Abstract
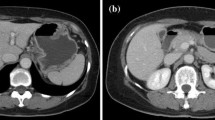
Little is known about the pathophysiology of liver complication seen in drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome (DIHS). We describe herein a 32-year-old Japanese man with DIHS due to salazosulfapyridine (SASP) associated with reactivation of human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) presenting with severe acute hepatic injury. The patient, with a 1-year history of ulcerative colitis (UC), presented with high fever and abnormally elevated liver enzymes. Six weeks prior to his symptoms, prednisolone (PSL) and SASP had been started because of UC aggravation. Besides fever and liver dysfunction, the appearance of atypical lymphocytes together with eosinophils and generalized erythematous maculopapular skin rash developed sequentially, and a diagnosis of DIHS was established. Despite cessation of SASP and increased dose of PSL, his initial abnormalities continued, and biphasic second alanine aminotransferase (ALT) flare with deep jaundice worsened. Based on the significant increase in the titer of HHV-6 IgG antibodies at the second peak of ALT level without HHV-6 IgM antibody elevation, strongly suggesting reactivation of the virus, HHV-6 was first considered to directly contribute to the deterioration of liver function. However, extensive histological analysis of the liver led to the realization that the cause of the DIHS liver injury was essentially drug-related hepatotoxicity induced by SASP, causing wide-ranging damage to both the hepatocytes and cholangiocytes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roujeau JC, Stern RS. Severe adverse cutaneous reactions to drugs. N Engl J Med. 1994;331:1272–85.
Vittorio CC, Muglia JJ. Anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome. Arch Intern Med. 1995;155:2285–90.
Shiohara T, Inaoka M, Kano Y. Drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome (DIHS): a reaction induced by a complex interplay among herpesviruses and antiviral and antidrug immune responses. Allergol Int. 2006;55:1–8.
Prussick R, Shear NH. Dapsone hypersensitivity syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:346–9.
Suzuki Y, Inagi R, Aono T, Yamanishi K, Shiohara T. Human herpesvirus 6 infection as a risk factor for the development of severe drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 1998;134:1108–12.
Tohyama M, Yahata Y, Yasukawa M, Inagi R, Urano Y, Yamanishi K, et al. Severe hypersensitivity syndrome due to sulfasalazine associated with reactivation of human herpesvirus 6. Arch Dermatol. 1998;134:1113–7.
Yamanishi K, Okuno T, Shiraki K, Takahashi M, Kondo T, Asano Y, et al. Identification of human herpesvirus 6 as a causal agent for exanthem subitum. Lancet. 1988;1:1065–7.
Clark DA, Griffiths PD. Human herpesvirus 6: relevance of infection in the immunocompromised host. Br J Haematol. 2003;120:384–95.
Hashimoto K, Yasukawa M, Tohyama M. Human herpesvirus 6 and drug allergy. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;3:255–60.
Takikawa H, Onji M. A proposal of the diagnostic scale of drug-induced liver injury. Hepatol Res. 2005;32:250–1.
Masaki T, Fukunaga A, Tohyama M, Koda Y, Okuda S, Maeda N, et al. Human herpesvirus 6 encephalitis in allopurinol-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. Acta Derm Venereol. 2003;83:128–31.
Ozaki Y, Tajiri H, Tanaka-Taya K, Mushiake S, Kimoto A, Yamanishi K, et al. Frequent detection of the human herpesvirus 6-specific genomes in the livers of children with various liver diseases. J Clin Microbiol. 2001;39:2173–7.
Harma M, Hockerstedt K, Lautenschlager I. Human herpesvirus 6 and acute liver failure. Transplantation. 2003;76:536–9.
Cacheux W, Carbonell N, Rosmorduc O, Wendum D, Paye F, Poupon R, et al. HHV-6-related acute liver failure in two immunocompetent adults: favourable outcome after liver transplantation and/or ganciclovir therapy. J Intern Med. 2005;258:573–8.
Kuribayashi K, Matsunaga T, Iyama S, Takada K, Sato T, Murase K, et al. Human herpesvirus 6 hepatitis associated with cyclosporine—a encephalitis after bone marrow transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia. Intern Med. 2006;45:475–8.
Kunisaki Y, Goto H, Kitagawa K, Nagano M. Salazosulfapyridine induced hypersensitivity syndrome associated with reactivation of human herpesvirus 6. Intern Med. 2003;42:203–7.
Nishimura T, Obata H, Fujino H, Sonoda A, Sakamoto K, Mizuno C, et al. Case of ulcerative colitis associated with drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome (DIHS) by salazosulfapyridine. Nippon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2007;104:36–41.
Michel F, Navellou JC, Ferraud D, Toussirot E, Wendling D. DRESS syndrome in a patient on sulfasalazine for rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2005;72:82–5.
Pirmohamed M, Arbuckle JB, Bowman CE, Brunner M, Burns DK, Delrieu O, et al. Investigation into the multidimensional genetic basis of drug-induced Stevens–Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Pharmacogenomics. 2007;8:1661–91.
Sotolongo RP, Neefe LI, Rudzki C, Ishak KG. Hypersensitivity reaction to sulfasalazine with severe hepatotoxicity. Gastroenterology. 1978;75:95–9.
Ribe J, Benkov KJ, Thung SN, Shen SC, LeLeiko NS. Fatal massive hepatic necrosis: a probable hypersensitivity reaction to sulfasalazine. Am J Gastroenterol. 1986;81:205–8.
Marinos G, Riley J, Painter DM, McCaughan GW. Sulfasalazine-induced fulminant hepatic failure. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1992;14:132–5.
Rubin R. Sulfasalazine-induced fulminant hepatic failure and necrotizing pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994;89:789–91.
Kano Y, Inaoka M, Shiohara T. Association between anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome and human herpesvirus 6 reactivation and hypogammaglobulinemia. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:183–8.
Nakashima H, Yamane K, Ihn H, Nakamura K, Watanabe R, Kuwano Y, et al. Drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome associated with transient hypogammaglobulinaemia and increase in serum IgE level. Dermatology. 2005;210:349–52.
Imai F, Suzuki T, Ishibashi T, Dohi Y. Effect of sulfasalazine on B cells. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1991;9:259–64.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miura, H., Nakano, M., Yoshimura, N. et al. Drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome associated with reactivation of human herpesvirus 6 presenting with severe hepatic injury. Clin J Gastroenterol 1, 127–132 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-008-0021-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-008-0021-4