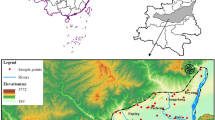
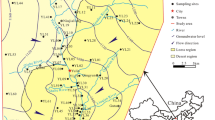
Abstract
The intensification of economic development, population growth, and energy consumption have led to the pollution of the groundwater in Gaobeidian City. This may exert great influence on human health. In the study, the chemical characteristics of the groundwater have been analyzed by Piper diagram and the possible health risks posed to the human health in Gaobeidian City has been evaluated using the model recommended by the Ministry of Environmental Protection of China. Furthermore, metal-species-weighted human health risk assessment is adopted for Cr6+, which is the major contributor to the carcinogenic health risk. The results show that groundwater is weakly alkaline, and the hydrochemical types is mainly Ca-HCO3. Non-carcinogenic pollutants mainly include arsenic (As), F−, and Fe. Carcinogenic pollutants mainly include Cr6+ and As. The carcinogenic risks of Cr6+ and As in the groundwater of all sampling sites greatly exceed their maximum acceptable limits, and contribution rate of Cr6+ is higher than that of As. The most important chemical species of Cr6+ is CrO42−, followed by CaCrO4(aq) and HCrO4−. The carcinogenic risk of above species is greater than the allowable limit. Among them, CrO4− exhibits the highest carcinogenic risk, and the maximum carcinogenic risk through ingestion to children and adults is 1.27E−03 and 5.98E−04, respectively. The economy in this area has developed rapidly because of its superior geographical location, but the groundwater pollution may have a great impact on the health of local residents, which must be paid attention to by local decision makers.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adimalla N, Li P (2019) Occurrence, health risks, and geochemical mechanisms of fluoride and nitrate in groundwater of the rock-dominant semi-arid region, Telangana State, India. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25(1–2):81–103. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1480353
Adimalla N, Qian H (2019) Spatial distribution and health risk assessment of fluoride contamination in groundwater of Telangana: a state-of-the-art. Geochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2019.125548
Adimalla N, Qian H, Li P (2019) Entropy water quality index and probabilistic health risk assessment from geochemistry of groundwaters in hard rock terrain of Nanganur County, South India. Geochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2019.125544
Broadway A, Cave M, Wragg J, Fordyce F, Bewley R, Graham M (2010) Determination of the bioaccessibility of chromium in Glasgow soil and the implications for human health risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 409(2):267–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.09.007
Cai L, Xu Z, Qi J, Feng Z, Xiang T (2015) Assessment of exposure to heavy metals and health risks among residents near Tonglushan mine in Hubei, China. Chemosphere 127:127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.01.027
Chanpiwat P, Lee B, Kim K, Sthiannopkao S (2014) Human health risk assessment for ingestion exposure to groundwater contaminated by naturally occurring mixtures of toxic heavy metals in the Lao PDR. Environ Monit Assess 186:4905–4923. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3747-0
Chen H, Teng Y, Lu S, Wang Y, Wu J, Wang J (2016) Source apportionment and health risk assessment of trace metals in surface soils of Beijing metropolitan, China. Chemosphere 144:1002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.09.081
Dai S, Li H, Yang Z, Dai M, Shi L (2018) Effects of biochar amendments on speciation and bioavailability of heavy metals in coal-mine-contaminated soil. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 24(7):1887–1900. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1429250
Ghosh S, Basu A, Saha R, Ghosh A, Mukherjee K, Saha B (2012) Micellar catalysis on picolinic acid promoted hexavalent chromium oxidation of glycerol. J Coord Chem 65(7):1158–1177. https://doi.org/10.1080/00958972.2012.669035
Gu Y, Huang H, Lin Q (2016) Concentrations and human health implications of heavy metals in wild aquatic organisms captured from the core area of daya bay's fishery resource reserve, south china sea. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 45:90–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2016.05.022
Guo X, Wei Z, Penn C, Xu T, Wu Q (2013) Effect of soil washing and liming on bioavailability of heavy metals in acid contaminated soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 77(2):432. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2011.0371
He S, Li P (2019) A MATLAB based graphical user interface (GUI) for quickly producing widely used hydrogeochemical diagrams. Geochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.Chemer.2019:125550
He X, Li P (2020) Surface water pollution in the middle Chinese Loess Plateau with special focus on hexavalent chromium (Cr6+): occurrence, sources and health risks. Expo Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-020-00344-x
He S, Wu J (2019) Hydrogeochemical characteristics, groundwater quality and health risks from hexavalent chromium and nitrate in groundwater of Huanhe Formation in Wuqi County, Northwest China. Expo Health 11(2):125–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-018-0289-7
He X, Wu J, He S (2019) Hydrochemical characteristics and quality evaluation of groundwater in terms of health risks in Luohe aquifer in Wuqi County of the Chinese Loess Plateau, northwest China. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25(1–2):32–51. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1531693
He X, Li P, Ji Y, Wang Y, Su Z, Elumalai V (2020a) Groundwater arsenic and fluoride and associated arsenicosis and fluorosis in China: occurrence, distribution and management. Expo Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-020-00347-8
He X, Li P, Wu J, Wei M, Ren X, Wang D (2020b) Poor groundwater quality and high potential health risks in the Datong Basin, northern China: research from published data. Environ Geochem Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00520-7
Hu Y, Wang X, Dong Z, Liu G (2015) Determination of heavy metals in the groundwater of the Huaibei plain, China, to characterize potential effects on human health. Anal Lett 48:349–359. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2014.940530
Ji Y, Wu J, Wang Y, Elumalai V, Subramani T (2020) Seasonal variation of drinking water quality and human health risk assessment in Hancheng City of Guanzhong Plain, China. Expo Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-020-00357-6
Kelley M, Brauning S, Schoof R, Ruby M (2002) Assessing oral bioavailability of metals in soil. Battelle Press, Columbus
Kiefer K, Muller A, Singer H, Hollender J (2019) New relevant pesticide transformation products in groundwater detected using target and suspect screening for agricultural and urban micropollutants with LC-HRMS. Water Res 165:114972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.114972
Lei M, Liao B, Qin P (2007) Evaluation of bioavailability of chemical forms of heavy metals in soil. J Eco-Environ 16(5):1551–1556. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2007.05.043
Li P, Wu J (2019a) Sustainable living with risks: meeting the challenges. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25(1–2):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1584030
Li P, Wu J (2019b) Drinking water quality and public health. Expo Health 11(2):73–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-019-00299-8
Li H, Qian X, Hu W, Wang Y, Gao H (2013) Chemical speciation and human health risk of trace metals in urban street dusts from a metropolitan city, Nanjing, SE China. Sci Total Environ 456–457(7):212–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.03.094
Li P, Qian H, Howard KWF, Wu J, Lyu X (2014a) Anthropogenic pollution and variability of manganese in alluvial sediments of the Yellow River, Ningxia, northwest China. Environ Monit Assess 186:1385–1398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3461-3
Li P, Wu J, Qian H, Lyu X, Liu H (2014b) Origin and assessment of groundwater pollution and associated health risk: a case study in an industrial park, northwest China. Environ Geochem Health 36:693–712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-013-9590-3
Li P, Qian H, Howard KWF, Wu J (2015) Heavy metal contamination of Yellow River alluvial sediments, northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 73(7):3403–3415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3628-4
Li P, Li X, Meng X, Li M, Zhang Y (2016a) Appraising groundwater quality and health risks from contamination in a semiarid region of northwest China. Expo Health 8(3):361–379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0205-y
Li P, Wu J, Qian H (2016b) Hydrochemical appraisal of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes and the major influencing factors: a case study in and around Hua County, China. Arab J Geosci 9(1):15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2059-1
Li P, Feng W, Xue C, Tian R, Wang S (2017) Spatiotemporal variability of contaminants in lake water and their risks to human health: a case study of the Shahu Lake tourist area, northwest China. Expo Health 9(3):213–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0237-3
Li H, Yu X, Zhang W (2018a) Risk assessment of groundwater organic pollution using hazard, intrinsic vulnerability, and groundwater value, Suzhou City in China. Expo Health 10:99–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-017-0248-8
Li P, He S, He X, Tian R (2018b) Seasonal hydrochemical characterization and groundwater quality delineation based on matter element extension analysis in a paper wastewater irrigation area, Northwest China. Expo Health 10(4):241–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-17-0258-6
Li P, He S, Yang N, Xiang G (2018c) Groundwater quality assessment for domestic and agricultural purposes in Yan’an City, northwest China: implications to sustainable groundwater quality management on the Loess Plateau. Environ Earth Sci 77(23):775. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-2018-7968-3
Li P, He X, Li Y, Xiang G (2019a) Occurrence and health implication of fluoride in groundwater of loess aquifer in the Chinese Loess plateau: a case study of Tongchuan, Northwest China. Expo Health 11(2):95–107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-018-0278-x
Li P, He X, Guo W (2019b) Spatial groundwater quality and potential health risks due to nitrate ingestion through drinking water: a case study in Yan’an City on the Loess Plateau of northwest China. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25(1–2):11–31. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1553612
Liu G, Wang J, Zhang E, Hou J, Liu X (2016) Heavy metal speciation and risk assessment in dry land and paddy soils near mining areas at southern China. Environ Sci Pollut R 23(9):8709–8720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6114-6
Liu B, Ai S, Zhang W, Huang D, Zhang Y (2017) Assessment of the bioavailability, bioaccessibility and transfer of heavy metals in the soil-grain-human systems near a mining and smelting area in NW China. Sci Total Environ 609(17):822–829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.215
Mashal K, Salahat M, Al-Qinna M, Al-Degs Y (2015) Spatial distribution of cadmium concentrations in street dust in an arid environment. Arab J Geosci 8(5):3171–3182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1367-1
Ministry of Environmental Protection of P.R. China (2004) Technical specifications for environmental monitoring of groundwater (HJ/T 164–2004). National standards for environmental protection of China. (in Chinese)
Ministry of Environmental Protection of the P.R. China (2014) Technical guidelines for risk assessment of contaminated sites, (HJ 25.3–2014). China Environmental Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Ministry of Health of the P.R. China, Standardization Administration of the P.R. China (2006) Standards for drinking water quality (GB 5749–2006). China Standard Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Mosley L, Daly R, Palmer D, Yeates P, Dallimore C, Biswas T, Simpson S (2015) Predictive modelling of pH and dissolved metal concentrations and speciation following mixing of acid drainage with river water. Appl Geochem 59:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2015.03.006
Nguyen V, Bang S, Viet P, Kim K (2009) Contamination of groundwater and risk assessment for arsenic exposure in Ha Nam Province. Vietnam Environ Int 35(3):472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2008.07.014
Ogunbanjo O, Onawumi O, Gbadamosi M, Ogunlana A, Anselm O (2016) Chemical speciation of some heavy metals and human health risk assessment in soil around two municipal dumpsites in Sagamu, Ogun state, Nigeria. Chem Spec Bioavailab 28(1–4):142–151. https://doi.org/10.1080/09542299.2016.1203267
Olujimi O, Oputu O, Fatoki O, Opatoyinbo O, Aroyewun O, Baruani J (2015) Heavy metals speciation and human health risk assessment at an illegal gold mining site in Igun, Osun State. J Health Pollut 5(8):19–32. https://doi.org/10.5696/i2156-9614-5-8.19
Piper A (1944) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analysis. Trans Am Geophys Union 25(1):27–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/0197-0186(84)90023-8
Ruby M, Davis A, Schoof R, Eberle S, Sellstone C (1996) Estimation of lead and arsenic bioavailability using a physiologically based extraction test. Environ Sci Technol 30(2):422–430. https://doi.org/10.1021/es950057z
Reis A, Patinha C, Noack Y, Robert S, Dias A, Silva E (2014) Assessing the human health risk for aluminium, zinc and lead in outdoor dusts collected in recreational sites used by children at an industrial area in the western part of the Bassin Minier de Provence, France. J Afr Earth Sci 99(278):724–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2013.08.001
Song N, Ma Y (2017) The toxicity of HCrO4- and CrO42- to barley root elongation in solution culture: pH effect and modelling. Chemosphere 171:537–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.12.050
Shi Y (2016) Study on the rational allocation of various water resources in Gaobeidian City, Jiangxi. Build Mater 7:127–128 (in Chinese)
Stefansson A, Gunnarsson I, Kaasalainen H, Arnorsson S (2015) Chromium geochemistry and speciation in natural waters, Iceland. Appl Geochem 62:200–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2014.07.007
Skevas T (2020) Evaluating alternative policies to reduce pesticide groundwater pollution in Dutch arable farming. J Environ Plan Manag 63(4):733–750. https://doi.org/10.1080/09640568.2019.1606618
Su Z, Wu J, He X, Elumalai V (2020) Temporal changes of groundwater quality within the groundwater depression cone and prediction of confined groundwater salinity using Grey Markov model in Yinchuan area of northwest China. Expo Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-020-00355-8
Tipping E (1994) Whamc-a chemical equilibrium model and computer code for waters, sediments, and soils incorporating a discrete site/electrostatic model of ion-binding by humic substances. Comput Geosci 20(6):973–1023. https://doi.org/10.1016/0098-3004(94)90038-8
Wang D, Wu J, Wang Y, Ji Y (2020a) Finding high-quality groundwater resources to reduce the hydatidosis incidence in the Shiqu County of Sichuan Province, China: analysis, assessment, and management. Expo Health 12:307–322. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-019-00314-y
Wang L, Huang T, Yang G, Lu C, Dong F, Li Y, Guan W (2020b) The precursor-guided hydrothermal synthesis of CuBi2O4/WO3 heterostructure with enhanced photoactivity under simulated solar light irradiation and mechanism insight. J Hazard Mater 381:120956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120956
Wongsasuluk P, Chotpantarat S, Siriwong W, Robson M (2014) Heavy metal contamination and human health risk assessment in drinking water from shallow groundwater wells in an agricultural area in Ubon Ratchathani province, Thailand. Environ Geochem Health 36(1):169–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-013-9537-8
Wu J, Sun Z (2016) Evaluation of shallow groundwater contamination and associated human health risk in an alluvial plain impacted by agricultural and industrial activities, Mid-West China. Expo Health 8(3):311–329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-015-0170-x
Wu J, Zhou H, He S, Zhang Y (2019) Comprehensive understanding of groundwater quality for domestic and agricultural purposes in terms of health risks in a coal mine area of the Ordos basin, north of the Chinese Loess Plateau. Environ Earth Sci 78(15):446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8471-1
Wu J, Zhang Y, Zhou H (2020) Groundwater chemistry and groundwater quality index incorporating health risk weighting in Dingbian County, Ordos basin of northwest China. Geochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2020.125607
Yang K, Im J, Jeong S, Nam K (2015) Determination of human health risk incorporating experimentally derived site-specific bioaccessibility of arsenic at an old abandoned smelter site. Environ Res 137:78–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2014.11.019
Zhai Y, Zhao X, Teng Y, Xiao L, Zhang J (2017) Groundwater nitrate pollution and human health risk assessment by using HHRA model in an agricultural area, NE China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 137:130–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.11.010
Zhang Y, Chen J, Shi W, Zhang D, Zhu T, Li X (2017) Establishing a human health risk assessment methodology for metal species and its application of Cr6+ in groundwater environments. Chemosphere 189:525–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.08.175
Zhang Y, Wu J, Xu B (2018) Human health risk assessment of groundwater nitrogen pollution in Jinghui canal irrigation area of the loess region, northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 77(7):273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7456-9
Zhou Y, Li P, Chen M, Dong Z, Lu C (2020a) Groundwater quality for potable and irrigation uses and associated health risk in southern part of Gu’an County, North Chinas Plain. Environ Geochem Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00553-y
Zhou Y, Li P, Xue L, Dong Z, Li D (2020b) Solute geochemistry and groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes: a case study in Xinle City, North China. Geochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2020.125609
Acknowledgements
This subject is supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, CHD (Grant Nos. 300102299505 and 300102290501) and Projects supported by the youth science and technology fund of Hebei GEO University (Grant No. QN201508) and Natural Science Foundation of Education Department in Hebei Province (Grant No. D2019403194). The authors are grateful to the anonymous reviewers and the editors who helped us in improving the quality of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Ning, J., Li, L. et al. Health Risk Assessment of Groundwater in Gaobeidian, North China: Distribution, Source, and Chemical Species of the Main Contaminants. Expo Health 12, 427–446 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-020-00365-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-020-00365-6