Abstract
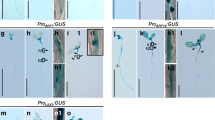
Plant growth-stimulating hormones brassinosteroids (BRs) function via interactions with other hormones. However, the mechanism of these interactions remains to be elucidated. The unique phenotypes of brassinosteroid insensitive2/dwarf12-D (bin2/dwf12-D) mutants, such as twisted inflorescences and leaves, suggested that BIN2, a negative regulator of BR signaling, may be involved in auxin signaling. Furthermore, previously, we showed that auxin stimulates DWF4 expression. To determine the possible role of BIN2/DWF12 in Auxin signaling, we measured DWARF4pro:GUS activity through both GUS histochemical staining and in vivo GUS assay. We found that the GUS activity in the bin2/dwarf12-1D background dramatically increased relative to control. In addition, the number of lateral roots (LR) in bin2/dwf12-1D was greater than wild type, and the optimal concentration for auxin-mediated lateral root induction was lower in bin2/dwf12-1D; these findings suggest that BIN2 plays a positive role in auxin signaling. In contrast, ABA repressed both DWF4pro:GUS expression and lateral root development. However, the degree of repression was lower in bin2/dwf12-1D background, suggesting that BIN2 plays a role in ABA-mediated DWF4pro:GUS expression and subsequently in lateral root development, too. Therefore, it is likely that BIN2 plays a role of signal integrator for multiple hormones, such as BRs, auxin, and ABA.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao F, Shen J, Brady SR, Muday GK, Asami T, Yang Z (2004) Brassinosteroids interact with auxin to promote lateral root development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 134(4):1624–1631
Blazquez MA, Green R, Nilsson O, Sussman MR, Weigel D (1998) Gibberellins promote flowering of Arabidopsis by activating the LEAFY promoter. Plant Cell 10(5):791–800
Choe S (2004) Brassinosteroid biosynthesis and metabolism. In: Davies PJ (ed) Plant hormones: biosynthesis, signal transduction, action! Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 156–178
Choe S, Dilkes BP, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Sakurai A, Feldmann KA (1998) The DWF4 gene of Arabidopsis encodes a cytochrome P450 that mediates multiple 22α-hydroxylation steps in brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Plant Cell 10(2):231–243
Choe S, Dilkes BP, Gregory BD, Ross AS, Yuan H, Noguchi T, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Tanaka A, Yoshida S, Tax FE, Feldmann KA (1999a) The Arabidopsis dwarf1 mutant is defective in the conversion of 24-methylenecholesterol to campesterol in brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 119(3):897–907
Choe S, Noguchi T, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Tissier CP, Gregory BD, Ross AS, Tanaka A, Yoshida S, Tax FE, Feldmann KA (1999b) The Arabidopsis dwf7/ste1 mutant is defective in the delta7 sterol C-5 desaturation step leading to brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Plant Cell 11(2):207–221
Choe S, Tanaka A, Noguchi T, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Ross AS, Tax FE, Yoshida S, Feldmann KA (2000) Lesions in the sterol Δ7 reductase gene of Arabidopsis cause dwarfism due to a block in brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Plant J 21(5):431–443
Choe S, Schmitz RJ, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Lee MO, Yoshida S, Feldmann KA, Tax FE (2002) Arabidopsis brassinosteroid-insensitive dwarf12 mutants are semidominant and defective in a glycogen synthase kinase 3β-like kinase. Plant Physiol 130(3):1506–1515
Claisse G, Charrier B, Kreis M (2007) The Arabidopsis thaliana GSK3/Shaggy like kinase AtSK3-2 modulates floral cell expansion. Plant Mol Biol 64(1–2):113–124
Clouse SD, Sasse JM (1998) BRASSINOSTEROIDS: essential regulators of plant growth and development. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:427–451
Clouse SD, Langford M, McMorris TC (1996) A brassinosteroid-insensitive mutant in Arabidopsis thaliana exhibits multiple defects in growth and development. Plant Physiol 111(3):671–678
Forde JE, Dale TC (2007) Glycogen synthase kinase 3: a key regulator of cellular fate. Cell Mol Life Sci 64(15):1930–1944
Gampala SS, Kim TW, He JX, Tang W, Deng Z, Bai MY, Guan S, Lalonde S, Sun Y, Gendron JM, Chen H, Shibagaki N, Ferl RJ, Ehrhardt D, Chong K, Burlingame AL, Wang ZY (2007) An essential role for 14-3-3 proteins in brassinosteroid signal transduction in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 13(2):177–189
Gao Y, Wang S, Asami T, Chen JG (2008) Loss-of-function mutations in the Arabidopsis heterotrimeric G-protein alpha subunit enhance the developmental defects of brassinosteroid signaling and biosynthesis mutants. Plant Cell Physiol 49(7):1013–1024
Geisler M, Girin M, Brandt S, Vincenzetti V, Plaza S, Paris N, Kobae Y, Maeshima M, Billion K, Kolukisaoglu UH, Schulz B, Martinoia E (2004) Arabidopsis immunophilin-like TWD1 functionally interacts with vacuolar ABC transporters. Mol Biol Cell 15(7):3393–3405
He JX, Gendron JM, Sun Y, Gampala SS, Gendron N, Sun CQ, Wang ZY (2005) BZR1 is a transcriptional repressor with dual roles in brassinosteroid homeostasis and growth responses. Science 307(5715):1634–1638
Ibanes M, Fabregas N, Chory J, Cano-Delgado AI (2009) Brassinosteroid signaling and auxin transport are required to establish the periodic pattern of Arabidopsis shoot vascular bundles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(32):13630–13635
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6(13):3901–3907
Jonak C, Hirt H (2002) Glycogen synthase kinase 3/SHAGGY-like kinases in plants: an emerging family with novel functions. Trends Plant Sci 7(10):457–461
Jope RS, Johnson GV (2004) The glamour and gloom of glycogen synthase kinase-3. Trends Biochem Sci 29(2):95–102
Kim GT, Fujioka S, Kozuka T, Tax FE, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Tsukaya H (2005) CYP90C1 and CYP90D1 are involved in different steps in the brassinosteroid biosynthesis pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 41(5):710–721
Kim HB, Kwon M, Ryu H, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, An CS, Lee I, Hwang I, Choe S (2006) The regulation of DWARF4 expression is likely a critical mechanism in maintaining the homeostasis of bioactive brassinosteroids in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 140(2):548–557
Kim BK, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Tsujimoto M, Choe S (2008) Castasterone is a likely end product of brassinosteroid biosynthetic pathway in rice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 374(4):614–619
Kim TW, Guan S, Sun Y, Deng Z, Tang W, Shang JX, Burlingame AL, Wang ZY (2009a) Brassinosteroid signal transduction from cell-surface receptor kinases to nuclear transcription factors. Nat Cell Biol 11(10):1254–1260
Kim WY, Wang X, Wu Y, Doble BW, Patel S, Woodgett JR, Snider WD (2009b) GSK-3 is a master regulator of neural progenitor homeostasis. Nat Neurosci 12(11):1390–1397
Kim Y, Lee YI, Seo M, Kim SY, Lee JE, Youn HD, Kim YS, Juhnn YS (2009c) Calcineurin dephosphorylates glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta at serine-9 in neuroblast-derived cells. J Neurochem 111(2):344–354
Li J, Chory J (1997) A putative leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase involved in brassinosteroid signal transduction. Cell 90(5):929–938
Li J, Nam KH (2002) Regulation of brassinosteroid signaling by a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase. Science 295(5558):1299–1301
Li J, Nagpal P, Vitart V, McMorris TC, Chory J (1996) A role for brassinosteroids in light-dependent development of Arabidopsis. Science 272(5260):398–401
Li J, Nam KH, Vafeados D, Chory J (2001) BIN2, a new brassinosteroid-insensitive locus in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 127(1):14–22
Li J, Wen J, Lease KA, Doke JT, Tax FE, Walker JC (2002) BAK1, an Arabidopsis LRR receptor-like protein kinase, interacts with BRI1 and modulates brassinosteroid signaling. Cell 110(2):213–222
Meijer L, Flajolet M, Greengard P (2004) Pharmacological inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase 3. Trends Pharmacol Sci 25(9):471–480
Mora-Garcia S, Vert G, Yin Y, Cano-Delgado A, Cheong H, Chory J (2004) Nuclear protein phosphatases with Kelch-repeat domains modulate the response to brassinosteroids in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev 18(4):448–460
Nam KH, Li J (2002) BRI1/BAK1, a receptor kinase pair mediating brassinosteroid signaling. Cell 110(2):203–212
Nemhauser JL, Mockler TC, Chory J (2004) Interdependency of brassinosteroid and auxin signaling in Arabidopsis. PLoS Biol 2(9):E258
Noguchi T, Fujioka S, Choe S, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Yuan H, Feldmann KA, Tax FE (1999) Brassinosteroid-insensitive dwarf mutants of Arabidopsis accumulate brassinosteroids. Plant Physiol 121(3):743–752
Ohnishi T, Szatmari AM, Watanabe B, Fujita S, Bancos S, Koncz C, Lafos M, Shibata K, Yokota T, Sakata K, Szekeres M, Mizutani M (2006) C-23 hydroxylation by Arabidopsis CYP90C1 and CYP90D1 reveals a novel shortcut in brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Plant Cell 18(11):3275–3288
Peng P, Yan Z, Zhu Y, Li J (2008) Regulation of the Arabidopsis GSK3-like kinase BRASSINOSTEROID-INSENSITIVE 2 through proteasome-mediated protein degradation. Mol Plant 1(2):338–346
Perez-Perez JM, Ponce MR, Micol JL (2002) The UCU1 Arabidopsis gene encodes a SHAGGY/GSK3-like kinase required for cell expansion along the proximodistal axis. Dev Biol 242(2):161–173
Piao HL, Pih KT, Lim JH, Kang SG, Jin JB, Kim SH, Hwang I (1999) An Arabidopsis GSK3/shaggy-like gene that complements yeast salt stress-sensitive mutants is induced by NaCl and abscisic acid. Plant Physiol 119(4):1527–1534
Ryu H, Kim K, Cho H, Park J, Choe S, Hwang I (2007) Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of BZR1 mediated by phosphorylation is essential in Arabidopsis brassinosteroid signaling. Plant Cell 17:2749–2762
Stavang JA, Gallego-Bartolome J, Gomez MD, Yoshida S, Asami T, Olsen JE, Garcia-Martinez JL, Alabadi D, Blazquez MA (2009) Hormonal regulation of temperature-induced growth in Arabidopsis. Plant J 60(4):589–601
Steber CM, McCourt P (2001) A role for brassinosteroids in germination in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 125(2):763–769
Szekeres M, Nemeth K, Koncz-Kalman Z, Mathur J, Kauschmann A, Altmann T, Redei GP, Nagy F, Schell J, Koncz C (1996) Brassinosteroids rescue the deficiency of CYP90, a cytochrome P450, controlling cell elongation and de-etiolation in Arabidopsis. Cell 85(2):171–182
Tanaka K, Asami T, Yoshida S, Nakamura Y, Matsuo T, Okamoto S (2005) Brassinosteroid homeostasis in Arabidopsis is ensured by feedback expressions of multiple genes involved in its metabolism. Plant Physiol 138(2):1117–1125
Tang W, Kim TW, Oses-Prieto JA, Sun Y, Deng Z, Zhu S, Wang R, Burlingame AL, Wang ZY (2008) BSKs mediate signal transduction from the receptor kinase BRI1 in Arabidopsis. Science 321(5888):557–560
Vert G, Chory J (2006) Downstream nuclear events in brassinosteroid signalling. Nature 441(7089):96–100
Vert G, Walcher CL, Chory J, Nemhauser JL (2008) Integration of auxin and brassinosteroid pathways by Auxin Response Factor 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(28):9829–9834
Wang X, Chory J (2006) Brassinosteroids regulate dissociation of BKI1, a negative regulator of BRI1 signaling, from the plasma membrane. Science 313(5790):1118–1122
Wang ZY, Nakano T, Gendron J, He J, Chen M, Vafeados D, Yang Y, Fujioka S, Yoshida S, Asami T, Chory J (2002) Nuclear-localized BZR1 mediates brassinosteroid-induced growth and feedback suppression of brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Dev Cell 2(4):505–513
Xue LW, Du JB, Yang H, Xu F, Yuan S, Lin HH (2009) Brassinosteroids counteract abscisic acid in germination and growth of Arabidopsis. Z Naturforsch C 64(3–4):225–230
Yan Z, Zhao J, Peng P, Chihara RK, Li J (2009) BIN2 functions redundantly with other Arabidopsis GSK3-like kinases to regulate brassinosteroid signaling. Plant Physiol 150(2):710–721
Yoo MJ, Albert VA, Soltis PS, Soltis DE (2006) Phylogenetic diversification of glycogen synthase kinase 3/SHAGGY-like kinase genes in plants. BMC Plant Biol 6:3
Zhang S, Cai Z, Wang X (2009) The primary signaling outputs of brassinosteroids are regulated by abscisic acid signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(11):4543–4548
Acknowledgments
This research was supported, in part, by Technology Development Program (110033-5) for Agriculture and Forestry, Ministry for Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Republic of Korea, BK21 Research Fellowships (to P.M.), and Basic Science Research Program (2010-0012736) through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology. S.D.G.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maharjan, P.M., Schulz, B. & Choe, S. BIN2/DWF12 Antagonistically Transduces Brassinosteroid and Auxin Signals in the Roots of Arabidopsis . J. Plant Biol. 54, 126–134 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-010-9138-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-010-9138-3