Abstract
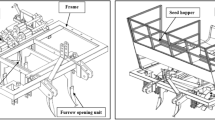
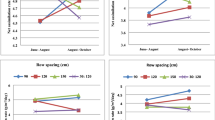
Sugarcane bud chip planting is the latest technique of sugarcane planting, wherein the bud along with a portion of the nodal region is chipped off and planted in protray with FYM soil and sand. Studies on mechanisation of the planting of settlings from sugarcane buds raised in portrays were carried out at Central Institute of Agricultural Engineering—Regional Centre, Coimbatore and Sugarcane Breeding Institute, Coimbatore and a tractor mounted two row mechanical planter for settlings raised from sugarcane bud chips was developed. It consists of mainframe which can be attached to standard three-point hitch arrangement of a 35 hp tractor. The metering mechanism, operator’s seat, furrow openers, soil openers and furrow closers are mounted on the main frame with necessary supports. The optimum speed of operation was standardized as 1.4 km/h by experimentation where the missing percentage was 2.33 %. The field capacity of the equipment was 0.15 ha/h. The biometric parameters viz., diameter of the cane, cane height, single cane weight, juice content and yield of the mechanically planted sugarcane settlings were on par with the manually planted sugarcane settlings. The juice quality of sugarcane from mechanically planted settling in terms of brix, CCS, sucrose and purity was at par with sugarcane from manual planting of settlings at the time of harvest. Cost economic analysis of planting with mechanical planter showed 40 and 85 %, saving in cost and labour, respectively over manual bud chip settling planting.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonynous (1983). Regional network for agricultural machinery. RNAM. Test codes and procedures for farm machinery. Technical series no.12, 219. Bangkok, Thailand.
Annamalai, S.J.K., N. Vijayan Nair, N. Rajendra Prasad, and Ravindra Naik. 2011. Final project report on development of bud chipping machine for and mechanical planter for seedlings in polybags raised from sugarcane bud chips, 125. Nabibagh, Bhopal, India: Central Institute of Agricultural Engineering.
Chaudhuri, D., V.V. Singh, and A.K. Dubey. 2002. Refinement and adoption of mechanical vegetable transplanter for Indian condition. Agricultural Engineering Today 26(5–6): 11–20.
Chen, J.C.P., and C.C. Chou. 1993. Cane sugar handbook: A manual for cane sugar manufacturers and their chemist, 12th ed., 120. New York: Wiley.
Dooley, J.H. 1983. Transplanters for forest nursery. Transactions of ASAE 26(6): 1661–1664.
Juric, T., R. Emert, and L. Sumanovae. 1997. An analysis of work by planter with two elastic disc for tobacco planting. Poljoprivreda 1(3): 19–24.
Kavitha, R. 2005. Mechanical transplanting of vegetable crops as influenced by soil, crop and operational parameters, 256. Ph.D thesis, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India.
Kavitha, R., and V.M. Duraisamy. 2007. Development and evaluation of semi automatic vegetable transplanter for plug seedlings. In Proceedings of the international agricultural engineering conference, Bangkok, Thailand, 3–6 December 2007, ed. V.M. Salokhe, H.P.W. Jayasuriya and P. Soni, 236. ISBN. 978-974-8257-48-8.
Ladeinde, M.A., S.R. Verma, and V. Baksher. 1995. Performance of semi automatic tractor mounted cassarh planter. Agricultural Mechanization in Asia, Africa and Latin America 26(1): 27–30.
Satpathy, S.K. 2003. Effect of selected parameters on the performance of a vegetable transplanter for different crops, 163. Unpublished M.Tech thesis, Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana, Punjab, India.
Splinter, W.E., and C.W. Suggs. 1959. Mechanical transplanting of bright-leaf tobacco. Part I. The effect of transplant size and speed on operational skips. Tobacco Science 3: 154–157.
Srivastava, A.K., C.E. Goering, and R.P. Rochrbach. 1994. Engineering principles of agricultural machines, 601. ASAE textbook no. 6. St. Joseph Charter Township: American Society of Agricultural Engineers, (Agricultural Engineering Handbook series).
Stevens, G.N. 1982. Equipment testing and evaluation, 154. Wrest Park, Silsoe, Bedford, England: National Institute of Agricultural Engineering.
Suggs, C.W. 1979. Development of a transplanter with multiple loading stations. Transactions of ASAE 22(2):260–263.
Tsuga, K. 1999. Development of fully automatic vegetable transplanter. Japan Agricultural Research Quarterly 34(1): 21–28.
Vijayan Nair, N. 2012. Sugarcane agriculture in India—100 years and beyond, 53. In Abstracts of background papers at SBI-Indian Sugar Industry, National Interactive workshop, June 26–27, 2012. Coimbatore, India: Sugarcane Breeding Institute.
Way, T.R., and M.E. Wright. 1987. Human transplanter in mechanical transplanting of sweet potato. Transactions of ASAE 30(2): 317–323.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naik, R., Annamalai, S.J.K., Nair, N.V. et al. Studies on Mechanisation of Planting of Sugarcane Bud Chip Settlings Raised in Protrays. Sugar Tech 15, 27–35 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-012-0187-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-012-0187-4