Abstract
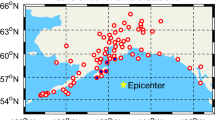
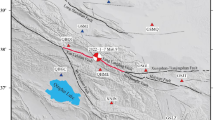
GPS technique has been widely used for monitoring large scale earthquake and long baseline approach is required if one is interested in relative positioning mode. Therefore, a proper modeling on the atmospheric effects should be performed because those effects are not fully removed in the long baseline case. In this study, GPS data is processed to monitor the displacement due to large scale earthquake based on the position-velocity-acceleration (PVA) model. PVA model is efficient in that both velocity and acceleration information, which can also be used for creating peak ground velocity and acceleration maps, are obtained simultaneously. The ionospheric disturbances due to crustal movement can also be monitored using the model. The algorithms are successfully applied to (Mw 9.0) Tohoku earthquake event occurred on March, 11, 2011 and the results show good agreements with those from the previous studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avallone, A., Marzario, M., Cirella, A., Piatanesi, A., Rovelli, A., Alessandro, C.D., D’Anastasio, E., D’Agostino, N., Giuliani, R., and Mattone, M., 2011, Very high rate (10 Hz) GPS seismology for moderatemagnitude earthquake: the case of the Mw 6.3 L’Aquila (central Italy) event. Journal of Geophysical Research, 116. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JB007834
Bovenga, F., Nitti, D.O., Ganas, A., and Chousianitis, K., 2011, Co-seismic deformation due to the Tohoku-Oki earthquake measured by ENVISAT-ASAR data and GPS. Proceedings of the Fringe 2011, Frascati, Sep. 19–23, p. 37.
Branzanti, M., Colosimo, G., Crespi, M., and Mazzoni, A., 2013, GPS near-real-time coseismic displacements for the great Tohoku-oki earthquake. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 10. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2012.2207704
Chen, C.H., Saito, A., Lin, C.H., Liu, J.Y., Tsai, H.F., Tsugawa, T., Otsuka, Y., Nishioka, M., and Matsumura, M., 2011, Long-distance propagation of ionospheric disturbance generated by the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake. Earth Planets and Space, 63. https://doi.org/10.5047/eps.2011.06.026
Daud, M.E., Sagiya, T., Kimata, F., and Kato, T., 2008, Long-baseline quasi-real time kinematic GPS data analysis for early tsunami warning. Earth Planets and Space, 60, 1191–1195.
Ducic, V., Artru, J., and Lognonné, P., 2003, Ionospheric remote sensing of the Denali earthquake Rayleigh surface waves. Geophysical Research Letters, 30. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003GL017812
Ge, L., Han, S., Rizos, C., Ishikawa, T., Hoshiba, M., Yoshida, Y., Izawa, M., Hashimon, N., and Himori, S., 2000, GPS seismometers with up to 20 Hz sampling rate. Earth Planets and Space, 52, 881–884.
Gelb, A., 1974, Applied Optimal Estimation. The M.I.T. Press, London, 374 p.
Goad, C.C. and Yang, M.A., 1997, New approach to precision airborne GPS positioning for photogrammetry. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 63, 1067–1077.
Grejner-Brzezinska, D.A., 1995, Analysis of GPS data processing techniques: in search of optimized strategy of orbit and Earth rotation parameter recovery. Ph.D. Thesis, The Ohio State University, Columbus, 204 p.
Hong, C.K., Park, C.H., Han, J., and Kwon, J.H., 2015, Medium to long range kinematic GPS positioning with position-velocity-acceleration model using multiple reference stations. Sensors, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150716895
Irwan, M., Kimata, F., Hirahara, K., Sagiya, T., and Yamagiwa, A., 2004, Measuring ground deformations with 1-Hz GPS data: the 2003 Tokachi-oki earthquake (preliminary report). Earth Planets and Space, 56, 389–393.
Kim, M.G. and Park, J.K., 2012, Monitoring the crustal movement before and after the earthquake by precise point positioning–Focused on 2011 Tohoku Earthquake. Journal of the Korean Society of Surveying, Geodesy, Photogrammetry and Cartography, 30, 477–484. (in Korean with English abstract)
Kouba, J. and Héroux, P., 2001, Precise point positioning using IGS orbit and clock products. GPS Solutions, 5, 12–28.
Larson, K.M., 2009, GPS seismology. Journal of Geodesy, 83, 227–233.
Larson, K.M., Bodin, P., and Gomberg, J., 2003, Using 1 Hz GPS data to measure deformations caused by the Denali Fault Earthquake. Science, 300, 1421–1424.
Li, X., Ge, M., Zhang, Y., Wang, R., Xu, P., Wickert, J., and Schuh, H., 2013, New approach for earthquake/tsunami monitoring using dense GPS networks. Scientific Reports, 3. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep02682
Liu, J., Tsai, H.F., Lin, C.H., Kamogawa, M., Chen, Y.I., Lin, C.H., Huang, B.S., Yu, S.B., and Yeh, Y.H., 2010, Coseismic ionospheric disturbances triggered by the Chi-Chi earthquake. Journal of Geophysical Research, 115. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JA014943.
Nikolaidis, R.M., Bock, Y., De Jonge, P.J., Shearer, P., Agnew, D.C., and van Domselaar, M., 2001, Seismic wave observations with the global positioning system. Journal of Geophysical Research, 106, 21897–21916.
Ohta, Y., Meilano, I., Kimata, F., and Hirahara, K., 2006, Large surface wave of the 2004 Sumatra-Andaman earthquake captured by the very long baseline kinematic analysis of 1-Hz GPS data. Earth Planets and Space, 58, 153–157.
Saastamoinen, J., 1972, Atmospheric correction for the troposphere and stratosphere in radio ranging satellites. The Use of Artificial Satellites for Geodesy. Geophysics Monograph Service, 15, 247–251.
Schüler, T., 2001, On ground-based GPS tropospheric delay estimation. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität der Bundeswehr München, Neubiberg, 364 p.
Tsugawa, T., Saito, A., Otsuka, Y., Nishioka, M., Maruyama, T., Kato, H., Nagatsuma, T., and Murata, K.T., 2011, Ionospheric disturbances detected by GPS total electron content observation after the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake. Earth Planets and Space, 63. https://doi.org/10.5047/eps.2011.06.035
Wu, Y.M., Shin, T.C., and Chang, C.H., 2001, Near real-time mapping of peak ground acceleration and peak ground velocity following a strong earthquake. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 91, 1218–1228.
Yang, M., Tang, C.H., and Yu, T.T., 2000, Development and assessment of a medium-range real-time kinematic GPS algorithm using an ionospheric information filter. Earth Planets and Space, 52, 783–788.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Korea Meteorological Administration Research and Development Program under Grant KMI2017-9060.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, CK., Lee, J. & Kwon, J.H. Monitoring of large scale earthquake using long-baseline based position-velocity-acceleration GPS model. Geosci J 23, 661–667 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-018-0068-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-018-0068-2