215–1227
Dickson JAD (1965) A modified staining technique for carbonates in thin section. Nature 205:587
Ditmar V Iraqi-Soviet Team (1971) Geological conditions and hydrocarbon prospects of the Republic of Iraq (Northern and Central parts). Manuscript report, INOC Library, Baghdad
Elderfield H (1988) The oceanic chemistry of the rare-earth elements. Phil Trans R Soc London 325:105–126
Elderfield H, Pagett R (1986) Rare earth elements in icthyoliths: variations with redox conditions and depositional environments. Sci Total Environ 49:175–197
Elderfield H, Upstill-Goddard R, Sholkovitz ER (1990) The rare-earth elements in rivers, estuaries, and coastal seas and their significance to the composition of ocean waters. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 54:971–991
Fu XG, Wang J, Zeng YH, Tan F, He J (2011) Geochemistry and origin of rare earth elements (REEs) in the Shengli River oil shale, northern Tibet, China. Chem Erde 71:21–30
German CR, Elderfield H (1989) Rare earth elements in Saanich Inlet, British Columbia, a seasonally anoxic basin. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 53:2561–2571
German CR, Elderfield H (1990) Application of the Ce anomaly as a paleoredox indicator: the ground rules. Paleoceanography 5:823–833
German CR, Holliday BP, Elderfield H (1991) Redox cycling of rare earth elements in the suboxic zone of the black Sea. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 55:3553–3588
German CR, Higgs NC, Thomson J, Mills R, Elderfield H, Blusztajn J, Fleer AP, Bacon MP (1993) A geochemical study of metalliferous sediment from the TAG hydrothermal mound, 26°08′ N, Mid-Atlantic Ridge. J Geophys Res 98:9683–9692
Gill IP, Moore CH, Aharon P (1995) Evaporitic mixed-water dolomitization on St. Croix, U.S.V.I. J Sed Res 65:591–604
Greaves MJ, Elderfield H, Sholkovitz ER (1999) Aeolian sources of rare earth elements to the Western Pacific Ocean. Mar Chem 68:31–38
Gregg JM, Sibley DF (1984) Epigenetic dolomitization, and the origin of xenotropic dolomite texture. J Sediment Petrol 54(3):908–931
Hernandez-Hinojosa V, Montiel-Garcia PC, Armstrong-Altrin JS, Nagarajan R, Kasper-Zubillaga JJ (2018) Textural and geochemical characteristics of beach sands along the western Gulf of Mexico, Mexico. Carpathian J Earth Environ Sci 13(1):161–174
Hua G, Yuansheng D, Lian Z et al (2013) Trace and rare earth elemental geochemistry of carbonate succession in the Middle Gaoyuzhuang Formation, Pingquan Section: implications for Early Mesoproterozoic ocean redox conditions. J Palaeogeogr 2:209–221
Jassim SZ, Goff JC (2006) Geology of Iraq. Publishers Dolin and Moravian Museum, Prague
Jones B, Manning DAC (1994) Composition of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of paleoredox conditions in ancient mudstones. Chem Geol 111:111–129
Kadhim LS, Hussein SA (2016) Petrography and geochemistry of Pila Spi Formation (Middle- Late Eocene) in Selected Sections / Northern Iraq. Iraqi J Sci 57:2291–2306
Kato Y, Nakao K, Isozaki Y (2002) Geochemistry of Late Permian Triassic pelagic cherts from southwest Japan: implications for an oceanic redox change. Chem Geol 182:15–34
Khanaqa PA (2011) Interpretation of new facies in the Pila Spi Formation (Middle – Late Eocene) in Sulaimanyia NE Iraq. Iraqi Bull Geol Min 7(3):33–45
Lawrence MG, Greig A, Collerson KD, Kamber BS (2006) Rare earth element and yttrium variability in south east Queensland waterways. Aquat Geochem 12:39–72
Liu YG, Miah MRU, Schmitt RA (1988) Cerium: a chemical tracer for paleo-oceanic redox condition. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 52:1361–1371
Lonoy A (2006) Making sense of carbonate system. AAPG 90(9):1381–1405
Lucia FJ (2007) Carbonate Reservoir Characterization: an integrated approach, 2nd edition. Springer Verlag, New York
Madhavaraju J, González-León CM (2012) Depositional conditions and source of rare earth elements in carbonate strata of the Aptian-Albian Mural Formation, Pitaycachi section, northeastern Sonora, Mexico. Revista Mexicana de Ciencias Geológicas 29(2):478–491
Madhavaraju J, Ramasamy S (1999) Rare earth elements in limestones of Kallankurichchi Formation of Ariyalur Group, Tiruchirapalli Cretaceous, Tamil Nadu. J Geol Soc India 54:291–301
Madhavaraju J, González-León CM, Lee YI, Armstrong-Altrin JS, Reyes-Campero LM (2010) Geochemistry of the Mural Formation (Aptian-Albian) of the Bisbee Group, Northern Sonora, Mexico. Cretac Res 31:400–414
Major RP, Vander Stoep GW, Holtz MH (1990) Delineation of unrecovered mobile oil in a mature dolomite reservoir: East Penwell San Andres Unit, University Lands, West Texas. The University of Texas at Austin, Bureau of Economic Geology, Report of Investigations No. 194, 52 pp
Masuzawa T, Koyama M (1989) Settling particles with positive Ce anomalies from the Japan Sea. Geophys Res Lett 16:503–506
Matilainen R, Tummavuori J (1999) Determination of SiO2 in lime mud by gravimetry. Fresenius J Anal Chem 364:700–704
Mitra R, Chakrabarti G, Shome D (2018) Geochemistry of the Palaeo-Mesoproterozoic Tadpatri shales, Cuddapah Basin, India: implications on provenance, paleoweathering and paleoredox conditions. Acta Geochem 37:715–733
Morad S, Al-Aasm IS, Sirat M, Sattar MM (2010) Vein calcite in Cretaceous carbonate reservoirs of Abu Dhabi: record of origin of fluids and diagenetic conditions. J Geochem Explor 106:156–170
Murray RW, Buchholtz MR, Brumsack HJ (1991) Rare earth elements in Japan Sea sediments and diagenetic behavior of Ce/Ce*, results from ODP leg 127. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 55:2453–2466
Murray RW, Buchholtz MR, Gerlach DC et al (1992) Interoceanic variation in the rare earth, major and trace element depositional chemistry of chert: perspectives gained from the DSDP and ODP record. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 56:1897–1913
Nagarajan R, Madhavaraju J, Armstron-Altrin JS, Nagendra R (2011) Geochemistry of Neoproterozoic limestones of the Shahabad Formation, Bhima Basin, Karnataka, southern India. Geosci J 15:9–25
Nath BN, Bau M, Ramalingeswara RB, Rao CM (1997) Trace and rare earth elemental variation in Arabian Sea sediments through a transect across the oxygen minimum zone. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 61:2375–2388
Nothdurft LD, Webb GE, Kamber BS (2004) Rare earth element geochemistry of Late Devonian reefal carbonates, canning basin, Western Australia: confirmation of a seawater REE proxy in ancient limestones. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68(2):263–283
Othman DH, Al-Qayim BA (2010) Lithofacies association, dolomitization, and potentiality of the Pila Spi formation, Taq Taq oil field, NE Iraq. Iraqi Bull Geol Min 6(2):95–114
Patra A, Singh PB (2017) Geochemistry of the Eocene limestones of the Jaisalmer Basin, Rajasthan, India: implications on depositional conditions and sources of rare earth elements. Geochem Int 55:1180–1192
Pattan JN, Masuzawa T, Borole DV, Parthiban G, Jauhari P, Yamamoto M (2005) Biological productivity, terrigenous influence and noncrustal elements supply to the central Indian Ocean Basin: paleoceanography during the past 1 Ma. J Earth Syst Sci 114:63–74
Piepgras DJ, Jacobsen SB (1992) The behaviour of rare earth elements in seawater: precise determination of ferromanganese crusts. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 56:851–1862
Piper DZ (1974) Rare earth elements in the sedimentary cycle, a summary. Chem Geol 14:285–304
Ramos-Vázquez MA, Armstrong-Altrin JS (2019) Sediment chemistry and detrital zircon record in the Bosque and Paseo del Mar coastal areas from the southwestern Gulf of Mexico. Mar Pet Geol 110:250–275
Randazzo AF, Zachos LG (1984) Classification and description of dolomitic fabrics of rocks from the Floridan aquifer, USA. Sed Geol 37:151–162
Reeder RJ (1983) Crystal chemistry of the rhombohedral carbonates. Min Soc Am Rev 11:1–48
Roy A, Chakrabarti G, Shome D (2018) Geochemistry of the Neoproterozoic Narji limestone, Cuddapah Basin, Andhra Pradesh, India: implication on palaeoenvironment. Arab J Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-4135-9
Schieber J (1988) Redistributionof rare earth elements during diagenesis of carbonate rocks from Mid-Proterozoic Newland Formation, Montana, USA. Chem Geol 69:111–126
Shields GA, Webb GE (2004) Has the REE composition of seawater changed over geologic time. Chem Geol 204:103–107
Sholkovitz ER (1990) Rare earth elements in marine sediments and geochemical standards. Chem Geol 88:333–347
Sholkovitz ER, Landing WM, Lewis BL (1994) Ocean particle chemistry: the fractionation of the rare earth elements between suspended particles and seawater. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 58:1567–1580
Sibley DF, Gregg JM (1987) Classification of dolomite rock textures. J Sediment Petrol 57:967–975
Siby K, Nath BN, Ramaswamy V et al (2008) Possible detrital, diagenetic and hydrothermal sources for Holocene sediments of the Andaman back arc basin. Mar Geol 247:178–193
Singh BP, Pawar JS, Patra A (2013) Geochemistry of Late Eocene/Oligocene calcretes (caliche) of the northwestern Himalaya, India. J Him Earth Sci 34(2):135–140
Sissakian VK (1997) Geological map of Arbeel and Mahabad Quadrangles, Sheets NJ-38-14 and NJ-38-15, scale 1: 250000, GEOSURV, Baghdad, Iraq
Sissakian VK (2000) Geological map of Iraq, sheet no.1, scale 1: 1000 000, 3rd ed. GEOSURV, Baghdad, Iraq
Srivastava VK, Singh BP (2017) Shoreface to estuarine sedimentation in the late Paleocene Matanomadh Formation, Kachchh, Western India. J. Asian Earth Sci 136:1–15
Srivastava VK, Singh BP (2018) Depositional environments and sources for the middle Eocene Fulra Limestone Formation, Kachchh Basin, western India: evidences from facies analysis, mineralogy, and geochemistry. Geol J 54:62–82. https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.3154
Srivastava VK, Singh BP (2019) Depositional environments and sources for the middle Eocene Fulra limestone Formation, Kachchh Basin, western India: evidences from facies analysis, mineralogy, and geochemistry. Geol J 54:62–82
Talbot MR (1990) A review of the palaeohydrological interpretation of carbon and oxygen isotopic ratios in primary lacustrine carbonates. Chem Geol Isot Geosci 80:26l–279l
Tandon SK, Andrews JE (2001) Lithofacies association and stable isotopes of palustrine and calcrete carbonates: examples from an Indian Maastrichtian regolith. Sedimentology 48:339–355
Tanner LH (2009) Continental carbonates as indicators of paleoclimate. In: Alonso-Zarza AM, Tanner L (eds) Carbonates in continental settings, developments in sedimentology 62, pp 179–214
Taylor SR, McLennan SM (1985) The continental crust: its composition and evolution. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford
Tobia FH (2018) Stable isotope and rare earth element geochemistry of the Baluti carbonates (Upper Triassic), Northern Iraq. Geosci J 22:975–987
Tobia FH, Shangola SS (2016) Mineralogy, geochemistry, and depositional environment of the Beduh shale (lower Triassic), Northern Thrust Zone, Iraq. Turk J Earth Sci 25:367–391
Toyoda K, Nakamura Y, Masuda A (1990) Rare earth elements of Pacific pelagic sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 54:1093–1103
Wang BS, Lee CP, Ho TY (2014) Trace metal determination in natural waters by automated solid phase extraction system and ICP-MS: the influence of low level Mg and Ca. Talanta 128:337–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.04.077
Webb GE, Kamber BS (2000) Rare earth elements in Holocene reefal microbialites: a shallow seawater proxy. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 64:1557–1565
Wright J, Seymour RS, Shaw HF (1984) REE and neodymium isotopes in conodont apatite variation with geological age and depositional environment. Geol Soc Am Spec Publ 196:325–340
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Mohamad Fakhre, Salahaddin University, Department of Geology, for his help in the petrographic section. We are thankful to an anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions and kind help in improving the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Domenico M. Doronzo
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tobia, F.H., Al-Jaleel, H.S. & Rasul, A.K. Elemental and isotopic geochemistry of carbonate rocks from the Pila Spi Formation (Middle–Late Eocene), Kurdistan Region, Northern Iraq: implication for depositional environment. Arab J Geosci 13, 925 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05884-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05884-9