Abstract
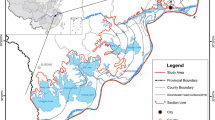
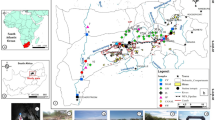
Interaction between surface water represented by the Euphrates River, natural springs, and Sawa Lake with groundwater (11 wells) in southern Iraq was investigated in this study. Water samples were collected for hydrochemistry and stable isotope (2H and 18O) analysis. Sampling of water from determined stations (10 stations along the Euphrates, 3 springs, and Sawa Lake) were carried out during two stages; the first was in October 2013(dry season) and the second one was in March 2014 (wet season). The aim of the research is to assess the interaction of groundwater–surface water, which includes Al-Atshan River (branch of the Euphrates River), Sawa Lake, and the groundwater in the study area by using hydrochemistry and stable isotope techniques. The results indicate that surface waters have a different type of water from that of groundwater. In δ 2H and δ 18O diagrams, all groundwater, springs, and Sawa Lake waters are plotted below the Global Meteoric Water Line (GMWL) and the local meteoric water line (LMWL) indicating the influence of evaporation processes and seasonal variation. The LMWL deviates by a d-excess about +13.71 toward the East Mediterranean meteoric water line (EMWL) indicating that the origin of the vapor source is the Mediterranean Sea. The river water has different isotopic compositions from that of groundwater, springs, and Sawa Lake. The final conclusion is that there is no clear influence of the groundwater on the river water while there is an intermixing between the groundwater in the different locations in the study area.














Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Adar E.M., Leibundgut Ch., (Eds.), (1995) Application of tracers in Arid Zone Hydrology. IAHS Publication No. 232, Wallingford.
Ali, SM (2012) Hydrological environmental assessment of Baghdad area, Ph.D. thesis, University of Baghdad, College of Science, Baghdad, Iraq
Ali K.K, Marouf B.A. (2002) Concentrations measurements of natural radionuclides in the sediments and water of the spring in Hit, 1: Kubaisa and Rahaliaya. The First scientific Conference of Iraqi scientific society in water reservoirs. Baghdad57–Kubaisa and Rahaliaya. The First scientific Conference of Iraqi scientific society in water reservoirs. Baghdad64
Ali KK, Al-Kubaisi QY, Al-Paruany KB (2015) Isotopic study of water resources in a semi-arid region, western Iraq. Environ Earth Sci 74:1671–1686
Al-Jiburi HK and Al-Basrawi NH (2009) Hydrogeology. Iraqi Bull. Geol. Min. Special Issue, 2009: Geology of Iraqi Southern Desert 77–91
Al-Jiburi HK and Al-Basrawi NH (2009) Hydrogeology. Iraqi Bull. Geol. Min. Special Issue, 2009: Geology of Iraqi Southern Desert 77–91
Al-Mitawki, KGM (2013) The impact of drain water on ground and surface water quality in Al-Shanafiya area, southwest Iraq, MSc. Thesis. University of Baghdad. Baghdad Iraq
Al-Mubarak MA and Amin RM (1983) Regional geological mapping of the eastern part of the Western Desert and the western part of the southern Desert. GEOSURV, int. rep. No. 1380
Al-Paruany KB (2012) Hydrochemical and isotopic study of water resources between Haditha Dam and site of Al-Baghdadi Dam, Ph.D. thesis, University of Baghdad, College of Science, Baghdad, Iraq
Al-Qurishi, RM (2014) Hydrochemistry of Sawa Lake, Southern Iraq, MSc. Thesis. University of Baghdad. Baghdad Iraq
Awadh SM, Ali KK, Aazzaw AT (2013) Geochemical exploration using surveys of spring water, hydrocarbon and gas seepage, and geobotany for determining the surface extension of Abu-Jir Fault Zone in Iraq: a new way for determining geometrical shapes of computational simulation models. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, Elsevier 124:218–229
Bumett WC, Bokuniewicz H, Huettel M, Moore WS, Taniguchi M (2003) Groundwater and pore water inputs to the coastal zone. Biogeochemistry 66:3–33
Clark I, Fritz P (1997) Environmental isotopes in hydrology, Lewis Publishers. new Lewis Publishers, New York, p. 328p
Diefendorf AF, Patterson WP (2005) Survey of stable isotope values in Irish surface waters. J Paleolimnol 34:257–269
Fritz P, Hennings CS, Suzolo O, Salati E (1979) Isotope hydrology in northern Chile. In: isotope hydrology 1978. IAEA, Vienna 2:525–544
Gat J (1971) Comments on stable isotope method in regional groundwater investigations. Water Resour Res 7:980--993
GEOSURV (1983) Hydrogeology, hydrochemistry and water resources in the Southern Desert (Blocks 1, 2, 3). GEOSURV, int. rep. no 1250–1256 GEOSURV, Baghdad, Iraq
Gibson JJ, Prepas EE, McEachern P (2002) Quantitative comparison of lake through flow, residency, and catchment runoff using stable isotopes: modelling and results from a survey of boreal lakes. J Hydrol 262:128–144
Graig H (1961) Isotopic variations in natural waters. Science 133:1702–1703
Hassan AH and Al-Khateeb AAG (2004) Geological survey in Lissan area in Karbala-Najaf plateau. GEOSURV. Baghdad, Iraq. Report No. 2870, 53p
IAEA International Atomic Energy Agency (2005) Isotope Hydrology Section. ihs@iaea.org, www.iaea.org/water.
Iraqi Meteorological Organization (IMO) (2013) Climate data of recorded in Al-Sammwa station for period from (1970–2013).
Jassas H, Merkel B (2014) Estimating groundwater recharge in the semiarid Al-Khazir Gomal Basin, North Iraq. Water 6:2467–2481
Jassim SZ. and Goff JC (2006) Geology of Iraq, Dolin Prague and Moravian Museum, Brno, 341p.
Krasny J (1982) Hydrogeological of the Mesopotamian plain and its environs: Diwaniya-Samawa area. In: Jassm, S.Z., Goff, J.C. (Eds.), Geology of Iraq. Dolin, Prague and Moravian Museum, Brno, Czech Rebublic.
Mather JR (1974) Climatology: fundamentals and applications’, McGraw-Hill, New
Mazor E (2004) Chemical and isotopic groundwater hydrology third edition. Weizmann Institute of Science Rehovot, New York, 465p
Mook WG (2000) Environmental isotopes in the hydrological cycle, principle and applications, IHP-V, No.39, Vol.4, UNESCO, Paris, 200p
Ostovari Y, Zare S, Beigi HV, Asgari K (2013) Effects of geological formation on groundwater quality in Lordegan Region, Chahar-mahal- va- Bakhtiyari, Iran. Intl J Agri Crop Sci 5(17):2013
Peters NE, Leibundgut Ch (Eds.) (1993) Tracers in Hydrology. IAHS Publication No. 215, Wallingford.
Porcelli D, Swarzenski PW (2003) The behavior of U- and Th-series nuclides in groundwater. Rev Mineral Geochem 52(1):317
Ramadhan AA and Al-Hadithy KB (2009) Use isotopes and chemical techniques in the study of Artificial Recharge in groundwater, Final report of Regional project RAS/8/103,IAEA 213p
Sissakian VK (2000) Geological map of Iraq. Scale 1: 1000 000, 3rd edit. GEOSURV, Baghdad, Iraq.
Tsujimura M, Abe Y, Tanaka T, Shimada J, Higuchi S, Yamanaka T, Davaa G, Oyunbaatar D (2007) Stable isotopic and geochemical characteristics of groundwater in Kherlen River basin, a semi-arid region in eastern Mongolia. J Hydrol 333:47–57
Wilde FD, Radtke DB, Gibs D (2005) Collection of water samples, geological survey techniques of water resource, book 9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Water Resources in Arid Areas
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, K.K., Ajeena, A.R. Assessment of interconnection between surface water and groundwater in Sawa Lake area, southern Iraq, using stable isotope technique. Arab J Geosci 9, 648 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2673-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2673-6