Abstract
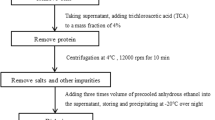
The purpose of this study was to screen for high-yield exopolysaccharide (EPS) producing lactic acid bacteria (LAB) from sugar beet molasses and to evaluate the production capacity of EPS using sugar beet molasses. A highly EPS-producing LAB strain LSBM1 isolated from sugar beet molasses was identified, and the fermentation conditions for EPS using sugar beet molasses as the substrate were optimized by the single-factor experiment and response surface methodology. Strain LSBM1 was identified as Leuconostoc suionicum based on morphological characteristics, and 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis. The optimal culture medium for EPS production was composed of 300 g/L beet molasses, 20.0 g/L yeast extract, 20.0 g/L K2HPO4·3H2O, 0.01 g/L MgSO4·7H2O, 0.01 g/L NaCl, 0.01 g/L CaCl2, 0.01 g/L MnSO4·H2O, 0.01 g/L FeSO4·7H2O, 0.01 g/L. The maximum EPS yield (31.78 g/L) was achieved under the optimized conditions of loading volume 200 mL/250 mL, inoculum size 2%, initial pH value 8.1, culture temperature of 37.59 °C, and culturing period 38.5 h. The in-vitro antioxidant activity showed that LSBM1 EPS had good scavenging activity against DPPH and ABTS radicals. Together, these results provide a LAB strain and the production conditions for obtaining high EPS yields using sugar beet molasses as substrate, and suggest that the harvested LAB-EPS might have potential applications as functional ingredients in the food industry.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aita, G.M., and H.W. Young. 2022. EPS-producing microorganisms from Louisiana’s crusher juice and the effect of processing conditions on EPS production. Sugar Tech 25 (2): 482–490. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12355-022-01235-Y.
Ale, E.C., V.A. Batistela, G.C. Olivar, J.B. Ferrado, and A.G. Binetti. 2020. Statistical optimisation of the exopolysaccharide production by Lactobacillus fermentum Lf2 and analysis of its chemical composition. International Journal of Dairy Technology 73 (1): 76–87. https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-0307.12639.
Dou, J., Y. Meng, L. Liu, J. Li, D. Ren, and Y. Guo. 2015. Purification, characterization and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from thinned-young apple. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 72: 31–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.07.053.
Du, R., H. Xing, Y. Yang, H. Jiang, Z. Zhou, and Y. Han. 2017. Optimization, purification and structural characterization of a dextran produced by L. mesenteroides isolated from Chinese sauerkraut. Carbohydrate Polymers 174: 409–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.06.084.
El-Sayed, H.M. 2016. Isolation of fermentative microbial isolates from sugar cane and beet molasses and evaluation for enhanced production of bioethanol. Energy Sources, Part a. Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects 38 (15): 2117–2180. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2015.1030050.
Ertan, F., B. Keskinler, and A. Tanriseven. 2021. Exploration of Cupriavidus necator ATCC 25207 for the production of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) using acid treated beet molasses. Journal of Polymers and the Environment 29 (7): 2111–2125. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10924-020-02020-2.
Ge, Z., F. Azi, X. Bao, X. Yin, X. Feng, and M. Zhang. 2023. Optimization and characterization of exopolysaccharides from Leuconostoc citreum BH10 and its functional properties in vitro. Food Production, Processing and Nutrition 5: 23. https://doi.org/10.1186/S43014-023-00134-3.
Han, J., F. Hang, B. Guo, Z. Liu, C. You, and Z. Wu. 2014. Dextran synthesized by Leuconostoc mesenteroides BD1710 in tomato juice supplemented with sucrose. Carbohydrate Polymers 112: 556–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.06.035.
Kim, K., G. Lee, H.D. Thanh, J.H. Kim, M. Konkit, and S. Yoon. 2018. Exopolysaccharide from Lactobacillus plantarum LRCC5310 offers protection against rotavirus-induced diarrhea and regulates inflammatory response. Journal of Dairy Science 101 (7): 5702–5712. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2017-14151.
Korcz, E., and V. László. 2021. Exopolysaccharides from lactic acid bacteria: Techno-functional application in the food industry. Trends in Food Science and Technology 110: 375–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TIFS.2021.02.014.
Lee, S.C., S.M. Jeong, S.Y. Kim, H.R. Park, K.C. Nam, and D.U. Ahn. 2006. Effect of far-infrared radiation and heat treatment on the antioxidant activity of water extracts from peanut hulls. Food Chemistry 94 (4): 489–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.12.001.
Lin, L., J. Xie, S. Liu, M. Shen, W. Tang, and M. Xie. 2017. Polysaccharide from Mesona chinensis: Extraction optimization, physicochemical characterizations and antioxidant activities. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 99: 665–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.03.040.
Liu, Y., B. Zhang, S.A. Ibrahim, S.S. Gao, H. Yang, and W. Huang. 2016. Purification, characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Flammulina velutipes residue. Carbohydrate Polymers 145: 71–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.03.020.
Liu, Z., Z. Zhang, L. Qiu, F. Zhang, X. Xu, and H. Wei. 2017. Characterization and bioactivities of the exopolysaccharide from a probiotic strain of Lactobacillus plantarum WLPL04. Journal of Dairy Science 100 (9): 6895. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2016-11944.
Lynch, K.M., E. Zannini, A. Coffey, and E.K. Arendt. 2018. Lactic acid bacteria exopolysaccharides in foods and beverages: Isolation, properties, characterization, and health benefits. Annual Review of Food Science and Technology 9 (1): 155–176. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-food-030117-012537.
Manfredini, M., and C. Cavani. 1980. Distillery effluents as animal feed: The use of condensed beet molasses stillage (CBMS) in broiler feeding. Animal Feed Science and Technology 5 (3): 233–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-8401(80)90033-4.
Mironescu, M., and I.D. Mironescu. 2011. Rheological behavior of a novel microbial polysaccharide. Romanian Biotechnological Letters 16 (2): 6105–6114.
Öz, Y.E., and M. Kalender. 2022. A novel static cultivation of bacterial cellulose production from sugar beet molasses: Series static culture (SSC) system. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 225: 1306–1314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.11.190.
Sharma, S.N., K. Patel, U. Lata, M. Singh, R.S. Krishania, and S.P. Singh. Sangwan. 2016. A novel approach of integrated bioprocessing of cane molasses for production of prebiotic and functional bioproducts. Bioresource Technology 219: 311–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.07.131.
Shukla, S., and A. Goyal. 2011. Optimization of fermentation medium for enhanced glucan sucrase and glucan production from Weissella confusa. Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology 54: 1117–1124. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-89132011000600006.
Sun, L., Y. Yang, P. Lei, S. Li, H. Xu, R. Wang, Y. Qiu, and Z. Wen. 2021. Structure characterization, antioxidant and emulsifying capacities of exopolysaccharide derived from Pantoea alhagi NX-11. Carbohydrate Polymers 261: 117872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117872.
Tang, W.D., M. Wang, W. Han, X. Chen, X. Jiang, M. Zhang, Q. Wu, and J. Wei. 2017. Structural characterization and antioxidant property of released exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus SRFM-1. Carbohydrate Polymers 173: 654–664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.06.039.
Tho, N.P., L.T. Son, N.T. Tho, B.D. Cuong, H.P. Toan, and H. Khanh. 2021. Enhancing the production and monosaccharide composition of exopolysaccharides of Lactobacillus plantarum VAL6 by applying thermal stress and increased carbon dioxide concentration. Microbiology 90 (4): 527–537. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261721040147.
Wang, X., C. Shao, L. Liu, X. Guo, Y. Xu, and L. Xin. 2017. Optimization, partial characterization and antioxidant activity of an exopolysaccharide from Lactobacillus plantarum KX041. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 103: 1173–1184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.05.118.
Wang, X., M. Xu, D. Xu, K. Ma, C. Zhang, G. Wang, and W. Li. 2022. Structural and prebiotic activity analysis of the polysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus helveticus SNA12. Carbohydrate Polymers 296: 119971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119971.
Wu, J.Y., Y.H. Zhang, L. Ye, and C.L. Wang. 2021. The anti-cancer effects and mechanisms of LAB exopolysaccharides in vitro: A review. Carbohydrate Polymers 253 (5): 117308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117308.
Xing, H., R. Du, F. Zhao, and Z. Zhou. 2018. Optimization, chain conformation and characterization of exopolysaccharide isolated from Leuconostoc mesenteroides DRP105. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 112: 1208–1216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.02.068.
Yang, X., Y. Ren, and L. Zhang. 2021. Structural characteristics and antioxidant properties of exopolysaccharides isolated from soybean protein gel induced by lactic acid bacteria. LWT-Food Science and Technology 150: 111811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111811.
Yoon, E.J., S.H. Yoo, J. Cha, and H.G. Lee. 2004. Effect of levan’s branching structure on antitumor activity. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 34 (3): 191–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2004.04.001.
Zeng, C., G. Ye, G. Li, H. Cao, Z. Wang, and S. Ji. 2022. RID serve as a more appropriate measure than phenol sulfuric acid method for natural water-soluble polysaccharides quantification. Carbohydrate Polymers 278 (2): 118928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118928.
Zhang, Q., J. Wang, Q. Sun, S.M. Zhang, X.Y. Sun, C.Y. Li, and J. Tang. 2021. Characterization and antioxidant activity of released exopolysaccharide from a potential probiotic Leuconostoc mesenteroides LM187. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 31 (8): 1144–1153. https://doi.org/10.4014/JMB.2103.03055.
Zhou, Q., F. Feng, Y. Yang, and F. Yan. 2018. Characterization of a dextran produced by Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides XG5 from homemade wine. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 107: 2234–2241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.10.098.
Zhu, Y., X. Wang, W. Pan, X. Shen, Y. He, and H. Yin. 2019. Exopolysaccharides produced by yogurt-texture improving Lactobacillus plantarum RS20D and the immunoregulatory activity. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 121: 342–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.09.201.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Students’ Research Interesting Training Support (2023243) by Sichuan Agricultural University, China.
Funding
This research was supported by the Students’ Research Interesting Training Support (2023243) by Sichuan Agricultural University, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Long, X., Hou, X., Li, S. et al. Fermentation Optimization and In-Vitro Antioxidant Activity of Exopolysaccharides Produced by Leuconostoc suionicum LSBM1 Using Sugar Beet Molasses. Sugar Tech (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-024-01396-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-024-01396-y