Abstract
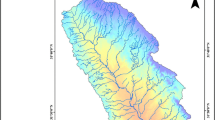
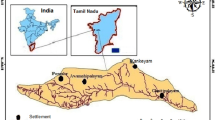
The remotely sensed data provides synoptic viewing and repetitive coverage for thematic mapping of natural resources. In the present study hydrogeomorphological mapping has been carried out in Kakund watershed, Eastern Rajasthan for delineating groundwater potential zones. IRS-1D LISS III Geocoded FCC data in conjunction with Survey of India toposheet (1:50000 scale) and field inputs were used for thematic mapping. Geomorphic units identified through visual interpretation of FCC include: alluvial plain, plateau, valley fills, intermontane valleys, burried pediment, residual hills, and linear ridges. In addition, lineaments were mapped since they act as conduit for groundwater recharge. Majority of the lineaments trends NE-SW and a few along NW-SE directions and are confined to the southern and southeastern parts of the watershed. Based on hydrogeomorphological, geological and lineament mapping the Kakund watershed has qualitatively been categorized into four groundwater potential zones, viz. good to very good, moderate to good, poor to moderate and very poor to poor. The study reveals that only 10.97% of the area has good to very good, 35.41% area with moderate to good, 49.04 % of the area has poor to moderatel, while remaining 4.57% has poor to very poor groundwater potential.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CGWB (1996) Groundwater resources and development potential of Bharatpur, Rajasthan. Tech Report, Central Groundwater Board (CGWB), western region, Jaipur.
Fermor, L.L. (1930) On the age of Aravalli Range. Rec. Geol. Surv. India, v.62, pt.4, pp.391–409.
Ghose, R. (1993) Remote Sensing for analysis of groundwater availability in an area with long unplanned mining history. Jour. Ind. Soc. Rem. Sens, v.21, pp.119–126.
Haridas, V.R., Aravindan, S. and Girish Gopinath (1998) Remote sensing and its applications for ground water favorable area identification. Quat. Jour. GARC, v.6, pp.18–22.
Heron, A.M. (1917) Biana-Lalsot Hills in eastern Rajputana. Rec. Geol. Surv. India, v.48, pt.4.
Iqbaluddin, Saifuddin and Akram Javed. (1997) Geomorphology and Landscape Evolution of Bharatpur District, Rajasthan. Jour. Ind. Soc. Rem. Sens, v.25, pp.177–186.
Khan, M.A. and Moharana, P.C. (2002) Use of Remote sensing and Geographical Information System in the delineation and characterization of groundwater prospect zones. Jour. Ind. Soc. Rem. Sens, v.30, pp.131–141.
Krishnamurthy, J., Venkatesa Kumar, N., Jayaraman, V. and Manivel, M. (1996) An approach to demarcate groundwater potential zones through remote sensing and a GIS. Int. Jour. Rem. Sens, v.17, pp.1867–1884.
Pradeep, K.J. (1998) Remote sensing technique to locate groundwater potential zones in upper Urmil River basin, district Chhatarpur, India. Jour. Ind. Soc. Rem. Sens, v.26, pp.135–147.
Saifuddin (1999) Land system studies using statistical image analysis techniques for remotely sensed data and GIS applications in parts of Yamuna basin in Aligarh, Mathura and Bharatpur districts. PhD Thesis, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh (Unpublished).
Saraf, A.K. and Choudhary, P.R. (1998) Integrated remote sensing and GIS for groundwater exploration and identification of artificial recharge sites. Int. Jour. Rem. Sens, v.19, pp.1825–1841.
Sankar, K. (2002) Evaluation of groundwater potential zones using remote sensing data in Upper Vaigai river basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Jour. Ind. Soc. Rem. Sens, v.30, pp.119–129.
Sharma, M. L. (1986) Geomorphology of Semi-arid Region. A case study of Gambhir river Basin, Rajasthan. Scientific Publishers, Jodhpur, 196p.
Umar, R. and Absar, A. (2003) Chemical characteristics of groundwater in parts of the Gambhir river basin, Bharatpur district, Rajasthan, India. Environmental Geology, v.44, pp. 535–544.
Venkatachalam, P., Murthy, C.V.S.S.B.R., Chowdhary, S. and Sharma, L.N. (1991) Groundwater potential zone mapping using a GIS approach. Asia-Pacific Remote Sensing Jour., v.4, pp.75–78.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Javed, A., Wani, M.H. Delineation of groundwater potential zones in Kakund watershed, Eastern Rajasthan, using remote sensing and GIS techniques. J Geol Soc India 73, 229–236 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-009-0079-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-009-0079-8