Abstract
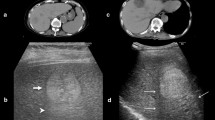
The caudate lobe of the liver is located deep within the body and surrounded by major blood vessels, such as inferior vena cava, portal vein, and hepatic veins. Thus, percutaneous biopsy is technically challenging. Herein, we report seven patients with focal liver lesions in the caudate lobe who underwent endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition (EUS-TA). Their median age was 56 (25–79) years, consisting five males and two females, and the median lesion size was 44 (19–77) mm. Transgastric EUS-TA was performed in all patients. The needles used were 22G and 25G in six patients and one patient, and the median procedure time was 18 (13–30) min. In all patients, adequate specimens were collected, and pathological diagnosis was possible (three intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, two metastatic tumors from pancreatic cancer, one hepatocellular carcinoma, and one focal nodular hyperplasia). No adverse events associated with the procedure were observed. EUS-TA can be the first choice for tissue acquisition of the caudate lobe lesions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buscarini L, Fornari F, Bolondi L, et al. Ultrasound-guided fine-needle biopsy of focal liver lesions: techniques, diagnostic accuracy and complications. A retrospective study on 2091 biopsies. J Hepatol. 1990; 11: 344–48.
Takano Y, Noda J, Yamawaki M, et al. Comparative study of an ultrasound-guided percutaneous biopsy and endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for liver tumors. Intern Med. 2021;60:1657–64.
Cotton PB, Eisen GM, Aabakken L, et al. A lexicon for endoscopic adverse events: report of an ASGE workshop. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;71:446–54.
Nguyen P, Feng JC, Chang KJ. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration (FNA) of liver lesions. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999;50:357–61.
tenBerge J, Hoffman BJ, Hawes RH, et al. EUS-guided fine needle aspiration of the liver: indications, yield, and safety based on an international survey of 167 cases. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002;55:859–62.
DeWitt J, LeBlanc J, McHenry L, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration cytology of solid liver lesions: a large single-center experience. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:1976–81.
Hollerbach S, Willert J, Topalidis T, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy of liver lesions: histological and cytological assessment. Endoscopy. 2003;35:743–9.
Lee YN, Moon JH, Kim HK, et al. Usefulness of endoscopic ultrasound-guided sampling using core biopsy needle as a percutaneous biopsy rescue for diagnosis of solid liver mass: combined histological-cytological analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;30:1161–6.
Oh D, Seo DW, Hong SM, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration can target right liver mass. Endosc Ultrasound. 2017;6:109–15.
Villavicencio Kim J, Dharan M. EUS diagnosis of hepatic angiomyolipoma. VideoGIE. 2023;8:175–7.
Ang TL, Wang LM, Kwek ABE, et al. Hepatic caudate lobe neuroendocrine carcinoma diagnosed by EUS-guided core biopsy (with video). Endosc Ultrasound. 2018;7:286–7.
Liu B, Long J, Wang W, et al. Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in the caudate lobe: US-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation combined with ethanol ablation. Clin Radiol. 2018;73:647–56.
Ishikawa K, Ishiwatari H, Sasaki K, et al. Optimization of endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue sample acquisition for commercially available comprehensive genome profiling. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;38:1794–801.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Takano, Y., Yamawaki, M., Noda, J. et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition for focal liver lesions in the caudate lobe: a report of seven cases. Clin J Gastroenterol 17, 334–337 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-023-01906-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-023-01906-7