Abstract
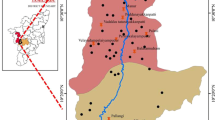
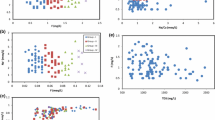
Groundwater has become a vital source of water for domestic and agricultural activities all over the world. The objective of this study is to investigate the fluoride-rich groundwater for assessing its suitability for drinking and irrigational purposes in Vaniyar River basin, Dharmapuri district, Tamil Nadu. About 650 groundwater samples were collected and analysed. Na–Cl and Ca–Mg–Cl–SO4 are the major hydrochemical types of groundwater present in this area. The concentrations of major ions are within the permissible limits of Bureau of Indian Standards in most of the area. Fluoride concentration exceeded the maximum permissible limit of the drinking water standards of 1.5 mg/l in 446 samples. The use of this groundwater for drinking purpose has caused dental and skeletal fluorosis to many of the residents of the area. The major source for fluoride in groundwater is due to the leaching of fluoride-bearing minerals in the rocks of this area. Fluoride ions from biotite and hornblende minerals leach into the groundwater and contribute to high fluoride concentration in this region. The groundwater of this area is characterised by high salinity and low sodium. Even though groundwater in the area is suitable for irrigation, it is not suitable for domestic purpose in most of the region.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghazadeh N, Mogaddam A (2010) Investigation of hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater in the Harzandat aquifer, northwest of Iran. Environ Monit Assess. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1575-4
Alexakis D (2011) Assessment of water quality in the Messolonghi-Etoliko and Neochorio region (West Greece) using hydrochemical and statistical analysis methods. Environ Monit Assess. doi:10.1007/s10661-011-1884-2
Baalousha H (2010) Assessment of a groundwater quality monitoring network using vulnerability mapping and geostatistics: a case study from Heretaunga Plains, New Zealand. Agric Water Manag 97:240–246
Bhargava DS, Killender DJ (1988) The technology of water resources in industries, a rational approach. J Ind Water Works Assoc 20:107–112
Brindha K, Rajesh R, Murugan R, Elango L (2012) Nitrate pollution in groundwater in some rural areas of Nalgonda district, Andhra Pradesh, India. J Environ Sci Eng 54:64–70
Bureau of Indian Standards Drinking water (BIS) (2013) Specification. IS: 10500, New Delhi
Carroll D (1962) Rainwater as a chemical agent of geological processes, A review U.S. Geological survey water- supply paper 1535
Davis SN, Wiest RJ (1966) Hydrogeology, vol 463. Wiley, New York
Doneen LD (1964) Water quality for agriculture. Department of Irrigation, University of California, Davis, p 48
Edmunds WM, Smedley PL (1996) Groundwater geochemistry and health with special reference to developing countries. Geol Soc Spec Pub 113:91–105
Freeze RA, Cherry JA (1979) Groundwater. PrenticeHall, Englewood Cliffs, p 604
Frengstad B, Skrede AK, Banks D, Krog JR, Siewers U (2000) The chemistry of Norwegian groundwater: III. The distribution of trace elements in 476 crystalline bedrock groundwaters, as analysed by ICPMS techniques. Sci Total Environ 246:21–40
Jagadeshan G, Kalpana L, Elango L (2015) Major ion signatures for identification of geochemical reactions responsible for release of fluoride from geogenic sources to groundwater and associated risk in Vaniyar River basin, Dharmapuri district, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-015-4250-9
Lahermo P, Backman B (1999) Nitrates in groundwater in Finland: the most endangering quality problem. Hydrogeol Land Use Manag: 329–333
Laluraj CM, Gopinath G, Dineshkumar PK (2005) Groundwater chemistry of shallow aquifers in the coastal zones of Cochin. Indus Appl Ecol Environ Res 3(1):133–139
Mishra PC, Behera PC, Patel RK (2005) Contamination of water due to major industries and open refuse dumping in the steel city of Orissa-a case study. J Environ Sci Eng 47:141–154
Nickson RT, McArthur JM, Shrestha B, Kyaw -Nyint TO, Lowry D (2005) Arsenic and other drinking water quality issues, Muzaffargarh District, Pakistan. Appl Geochem 20:55–68
Omo-Irabor O, Olobaniyi SB, Oduyemi K, Akunna J (2008) Surface and groundwater water quality assessment using multivariate analytical methods: a case study of the Western Niger Delta, Nigeria. Phys Chem Earth 33:666–673
Piper AM (1944) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analysis. Trans Geophysics Union 25:914–923
Ramesh K, Elango L (2006) Groundwater quality assessment in Tondiar basin, Indian. J Environ Protect 26:497–504
Rao NS (2006) Nitrate pollution and its distribution in the groundwater of Srikakulam district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Geol 51:631–645
Reimann C, Caritat P (1998) Chemistry elements in the environment. Factsheets for the geochemists and environmental scientist: 398
Richards LA (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of saline and Alkali soils, USDA handbook No. 60, vol 160. Printing Office, Washington DC
Sahinci A (1991) Geochemistry of natural waters (in Turkish). Reform Printing Office, Izmir, p 548
Saleh A, Al-Ruwaih F, Shehata M (1999) Hydrogeochemical processes operating within the main aquifers of Kuwait. J Arid Environ 42:195–209
Sarala C, Ravi Babu P (2012) Assessment of groundwater quality parameters in and around Jawaharnagar, Hyderabad. Int J Sci Res Publ 2:1–6
Sathish S, Elango L (2011) Groundwater quality and vulnerability mapping of an unconfined coastal aquifer. J Spat Hydrol 11:18–33
Sawyer GN, Cartly DL, Parkin GF (2003) Chemistry for environmental engineering and science, 5th edn. McGraw Hill, New York 152
Sujatha D, Reddy BR (2012) Quality Characterization of groundwater in the south-eastern part of the Ranga Reddy District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Geol 44:579–586
Todd DK (2001) Groundwater Hydrology. Wiley, Canada, pp 280–281
Wilcox LV (1955) Classification and use of irrigation waters USDA Circular 969, Washington, DC, United State of Africa
World health organisation (WHO) (2004) Fluoride in drinking-water, background document for development of WHO guidelines for drinking water quality 17
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the University of Grants Commission with Centre with Potential for Excellence in Environmental Sciences (Grant no. F.No.1-9/2002 (NS/PE)) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jagadeshan, G., Elango, L. Suitability of Fluoride-Contaminated Groundwater for Various Purposes in a Part of Vaniyar River Basin, Dharmapuri District, Tamil Nadu. Water Qual Expo Health 7, 557–566 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-015-0172-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-015-0172-8