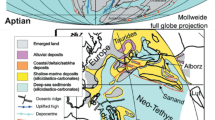
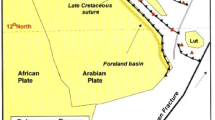
Abstract
Petrographic and geochemical studies were carried out on the Paleocene–Eocene carbonates of the Kolosh Formation in the High Folded Zone to infer the environment of deposition, diagenetic overprints, and their origin. The petrographic study revealed five main microfacies; packstone, wackestone, mudstone, grainstone, and crystalline carbonate. There are different depositional environments from shoal to shallow marine environments (mid-ramp conditions) that are adequate for mixing continental material with seawater. Several evidences of diagenetic processes were observed, such as micritization, neomorphism, and dolomitization. Petrographic and geochemical analyses show the dominance of calcite and dolomite minerals. The contents of major oxides and the concentrations of trace elements were normalized to Post-Archean Australian Shale (PAAS) values. The Paleocene–Eocene carbonates are enriched in CaO, MgO, Cr, and Ni, whereas are highly depleted in Na2O, K2O, TiO2, Al2O3, Rb, Ba, Th, and Zr. The low contents of Al2O3 and SiO2 refer to a low siliciclastic involvement during the deposition of the Paleocene–Eocene carbonate. The REEs average content is lower (15.60 ppm) than that of marine carbonates (28 ppm). The REE patterns (normalized to PAAS) display a seawater-like type, while a slightly lower average Y/Ho value (33.66) relative to that of typical seawater (~ 44 to 74) refers to the alteration of the seawater by the freshwater. The REEs of this study are comparable with the limestone of the Middle Eocene Fulra Formation and Arabian Sea carbonates. Paleocene–Eocene carbonates have δ13CPDB ranging between − 13.31 and 1.25‰PDB, and δ18O from − 6.30 to 0.12‰PDB. The negative values and no correlation between δ13C and δ18O indicate that modification of the primordial composition of the isotopes is not a result of diagenesis only, but other factors, such as temperature, and organic matter have an important role. The negative Ce/Ce*, Th/U ratios, and authigenic U suggest their accompanying the deposition of the carbonates in oxidizing conditions. The paleotemperature of the studied carbonates (~ 12 to 42 °C) is slightly higher than other global records in the Paleocene–Eocene, which may propose the variations in the composition of oxygen isotope and modification in the geochemical characteristics during the post-carbonate deposition time.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedini A, Calagari AA (2015) Rare earth element geochemistry of the Upper Permian limestone: the Kanigorgeh mining district, NW Iran. Turk J Earth Sci 24:365–382
Adelabu IO, Opeloye SA, Oluwajana OA (2021) Petrography and geochemistry of Paleocene–Eocene (Ewekoro) limestone, eastern Benin basin, Nigeria: implications on depositional environment and post-depositional overprint. Heliyon. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08579
Ader M, Macouin M, Trindade RIF, Hadrien MH, Yang Z, Sun Z, Besse J (2009) A multilayered water column in the Ediacaran Yangtze platform insights from carbonate and organic matter paired δ13C. Earth Planet Sci Lett 288:213–227
Ali MY (1995) Carbonate cement stratigraphy and timing of diagenesis in a Miocene mixed carbonate-clastic sequence, offshore Sabah, Malaysia: constraints from cathodoluminescence, geochemistry, and isotope studies. Sed Geol 99:191–214
Allan JR, Matthews RK (1977) Carbon and oxygen isotopes as diagenetic and stratigraphic tools: data from surface and subsurface of Barbados, West Indies. Geology 5:16–20
Allan JR, Matthews RK (1982) Isotope signatures associated with early meteoric diagenesis. Sedimentology 29:797–817
Allwood AC, Kamber BS, Walter MR, Burch IW, Kanik I (2010) Trace elements record depositional history of an Early Archean stromatolitic carbonate platform. Chem Geol 270:148–163
Al-Qayim B, Al-Shaibani S (1989) Stratigraphic analysis of Cretaceous–Tertiary contact, Northwest Iraq. J Geol Soc Iraq 22:41–52
Al-Qayim B, Al-Shaibani SH, Nisan B (1988) Stratigraphic evolution of Paleogene sequence Haibat Sultan, Northeastern Iraq. J Geol Soc Iraq 21:51–61
Al-Qayim BA, Al-Mutwali MM, Nissan BY (2008) Flysch–molasse sediments of the Paleogene foreland basin of North Iraq. Iraqi Bull Geol Min 4:1–20
Anderson R, Bacon MP, B y PG, (1983) Removal of 230Th and 234Pb at ocean margins. Earth Planet Sci Lett 66:73–90
Arabas A (2016) Middle–upper Jurassic stable isotope records and seawater temperature variations: new palaeoclimate data from marine carbonate and belemnite rostra (Pieniny Klippen Belt, Carpathians). Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 446:284–294
Armenteros I, Edwards N (2012) Palaeogeographic, palaeoclimatic, palaeohydrological and chemical/biochemical controls on the accumulation of late Eocene coastal lacustrine–palustrine limestones, Southern England. Sed Geol 281:101–118
Armstrong-Altrin JS, Verma SP, Madhavaraju J, Lee YI, Ramasamy S (2003) Geochemistry of Late Miocene Kudankulam Limestones, South India. Int Geol Rev 45:16–26
Armstrong-Altrin JS, Lee YI, Verma SP, Worden RH (2009) Carbon, oxygen, and strontium isotope geochemistry of carbonate rocks of the Upper Miocene Kudankulam Formation, Southern India: implications for paleoenvironment and diagenesis. Chem Erde 69:45–60
Armstrong-Altrin JS, Madhavaraju J, Sial AN, Kasper-zubillaga JJ, Nagarajan R, Flores-Castro K, Rodríguez JL (2011) Petrography and stable isotope geochemistry of the Cretaceous El Abra Limestones (Actopan), Mexico: implication on diagenesis. J Geol Soc India 77:349–359
Banner JL, Hanson GN, Meyers WJ (1988) Water–rock interaction history of regionally extensive dolomites of the Burlington–Keokuk Formation (Mississippian): isotopic evidence. Sedimentol Geochem Dolostones 43:97–113
Bathurst RG (1975) Carbonate sediments and their diagenesis, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1–657
Bau M (1991) Rare-earth element mobility during hydrothermal and metamorphic fluid–rock interaction and the significance of the oxidation state of europium. Chem Geol 93:219–230
Bau M (1996) Controls on the fractionation of isovalent trace elements in magmatic and aqueous systems: evidence from Y/Ho, Zr/Hf, and lanthanide tetrad effect. Contrib Miner Petrol 123:323–333
Bau M, Dulski P (1996) Anthropogenic origin of positive gadolinium anomalies in river waters. Earth Planet Sci Lett 143:245–255
Bellanca A, Masetti D, Neri R (1997) Rare earth elements in limestone/marlstone couplets from the Albian–Cenomanian Cismon section (Venetian region, northern Italy): assessing REE sensitivity to environmental changes. Chem Geol 141:141–152
Bellen RV, Dunnington HV, Wetzel R, Morton D (1959) Lexique stratigraphique international. Asie, Iraq 3(10a):1–324
Bertram CJ, Elderfield H (1993) The geochemical balance of the rare earth elements and neodymium isotopes in the oceans. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 57:1957–1986
Broecker WS (1982) Glacial to interglacial changes in ocean chemistry. Prog Oceanogr 11:151–197
Brookins DG (1989) Aqueous geochemistry of rare earth elements. In: Lipin BR, McKay GAŽ (eds) Geochemistry and mineralogy of rare earth elements. Rev Miner Geoch, vol 21, pp 201–225
Buday T (1980) The regional geology of Iraq, stratigraphy, and paleontology. Dar Al-Kutb Publishing House, University of Mosul, Iraq, pp 1–445
Buday T, Jassim SZ (1987) The regional geology of Iraq, vol. 2: tectonism, magmatism, and metamorphism. GEOSURV, Baghdad, pp 1–352
Budd DA, Land LS (1990) Geochemical imprint of meteoric diagenesis in Holocene ooid sands, Schooner Cays, Bahamas: correlation of calcite cement geochemistry with extent ground waters. J Sed Pet 60:361–378
Chen Z, Gao A, Liu Y, Sun H, Shi X, Yang Z (2003) REE geochemistry of surface sediments in the Chukchi Sea. Sci China (series D) 46:603–611
Coniglio M, Myrow P, White T (2000) Stable carbon and oxygen isotope evidence of Cretaceous sea-level fluctuations recorded in septarian concretions from Pueblo, Colorado, USA. J Sed Res 70:700–714
Craig H (1965) The measurement of oxygen isotopes paleotemperatures. In: Tongiorgi E (ed) Proceedings of Spoleto conference on stable isotopes in oceanographic studies and paleotemperatures. Pisa 3, pp 3–24
Danielson A, Moller P, Dulski P (1992) The europium anomalies in banded iron formations and the thermal history of the oceanic-crust. Chem Geol 97:89–100
De Baar HJ, German CR, Elderfield H, Van Gaans P (1988) Rare earth element distributions in anoxic waters of the Cariaco Trench. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 52:1203–1219
De Baar HJW, Schuf J, Byrne RH (1991) Solution chemistry of the rare earth elements in seawater. Eur J Solid State Inorg Chem 28:357–373
Dean WE, Arthur MA (1998) Geochemical expressions of cyclicity in Cretaceous pelagic limestone sequences: Niobrara For[mation, Western Interior Seaway. Concepts in sedimentology and paleontology. In: Dean WE, Arthur MA (eds) Stratigraphy and Paleoenvironments of the Cretaceous Western Interior Seaway, US. Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists, pp 227–255
Derry LA, Jacobsen SB (1990) The chemical evolution of Precambrian seawater: evidence from REEs in banded iron formations. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 54:2965–2977
Deshpande RD, Bhattacharya SK, Jani RA, Gupta SK (2003) Distribution of oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in shallow groundwaters from southern India: influence of a dual monsoon system. J Hydrol 271:226–239
Ditmar V, Iraqi-Soviet Team (1972) Geological conditions and hydrocarbon prospects of the Republic of Iraq, Northern and Central Iraq. INOC Library, Baghdad
Dunham RH (1962) Classification of carbonate rocks according to depositional texture. In: Ham WE (ed) Classification of carbonate rocks. AAPG, Memoir 1, pp 108–121
Elderfield H (1988) The oceanic chemistry of the rare-earth elements. Philos Trans Roy Soc Lond Ser Math Phys Sci 325:105–126
Elderfield H, Pagett R (1986) Rare earth elements in icthyoliths: variations with redox conditions and depositional environments. Sci Total Environ 49:175–197
Flugel E (2004) Microfacies of carbonate rocks: analysis, interpretation, and application. Springer, Berlin
Frank TD, Arthur MA, Dean WE (1999) Diagenesis of lower Cretaceous pelagic carbonates, North Atlantic: paleoceanographic signals obscured. J Foram Res 29:340–351
Frimmel HE (2009) Trace element distribution in Neoproterozoic carbonates as a palaeoenvironmental indicator. Chem Geol 258:338–353
Gao G, Dworkin SI, Land LS, Elmore RD (1996) Geochemistry of late Ordovician Viola limestone, Oklahoma: implications for marine carbonate mineralogy and isotopic compositions. J Geol 104:359–367
German CR, Elderfield H (1989) Rare earth elements in Saanich Inlet, British Columbia, a seasonally anoxic basin. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 53(10):2561–2571
German CR, Elderfield H (1990) Application of the Ce anomaly as a paleoredox indicator: the ground rules. Paleoceanography 5:823–833
German CR, Higgs NC, Thomson J, Mills R, Elderfield H, Blusztajn J, Fleer AP, Bacon MP (1993) A geochemical study of metalliferous sediment from the TAG Hydrothermal Mound, 26° 08′ N, Mid-Atlantic Ridge. J Geophys Res 98:9683–9692
Greaves MJ, Elderfield H, Sholkovitz ER (1999) Aeolian sources of rare earth elements to the Western Pacific Ocean. Mar Chem 68:31–38
Higgins JA, Blättler CL, Lundstrom EA et al (2018) Mineralogy, early marine diagenesis, and the chemistry of shallow-water carbonate sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 220:512–534
Hollis CJ, Taylor KWR, Handley L, Pancost RD, Huber M, Creech JB, Hines BR, Crouch EM, Morgans HEG, Crampton JS, Samantha GS, Pearson PN, Zachos JC (2012) Early Paleogene temperature history of the Southwest Pacific Ocean: reconciling proxies and models. Earth Planet Sci Lett 349–350:53–66
Huber BT, Norris RD, Macleod KG (2002) Deep-sea paleotemperature record of extreme warmth during the Cretaceous. Geology 30:123–126
Hudson JD (1977) Stable isotopes and limestone lithification. J Geol Soc 133:637–660
Inglis GN, Bragg F, Burls NJ, Cramwinckel MJ, Evans D, Foster GL, Huber M, Lunt DJ, Siler N, Steinig S, Tierney JE, Wilkinson R, Anagnostou E, De Boer AM, Jones TD, Edgar KM, Hollis CJ, Hutchinson DK, Pancost RD (2020) Global mean surface temperature and climate sensitivity of the early Eocene Climatic Optimum (EECO), Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), and latest Paleocene. Clim past 16:1953–1968
Jacobsen SB, Kaufman AJ (1999) The Sr, C and O isotopic evolution of Neoproterozoic seawater. Chem Geol 161:37–57
Jassim SZ, Buday T (2006) Tectonic framework. In: Jassim SZ, Goff JC (eds) Geology of Iraq, Dolin. Prague and Morarian Museum, Brno, pp 45–56
Jassim SZ, Goff JC (2006) Geology of Iraq. Dolin, Prague, pp 1–341
Jassim SZ, Buday T, Cicha I, Prouza V (2006) Late Permian–Liassic Megasequence AP6. In: Jassim SZ, Goff JC (eds) Geology of Iraq, Dolin. Prague and Morarian Museum, Brno, pp 104–116
Jiang L, Worden RH, Cai CF (2014) Thermochemical sulfate reduction and fluid evolution of the Lower Triassic Feixianguan Formation sour gas reservoirs, northeast Sichuan Basin, China. Am Assoc Petrol Geol Bull 98:947–973
Johannesson KH, Tang J, Daniels JM, Bounds WJ, Burdige DJ (2006) Rare earth element concentrations and speciation in organic-rich blackwaters of the Great Dismal Swamp, Virginia, USA. Chem Geol 209:271–294
Kassab IIM (1976) Some Upper Cretaceous planktonic foraminiferal genera from northern Iraq. Micropaleon 22:215–238
Kato Y, Nakao K, Isozaki Y (2002) Geochemistry of Late Permian Triassic pelagic cherts from southwest Japan: implications for an oceanic redox change. Chem Geol 182:15–34
Kemp RA, TruemaN CN (2003) Rare earth elements in Sol nhofen biogenic apatite: geochemical clues to the palaeoenvironment. Sed Geol 155:109–127
Klinkhammer GP, Elderfield H, Edmond JM, Mitra A (1994) Geochemical implications of rare earth element patterns in hydrothermal fluids from mid-ocean ridges. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 58:5105–5113
Kumar B, Sharma SD, Sreenivas B, Dayal AM, Rao MN, Dubey N, Chawla BR (2002) Carbon, oxygen and strontium isotope geochemistry of Proterozoic carbonate rocks of the Vindhyan Basin, central India. Precamb Res 113:43–63
Latorre C, Quade J, Mcintosh WC (1997) The expansion of C4 grasses and global change in the late Miocene: stable isotope evidence from the Ameritas. Earth Planet Sci Lett 146:83–96
Lawrence MG, Greig A, Collerson KD, Kamber BS (2006) Rare earth element and yttrium variability in South East Queensland waterways. Aquat Geoch 12:39–72
Madhavaraju J, González-León CM (2012) Depositional conditions and source of rare earth elements in carbonate strata of the Aptian–Albian Mural Formation, Pitaycachi section, northeastern Sonora, Mexico. Rev Mex Cienc Geol 29:478–491
Madhavaraju J, Lee YI (2009) Geochemistry of the Dalmiapuram Formation of the Uttatur Group (Early Cretaceous), Cauvery basin, southeastern India: implications on provenance and paleo-redox conditions. Rev Mex Cienc Geol 26:380–394
Madhavaraju J, Ramasamy S (1999) Rare earth elements in limestones of Kallankurichchi Formation of Ariyalur Group, Tiruchirapalli Cretaceous, Tamil Nadu. J Geol Soc India 54:291–301
Madhavaraju J, Kolosov I, Buhlak D, Armstrong-Altrin JS, Ramasamy S, Mohan SP (2004) Carbon and oxygen isotopic signatures in Albian–Danian limestones of Cauvery Basin, Southeastern India. Gondwana Res 7:519–529
Madhavaraju J, González-León CM, Lee YI, Armstrong-Altrin JS, Reyes-Campero LM (2010) Geochemistry of the Mural Formation (Aptian–Albian) of the Bisbee Group, Northern Sonora, Mexico. Cret Res 31:400–414
Madhavaraju J, Lee YI, González-León CM (2013) Diagenetic significance of carbon, oxygen, and strontium isotopic compositions in the Aptian–Albian mural Formation in Cerro Pimas area, northern Sonora, Mexico. J Iberian Geol 39:73–88
Madhavaraju J, Löser H, Scott RW, Sandeep S, Sial AN, Ramasamy S (2017) Petrography, geochemistry and stable isotopes of carbonate rocks Lower Cretaceous Alisitos Formation, Los Torotes Section, Baja California. Rev Mex Cienc Geol 34:63–77
Madi A, Bourque PA, Mamet BI (1996) Depth-related ecological zonation of a Carboniferous carbonate ramp: upper VisCan of BCchar Basin, Western Algeria. Facies 35:59–80
Maliva RG, Dickson JAD (1997) Ulster White Limestone Formation (Upper Cretaceous) of Northern Ireland: effects of basalt loading on chalk diagenesis. Sedimentology 44:105–112
Marshall JD (1992) Climatic and oceanographic isotopic signals from the carbonate rock record and their preservation. Geol Mag 129:143–160
McLennan SM (1989) Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks: influence of provenance and sedimentary processes. (Lipin, B. R. and McKay, G. A., eds.), Geochemistry and mineralogy of rare earth elements. Rev Miner 21:169–200
Morad S, Eshete M (1990) Petrology, chemistry and diagenesis of calcite concretions in Silurian shales from central Sweden. Sed Geol 66:113–134
Murphy K, Raymond J (1984) Rare earth element fluxes and geochemical budget in the eastern equatorial Pacific. Nature 307:444–447
Murray RW, Buchholtz MR, Brumsack HJ (1991) Rare earth elements in Japan Sea sediments and diagenetic behavior of Ce/Ce*, results from ODP leg 127. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 55:2453–2466
Nagarajan R (2003) Geochemistry and depositional environment of Neoproterozoic sediments of Bhima basin, Karnataka, South India. Chennai India, Anna University, PhD Thesis, pp 1–292
Nagarajan R, Sial AN, Armstrong-Altrin JS, Madhavaraju J, Nagendra R (2008) Carbon and oxygen isotope geochemistry of Neoproterozoic limestones of the Shahabad Formation, Bhima basin, Karnataka, southern India. Rev Mex Cienc Geol 25:225–235
Nagarajan R, Madhavaraju J, Armstron-Altrin JS, Nagendra R (2011) Geochemistry of Neoproterozoic limestones of the Shahabad Formation, Bhima Basin, Karnataka, southern India. Geosci J 15:9–25
Nagarajan R, Armstrong-Altrin J, Sial A, Nagendra R, Ellam R (2013) Carbon, oxygen, and strontium isotope geochemistry of the Proterozoic carbonate rocks, Bhima basin, south India: implication for diagenesis. Carpathian J Earth Environ Sci 8:25–38
Nagendra R, Nagarajan R, Bakkiaraj D, Armstrong-Altrin JS (2011) Depositional and post-depositional setting of Maastrichtian limestone, Ariyalur Group, Cauvery Basin, South India: a geochemical appraisal. Carbon Evapor 26:127–147
Nath BN, Roelandts I, Sudhakar M, Plueger WL (1992) Rare Earth Element patterns of the Central Indian Basin sediments related to their lithology. Geophys Res Lett 19:1197–1200
Nath BN, Bau M, Ramalingeswara RB, Rao CM (1997) Trace and rare earth elemental variation in Arabian Sea sediments through a transect across the oxygen minimum zone. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 61:2375–2388
Nelson CS, Smith AM (1996) Stable oxygen and carbon isotope compositional fields for skeletal and diagenetic components in New Zealand Cenozoic nontropical carbonate sediments and limestones: a synthesis and review. NZ J Geol Geophys 39:93–107
Nesbitt HW (1979) Mobility and fractionation of rare earth elements during weathering of a granodiorite. Nature 279:206–210
Nothdurft LD, Webb GE, Kamber BS (2004) Rare earth element geochemistry of Late Devonian reefal carbonates, Canning Basin, Western Australia: confirmation of a seawater REE proxy in ancient limestones. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68:263–283
Nozaki Y, Horibe Y, Tsubota H (1981) The water column distribution of thorium isotopes in the western North Pacific. Earth Planet Sci Lett 54:203–216
Nozaki Y, Zhang J, Amakawa H (1997) The fractionation between Y and Ho in the marine environment. Earth Planet Sci Lett 148:329–340
Nozaki Y, Lerche D, Alibo DS, Snidvongs A (2000) The estuarine geochemistry of rare earth elements and indium in the Chao Phraya River, Thailand. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 64:3983–3994
Oertli HJ (1964) The Venice system for the classification of marine waters according to salinity. Pubblicazionl Della Stazione Zoologicadi Napoli 33(Supplement):1–611
Oliver E, Neri R, Bellanca A, Riding R (2010) Carbonate stromatolites from a Messinian hypersaline setting in the Caltanissetta Basin, Sicily: petrographic evidence of microbial activity and related stable isotope and rare earth element signatures. Sedimentology 57:142–161
Özkan AM (2019) Geochemical features of rare earth elements in the dolomites of the Bozdağ Formation (early Silurian–middle Devonian) from Söğütözü-Hladik (Konya/Turkey) area. Int J Eng Sci 8:30–46
Palmer MR (1985) Rare earth elements in foraminifera tests. Earth Planet Sci Lett 73:285–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-821X(85)90077-9
Pancost RD, Taylor KW, Inglis GN, Kennedy EM, Handley L, Hollis CJ, Crouch EM, Pross J, Huber M, Schouten S, Pearson PN (2013) Early Paleogene evolution of terrestrial climate in the SW Pacific, Southern New Zealand. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 14:5413–5429
Piepgras DJ, Jacobsen SB (1992) The behavior of rare earth elements in seawater: precise determination of variations in the North Pacific water column. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 56:1851–1862
Piper DZ (1974) Rare earth elements in the sedimentary cycle: a summary. Chem Geol 14:285–304
Poulson SR, John BE (2003) Stable isotope and trace element geochemistry of the basal Bouse Formation carbonate, southwestern United States: implications for the Pliocene uplift history of the Colorado plateau. Geol Soc Am Bull 115:434–444
Redivo HV, Mizusaki AM, Santana AV (2019) REE patterns and trustworthiness of stable carbon isotopes of Salitre Formation, Irecê Basin (Neoproterozoic), São Francisco Craton. J South Am Earth Sci 90:255–264
Roy A, Chakrabarti G, Shome D (2018) Geochemistry of the Neoproterozoic Narji limestone, Cuddapah Basin, Andhra Pradesh, India: implication on palaeoenvironment. Arab J Geosci 11:1–13
Santos RV, De Alvarenga CJS, Babinski M, Ramos MLS, Cukrov N, Fonseca MA, Da Nóbrega SA, Dardenne MA, Noce CM (2004) Carbon isotopes of Mesoproterozoic–Neoproterozoic sequences from Southern São Francisco craton and Araçuaí Belt, Brazil: Paleographic implications. J South Am Earth Sci 18:27–39
Scott RW (2002) Albian caprinid rudists from Texas re-evaluated. J Paleont 76:408–423
Shackleton NJ, Kennett JP (1975) Paleotemperature history of the Cenozoic and the initiation of Antarctic glaciation: oxygen and carbon isotope analyses in DSDP Sites 277, 279 and 281, Initial Reports of Deep-Sea Drilling Project, 29. U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, pp 743–752
Shields GA (1999) Working towards a new stratigraphic calibration scheme for the Neoproterozoic–Cambrian. Eclo Geol Helvetiae 92:221–233
Shields G, Stille P (2001) Diagenetic constraints on the use of cerium anomalies as palaeoseawater redox proxies: an isotopic and REE study of Cambrian phosphorites. Chem Geol 175:29–48
Siby K, Nath BN, Ramaswamy V, Naman D, Rao T, Raju KK, Selvaraj K, Chen CTA (2008) Possible detrital, diagenetic and hydrothermal sources for Holocene sediments of the Andaman backarc basin. Mar Geol 247:178–193
Sinanoglu D, Sasmaz A (2019) Geochemical evidence on the depositional environment of Nummulites accumulations around Elazig, Sivas, and Eskişehir (Turkey) in the middle Eocene sub-epoch. Arab J Geosci 12:1–10
Singh BP, Pawar JS, Patra A (2013) Geochemistry of Late Eocene/Oligocene calcretes (caliche) of the northwestern Himalaya, India. Himal Geol 34:135–140
Singh BP, Bhargava ON, Chaubey RS, Kishore N, Prasad SK (2015) Early Cambrian Trail Archaeonassa from the Sankholi Formation (Tal Group), Nigali Dhar Syncline (Sirmur District), Himachal Pradesh. J Geol Soc India 85:717–721
Singh AK, Tewari VC, Sial AN, Khanna PP, Singh NI (2016) Rare earth elements and stable isotope geochemistry of carbonates from the mélange zone of Manipur ophiolitic complex, Indo-Myanmar Orogenic Belt, Northeast India. Carbon Evaporites 31:139–151
Sissakian VK, Al-Jibouri BS (2012) Stratigraphy of the low folded zone. Iraqi Bull Geol Min 5:63–132
Sissakian VK, Fouad SF (2012) Geological map of Iraq, scale 1: 1 000 000. Iraq Geological Survey, Baghdad
Sissakian VK, Ahad AA, Al-Ansari N, Hassan R, Knutsson S (2016) The regional geology of Dokan area, NE Iraq. J Earth Sci Geotech Eng 6:35–63
Song H, Wignall PB, Tong J, Bond DP, Song H, Lai X, Zhang K, Wang H, Chen Y (2012) Geochemical evidence from bio-apatite for multiple oceanic anoxic events during Permian–Triassic transition and the link with end-Permian extinction and recovery. Earth Planet Sci Lett 353:12–21
Song C, Herong G, Linhua S (2014) Geochemical characteristics of REE in the Late Neo-Proterozoic limestone from northern Anhui Province, China. Chin J Geochem 33:187–193
Srivastava P (2001) Paleoclimatic implications of pedogenic carbonates in Holocene soils of the Gangetic Plains, India. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 172:207–222
Srivastava VK, Singh BP (2019) Depositional environments, and sources for the middle Eocene Fulra limestone formation, Kachchh basin, western India: evidence from facies analysis, mineralogy, and geochemistry. Geol J 54:62–82
Steuber T (2002) Plate tectonic control on the evolution of Cretaceous platform-carbonate production. Geology 30:259–262
Steuber T, Veizer J (2002) Phanerozoic record of plate tectonic control of seawater chemistry and carbonate sedimentation. Geology 30:1123–1126
Steuber T, Rauchm MJP, Graaf J, Malkoč M (2005) Low-latitude seasonality of Cretaceous temperatures in warm and cold episodes. Nature 437:1341–1344
Sverjensky DA (1984) Europium redox equilibria in aqueous solution. Earth Planet Sci Lett 67:70–78
Talbot MR (1990) A review of the palaeohydrological interpretation of carbon and oxygen isotopic ratios in primary lacustrine carbonates. Chem Geol 80:26l–279
Taylor SR, McLennan SM (1985) The continental crust: its composition and evolution. https://doi.org/10.1029/95RG00262
Tehrani PN, Calagari AA, Roldan FV, Simmonds V, Siahcheshm K (2018) C and O stable isotopes and rare earth elements in the Devonian carbonate host rock of the Pivehzhan iron deposit, NE Iran. Geol Acta 16:125–148
Tewari VC, Sial AN (2007) Neoproterozoic–Early Cambrian isotopic variation and chemostratigraphy of the Lesser Himalaya, India, Eastern Gondwana. Chem Geol 237:64–88
Tobia FH (2018) Stable isotope and rare earth element geochemistry of the Baluti carbonates (Upper Triassic), Northern Iraq. Geosci J 22:975–987
Toyoda K, Nakamura Y, Masuda A (1990) Rare earth elements of Pacific pelagic sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 54:1093–1103
Turekian KK, Wedepohl KH (1961) Distribution of elements in some major units of earth’s crust. Geol Soc Am Bull 72:175–192
Vincent B, Rambeau C, Emmanuel L, Loreau JP (2006) Sedimentology and trace element geochemistry of shallow-marine carbonates: an approach to paleoenvironmental analysis along the Pagnysur-Meuse Section (Upper Jurassic, France). Facies 52:69–84
Walker A, Hance RJ, Allen JG, Briggs GG, Chen YL, Gaynor JD, Hogue EJ, Malquori A, Moody K, Moyer JR, Pestemer W (1983) EWRS Herbicide-Soil Working Group: collaborative experiment on simazine persistence in soil. Weed Res 23:373–383
Wang BS, Lee CP, Ho TY (2014) Trace metal determination in natural waters by automated solid phase extraction system and ICP–MS: the influence of low-level Mg and Ca. Talanta 128:337–344
Webb GE, Kamber BS (2000) Rare earth elements in Holocene reefal microbialites: a shallow seawater proxy. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 64:1557–1565
Whittaker SG, Kyser TK (1993) Variations in the neodymium and strontium isotopic composition and REE content of molluscan shells from the Cretaceous Western Interior Seaway. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 57:4003–4014
Wignall PB, Myers KJ (1988) Interpreting benthic oxygen levels in mudrocks: a new approach. Geology 16:452–455
Wignall PB, Twitchett RJ (1996) Oceanic anoxia and the end Permian mass extinction. Science 272:1155–1158
Wignall PB, Zonneveld JP, Newton RJ, Amor K, Sephton MA, Hartley S (2007) The end Triassic mass extinction record of Williston Lake, British Columbia. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 253:385–406
Wright VP (1990) Equatorial aridity and climatic oscillations during the Carboniferous, Southern Britain. J Geol Soc 147:359–363
Wright J, Seymour RS, Shaw HF (1984) REE and neodymium isotopes in conodont apatite. Variation with geological age and depositional environment. Geol Soc Am Spec Pap 196:325–340
Yoshioka H, Asahara Y, Tojo B, Kawakami S (2003) Systematic variations in C, O, and Sr isotopes and elemental concentrations in Neoproterozoic carbonates in Namibia: implications for a glacial to interglacial transition. Precamb Res 124:69–85
Zhao YY, Zheng YF, Chen F (2009) Trace element and strontium isotope constraints on sedimentary environment of Ediacaran carbonates in southern Anhui, South China. Chem Geol 265:345–362
Acknowledgements
The authors are indebted to thank Dr. Dilshad Omer Ali, Salahaddin University, Department of Earth Sciences and Petroleum, for his help in the fieldwork. The authors are thankful to the anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions and kind help in improving the quality of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SSS carried out study sampling, data collection, result interpretation and approved the final manuscript. Ass. Prof. HSA-J fieldwork and data collection. Prof. FHT supervised the methodology, reviewed, revised, and provided inputs for improvement.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shangola, S.S., Al-Jaleel, H.S. & Tobia, F.H. Stable isotopes and rare-earth elements of carbonate rocks, Paleocene–Eocene Kolosh Formation, High Folded Zone, NE Iraq: implication for depositional environment and Diagenesis. Carbonates Evaporites 38, 77 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-023-00899-1
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-023-00899-1