Abstract
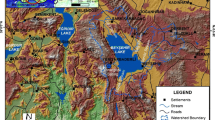
Groundwater crisis under the changed climate scenario has now become a global concern. Land use and land cover change and rapid urbanization are some of the prime causes of it. Aquifers are in a vulnerable condition due to the extensive abstraction and over exploitation as the groundwater draft exceeds the groundwater recharge. It is in this context, the present study has been carried out to identify groundwater potential zones of Garbeta block of Paschim Medinapore district of West Bengal, India, which is located in a critical terrain condition and faces extreme water scarcity in terms of both surface and groundwater availability. The region experiences an average annual groundwater level fluctuation between 9 and 11 m. Demarcation of the groundwater potential zones has been made using Fuzzy Analytical Hierarchy Process (Fuzzy AHP) integrated with geospatial techniques. Fuzzy weights have been entrusted to eleven physical parameters namely land use and land cover, soil, geology geomorphology, lineament density, drainage density, relative relief, distance from river, slope, groundwater level fluctuation and normalised difference water index (NDWI), and the final map has been prepared within geospatial environment. The groundwater potential zones have been classified into five classes: very low potential (18.30%), low potential (26.42%), moderate potential (25.99%), high potential (19.55%) and very high potential (9.75%). The calculated results have been validated through field based groundwater level survey. Such studies will provide new vision and incur valuable information to the stakeholders for sustainable water resources management and effective identification of suitable locations for groundwater extraction.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal E, Agarwal R, Garg RD, Garg PK (2013) Delineation of groundwater potential zone: an AHP/ANP approach. J Earth Syst Sci 122:887–898. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-013-0309-8
Aggarwal R, Singh S (2013) AHP and extent AHP approach for prioritization of performance measurement attributes. International Journal of Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1082718
Ahmed K ,Shahid S , Harun S B, Ismail T , Nawaz N, Shamsudin S (2015) Assessment of groundwater potential zones in an arid region based on catastrophe theory. Earth Sci Inform 8:539–549. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-014-0173-3
Alam A, Bhat MS, Maheen M (2019) Using Landsat satellite data for assessing the land use and land cover change in Kashmir valley. GeoJournal. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-019-10037-x
Andualem TG, Demeke GG (2019) Groundwater potential assessment using GIS and remote sensing: a case study of Guna tana landscape, upper blue Nile basin. Ethiopia J Hydrol 24:100610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2019.100610
Aouragh MH, Essahlaoui A, Ouali AQ, Hmaidi AE, Kamel S (2016) Groundwater potential of Middle Atlas Plateaus, Morocco, using fuzzy logic approach, GIS and remote sensing. Geomat Nat Haz Risk 8:194–206. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2016.1181676
Ayag Z (2005) A Fuzzy AHP based simulation approach to concept evaluation in a NDP environment. IIE Transcactions.37:827-842.https://doi.org/10.1080/07408170590969852
Ayhan MB (2013) A Fuzzy AHP approach for supplier selection problem: a case study in a gear motor company. International Journal of Managing Value and Supply Chains 4:11–23. https://doi.org/10.5121/ijmvsc.2013.4302
Behzad HRM, Charchi A, Kalantari N, Nejad MA, Vardanjani HK (2019) Delineation of groundwater potential zones using remote sensing (RS), geographical information system (GIS) and analytic hierarchy process (AHP) technique: a case study in the Leylia- Keynow watershed , southwest of Iran. Carbonates Evaporites 34:1307–1319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-018-0420-7
Bhunia GS, Samanta S, Pal DK, Pal B (2012) Assessment of groundwater potential zone in Paschim Medinapore district, West Bengal- a meso scale study using GIS and remote sensing approach. J Environ Earth Sci 2:42–59
Biswas A, Jana A, SharmaShashi P (2012) Delineation of groundwater potential zones using satellite remote sensing and geographic information system techniques: a case study from Ganjam district, Orissa, India. Res. J. Recent Sci 1:59–66
Bonsor HC, Macdonald AM, Davis J (2014) Evidence for extreme variations in the permeability of laterite form a detailed analysis of well behaviour in Nigeria. Hydrol Process 28:3563–3573. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.9871
Central Ground Water Board (2018) Ministry of water resources, river development and ganga rejuvenation, government of India (2017–2018) ground water year book- India 2017-2018
Chang DY (1996) Applications of extent analysis method on FuzzyAHP. Eur J Oper Res 95:649–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-2217(95)00300-2
Fashae OA, Tijani MN, Talabi AO, Adedeji OI (2013) Delineation of groundwater potential zones in crystalline basement terrain of SW-Nigeria : an integrated GIS and remote sensing approach. Appl Water Sci 4:19–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-013-0127-9
Ghosh KG (2019) Spatial and temporal appraisal of drought jeopardy over the Gangetic West Bengal, eastern India. Geoenviron Disasters 6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40677-018-0117-1
Ghosh S, Guchhait SK (2020) Laterites of Bengal characterization. Geochronology and Evolution Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-22937-5
Ghosh KP, Bandyopadhyay S, Jana NC (2016) Mapping of groundwater potential zones in hard rock terrain using geoinformatics : a case of Kumari watershed in Western part of West Bengal. Model Earth Syst Environ 2:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-015-0044-z
Giordano M (2009) Global groundwater? Issues and solution. Annual Review of Environment and Resources 34:153–178. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.environ.030308.100251
Halder S, Roy MB, Roy PK (2020) Analysis of groundwater level trend and groundwater drought using standard groundwater level index: a case study of an eastern river basin of West Bengal. India SN Applied Science 2:507. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-2302-6
Horton RE (1945) Erosional development of streams and their drainage basins: hydrophysical approach to quantitative morphology. Bull Geol Soc Am 56(275–3):70. https://doi.org/10.1177/030913339501900406
Javed A, Wani MH (2009) Delineation of groundwater potential zones in Kakund watershed, eastern Rajasthan, using remote sensing and GIS techniques. J Goel Soc India 73:229–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-009-0079-8
Jayawickrama H M M M, Kulatunga A K, Mathavan S (2017) Fuzzy AHP based plant sustainability evaluation method.Procedia Manuf 8: 571–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2017.02.073
Kundzewicz ZW, Doll P (2009) Will groundwater ease freshwater stress under climate change? Hydrol Sci J 54:665–675. https://doi.org/10.1623/hysj.54.4.665
Magesh NS, Chandrasekar N, Soundranayagam JP (2012) Delineation of groundwater potential zones in Theni district, Tamil Nadu, using remote sensing, GIS and MIF techniques. Geosci Front 3:189–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2011.10.007
Mardani A, Jusoh A, Nor MDK, Khalifah Z, Zakwan VA (2015) Multi criteria decision-making technique and their applications – a review of the literature from 2000-2014. Econ Res 28:516–571. https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677X.2015.1075139
Mcfeeters SK (1996) The use of the normalized difference water index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. International Journal of Remote Sensing 17:1425–1432. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431169608948714
Melton M A (1957) An analysis of the relations among the elements of climate, surface properties and geomorphology. Technical Report 11, Department of Geology, Columbia University, New York
Moustafa M (2017) Groundwater flow dynamic investigation without drilling boreholes. Appl Water Sci 7:481–488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-015-0267-1
Mukherjee P, Singh CK, Mukherjee S (2012) Delineation of groundwater potential zone in arid region of India - a remote sensing and GIS approach. Water Resour Manag 26:2643–2672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-012-0038-9
Mulubrhan F, Mokhtar AA, Muhammad M (2014) Comparative analysis between fuzzy and traditional analytical hierarchy process. Matec Web of Conference 13. https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/20141301006
Nair HC, Padmalal D, Joseph A, Vinod PG (2017) Delineation of groundwater potential zones in river basins using geospatial tools—an example from Southern Western Ghats, Kerala, India. J geovis spat anal 1:5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41651-017-0003
Ozdagoglu A, Ozdagoglu G (2007) Comparison of AHP and Fuzzy AHP for the multicriteria decision making processes with linguistic evaluations. İstanbul Ticaret Universitesi Fen Bilimleri Dergisi 6:65–85
Panahi RM, Mousavi SM, Rahimzadegan M (2017) Delineation of groundwater potential zones using remote sensing, GIS and AHP technique in Tehran- Karag Plain. Iran Environ Earth Sci 76:792. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12665-017-7/126-3
Peng SH, Tang C (2015) Blending the analytic hierarchy process and fuzzy logical systems in scenic beauty assessment of check dams in streams. Water 7:6983–6998. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7126670
Rafati S, Nikeghbal M (2017) Groundwater exploration using fuzzy logic approach in GIS for an area around an anticline, Fars Province. Int Arch Photogramm Remote Sens Spat Inf Sci 42:441–445. https://doi.org/10.5194/isprs-archives-XLII-4-W4-441-2017
Sener E, Sener S, Davraz A (2018) Groundwater potential mapping by combining fuzzy-analytic hierarchy process and GIS in Beyşehir Lake Basin, Turkey. Arab J Geosci 11:187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3510-x
Shit PK, Bhunia GS, Maiti R (2014) Morphology and development of selected badlands in south Bengal. India Indian Journal of Geography and Environment 13:161–171
Shit PK, Paira R, Bhunia G, Maiti R (2015) Modeling of potential gully erosion hazard using geo-spatial technology at Garbheta block, West Bengal in India. Modeling Earth System and Environment 1:2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-015-0001-x
Siva G, Nasir N, Selvakumar R (2017) Delineation of groundwater potential zone in sengipatti for Thanjavur district using analytical hierarchy process. Earth Environ Sci 80:012063. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/80/1/012063
Suhag R (2016) Overview of ground water in India
Tang YC, Lin TW (2011) Application of the fuzzy analytic hierarchy process to the lead-free equipment selection decision. International Journal of Business and System Research 5:35–56. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJBSR.2011.037289
Todd DK (2009) Groundwater hydrology. Wiley, Delhi
Turner SWD, Hejazi M, Yonkofski C, Kim SH, Kyle P (2019) Influence of groundwater extraction costs and resource depletion limits on simulated global nonrenewable water withdrawals over the twenty-first century. Earth’s Future 7:123–125. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018EF001105
Wada Y, Beek LPHV, Kempen CMV, Reckman JWTM, Vasak S, Bierkens MFP (2010) Global depletion of groundwater resources. Geophys Res Lett 37:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010GL044571
Wang YM, Chin KS (2011) Fuzzy analytic hierarchy process: a logarithmic fuzzy preference programming methodology. Int J Approx Reason 52:541–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijar.2010.12.004
Yeh HF, Cheng YS, Lin HI, Lee CH (2016) Mapping groundwater recharge potential zone using a GIS approach in Hualian River, Taiwan. Sustainable Environment Research 26:33–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.serj.2015.09.005
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Survey of India (SOI) for providing the topographical sheets, Central Ground water Board (CGWB), Government of India, for providing groundwater level data of wells and National Bureau of Soil Survey and Land Utilisation Planning (NBSSLUP) Government of India, for providing the soil map. The authors share their gratitude towards the Digital Library of School of Water Resources Engineering, Jadavpur University for allowing to access all the GIS and statistical softwares. Lastly, the authors are grateful to the research scholars of the department for helping to conduct the field survey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Biswajeet Pradhan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halder, S., Roy, M.B. & Roy, P.K. Fuzzy logic algorithm based analytic hierarchy process for delineation of groundwater potential zones in complex topography. Arab J Geosci 13, 574 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05525-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05525-1