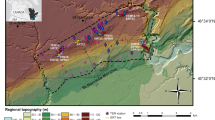
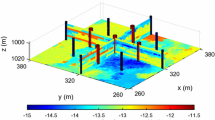
Abstract
In this paper, we argue the need for high-resolution characterization of the subsurface and discuss difficulties of traditional characterization approaches to meet this need. Necessary and sufficient conditions are then presented for well-posedness of groundwater inverse problems associated with identifying spatially distributed parameters. Non-uniqueness and large uncertainty in model calibration are subsequently attributed to difficulties in collecting information to meet these conditions. Using an example, we show that a tomographic survey can make problems of identification of spatially distributed parameters better posed. We subsequently present some recent advances in hydrologic/geophysical characterization of the subsurface using information fusion based on tomographic survey concepts. This paper includes hydraulic and electrical resistivity tomographic surveys as well as fusion of hydraulic and resistivity tomography and fusion of hydraulic and tracer tomography.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bear, J., 1972, Dynamics of fluids in porous media. Dover, NY, 764 p.
Beckie, R. and Harvey, C.F., 2002, What does a slug test measure: An investigation of instrument response and the effects of heterogeneity. Water Resour. Res., 38, 1290, doi:10.1029/2001WR001072.
Bevan, M.J., Endres, A.L., Rudolph, D.L., and Parkin, G., 2005, A field scale study of pumping-induced drainage and recovery in an unconfined aquifer. Journal of Hydrology, 315, 52–70.
Bevan, M.J., Endres, A.L., Rudolph, D.L., and Parkin, G., 2003, The noninvasive characterization of pumping induced dewatering using ground penetrating radar. Journal of Hydrology, 281, 55–69.
Binley, A., Winship, P., Middleton, R., Pokar, M., and West, J., 2001, High-resolution characterization of vadose zone dynamics using cross-borehole radar. Water Resour. Res., 37, doi:10.1029/2000WR000089.
Binley, A., Henry-Poulter, S., and Shaw, B., 1996, Examination of solute transport in an undisturbed soil column using electrical resistance tomography. Water Resour. Res., 32, 763–770, 10.1029/95WR02995.
Bohling, G.C., Zhan, X., Butler Jr., J.J., and Zheng, L., 2002, Steady shape analysis of tomographic pumping tests for characterization of aquifer heterogeneities. Water Resour. Res., 38, 1324, doi:10.1029/2001WR001176.
Brauchler, R., Liedl, R., and Dietrich P., 2003, A travel time based hydraulic tomographic approach. Water Resour. Res., 39, 1370, doi:10.1029/2003WR002262.
Bredehoeft, J.D., 2003, From models to performance assessment: the conceptualization problem, Ground Water, 41, 571.
Cirpka, O.A. and Kitanidis, P.K., 2001, Sensitivity of temporal moments calculated by the adjoint-state method and joint inversing of head and tracer data. Adv. Water Resour. 24, 89–103.
Daily, W., Ramirez, A., LaBrecque, D., and Nitao, J., 1992, Electrical resistivity tomography of vadose water movement. Water Resour. Res., 28, 1429–1442.
Day-Lewis, F.D. and Lane, J.W. Jr., 2004, Assessing the Resolution-Dependent Utility of Tomograms for Geostatistics. Geophysical Research Letters, 31, L07503, doi:10.1029/2004GL019617.
Day-Lewis, F.D., Lane, J.W. Jr., Harris, J.M., and Gorelick, S.M., 2003, Time-Lapse Imaging of Saline Tracer Tests Using Cross-Borehole Radar Tomography. Water Resources Research, 39, 1290, doi:10.1029/2002WR001722.
Day-Lewis, F.D., Singha, K., and Binley, A.M., 2005, Applying Petrophysical Models to Radar Traveltime and Electrical Resistivity Tomograms: Resolution-Dependent Limitations. J. of Geophysical Research, 110, B08206, doi:10.1029/2004JB005369.
Day-Lewis, F.D., Lane, J.W. Jr., and Gorelick, S.M., 2004, Combined Interpretation of Radar, Hydraulic and Tracer Data from a Fractured-Rock Aquifer. Hydrogeology Journal, 14, 1–14, doi: 10.1007/s10040-004-0372-y.
Domenico, P.A. and Schwartz, F.W., 1990, Physical and chemical hydrogeology. John Wiley and Son, 824 p.
Ellis, R.G. and Oldenburg, S.W., 1994, The pole-pole 3-D dc resistivity inverse problem: a conjugate gradient approach. Geophysical Journal International 119, 187–194.
Endres, A.L., Clement, W.P., and Rudolph D.L., 2000, Ground penetrating radar imaging of an aquifer during a pumping test. Ground Water, 38, 566–576.
Englert, A., Zhu, J., Kemna, A., Vanderborght, J., Vereecken, H., and Yeh, T.-C.J., 2005, Potential of electrical resistivity tomography characterizing transport processes in groundwater-synthetic case studies. AGU, H37.
Gottlieb, J. and Dietrich, P., 1995, Identification of the permeability distribution in soil by hydraulic tomography. Inverse Probl., 11, 353–360.
Harter, T. and Yeh, T.-C.J., 1996 Conditional stochastic analysis of solute transport in heterogeneous, variably saturated soils. Water Resour. Res., 32, 1585–1596.
Harvey, C.F. and Gorelick, S.M., 1995a, Mapping hydraulic conductivity: sequential conditioning with measurements of solute arrival time, hydraulic head, and local conductivity. Water Resour. Res., 31, 1615–1626.
Harvey, C.F. and Gorelick, S.M., 1995b, Temporal moment-generating equations: Modeling transport and mass transfer in heterogeneous aquifers. Water Resour. Res., 31, 1895–1912, 10.1029/95WR01231.
Illman, W.A., Liu, X., and Craig, A., 2007, Steady-state hydraulic tomography in a laboratory aquifer with deterministic heterogeneity: Multi-method and multiscale validation of K tomograms. J. of Hydrology, 341, 222–234.
Kemna, A., Vanderborght, J., Kulessa, B., and Vereecken, H., 2002, Imaging and characterization of subsurface solute transport using electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) and equivalent transport models. J. of Hydrology, 267, 125–146.
Kitanidis, P.K., 1995, Quasi-linear geostatistical theory for inversing. Water Resour. Res., 31, 2411–2420.
Konikow, L. and Bredehoeft, J.D., 1992, Groundwater models cannot be validated. Advances in Water Resources, 15, 75–83.
Li W., Nowak, W., and Cirpka, O.A., 2005, Geostatistical inverse modeling of transient pumping tests using temporal moments of drawdown. Water Resour. Res., 41, W08403, doi:10.1029/2004WR003874.
Li, B. and Yeh, T.-C.J., 1999, Cokriging estimation of the conductivity field under variably saturated flow conditions. Water Resour. Res., 35, 3663–3674.
Li, Y. and Oldenburg, D.W., 1994, Inversion of 3D dc-resistivity data using an approximate inverse mapping. Geophysical Journal International 116, 527–537.
Li, Y. and Oldenburg, D.W., 2000, Incorporating geological dip information into geophysical inversions. Geophysics, 65, 148–157.
Liu, S., Yeh, T.-C.J., and Gardiner, R., 2002, Effectiveness of hydraulic tomography: sandbox experiments. Water Resour. Res. 38, 10.1029/2001WR000338.
Liu, S.-Y. and Yeh, T.-C.J., 2004, An integrative approach for monitoring water movement in the vadose zone. Vadose Zone Journal, 3, 681–692.
Liu, X.W., Illman, A., Craig, A.J., Zhu, J., and Yeh, T.-C.J. 2007, Laboratory sandbox validation of transient hydraulic tomography. Water Resour. Res., 43, W05404, doi:10.1029/2006WR005144.
McLaughin, D. and Townley, L.R., 1996, A reassessment of the groundwater inverse problem. Water Resour. Res., 32, 1131–1161.
Moysey, S., Singha, K., and Knight, R., 2005, Inferring field-scale rock physics relations through numerical simulation. Geophysical Research Letters, 32, L08304, doi:10.1029/2004GL022152.
National Research Council (NRC), 2000, Seeing into the earth: non-invasive characterization of the shallow subsurface for environmental and engineering application. Board on Earth Sciences and Resources, Water Science and Technology Board, Commission on Geosciencce, Environment, and Resources, National Academy Press, Washington D.C.
Oldenburg, D.W. and Li, Y., 1999, Estimating depth of investigation in dc resistivity and Ip surveys. Geophysics, 64, 403–416.
Oreskes, N., Shrader-Frechette, K., and Belitz, K., 1994, Verification, validation, and confirmation of numerical models in the earth sciences. Science, 263, 641–646.
Rizzo, E., Suski, B., and Revil, A., 2004, Self-potential signals associated with pumping tests experiments. J. Geophys. Res., 109, B10203, doi:10.1029/2004JB003049.
Rubin, Y. and Hubbard, S., 2005, Hydrogeophysics. Springer, The Netherlands, 523p.
Singha K. and Gorelick, S.M., 2005, Saline tracer visualized with three-dimensional electrical resistivity tomography: Field-scale spatial moment analysis. Water Resour. Res., 41, W05023, doi: 10.1029/2004WR003460.
Straface, S., Yeh, T.-C.J., Zhu, J., and Troisi, S., 2006, Sequential Aquifer Tests at a Well Field, Montalto Uffugo Scalo, Italy. Water Resour. Res., 43, W07432, doi:10.1029/2006WR005287.
Vasco, D.W., Keers, H., and Karasaki, K., 2000, Estimation of reservoir properties using transient pressure data: An asymptotic approach. Water Resour. Res., 36, 3447–3465.
Vereecken, H., Binley. A., and Cassiani, G., 2006, Applied Hydrogeophysics. Springer, 396p.
Wu, C.-M., Yeh, T.-C.J., Zhu, J., Lee, T.H., Hsu, N.-S., Chen, C.-H., and Sancho, A.F., 2005, Traditional analysis of aquifer tests: Comparing apples to oranges? Water Resour. Res., 41, W09402, doi:10.1029/2004WR003717.
Yeh, T.-C.J. and Šimůnek, J., 2002, Stochastic fusion of information for characterizing and monitoring the vadose zone. Vadose Zone Journal, 1, 207–221.
Yeh, T.-C.J., Zhu, J., Englert, A., Guzman, A., and Flaherty, S., 2006, A Successive Linear Estimator for Electrical Resistivity Tomography. In: Vereecken, H. (eds), Hydrogeophysics.
Yeh, T.-C.J. and Liu, S., 2000, Hydraulic tomography: Development of a new aquifer test method. Water Resour. Res., 36, 2095–2105.
Yeh, T.-C.J. and Zhang, J., 1996, A geostatistical inverse method for variably saturated flow in the vadose zone. Water Resour. Res., 32, 2757–2766, 10.1029/96WR01497.
Yeh, T.-C.J., Liu, S., Glass, R.J., Baker, K., Brainard, J.R., Alumbaugh, D., and LaBrecque, D., 2002, A geostatistically based inverse model for electrical resistivity surveys and its applications to vadose zone hydrology. Water Resour. Res., 38, 1278, doi: 10.1029/2001WR001204.
Yeh, T.-C.J., Hsu, K., Lee, C., Wen, J., and Ting, C., 2004, On the Possibility of Using River Stage Tomography to Characterize the Aquifer Properties of the Choshuishi Alluvial Fan, Taiwan. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2004AGUFM.H11D0329Y.
Zhang, J., Mackie, R.L., and Madden, T., 1995, 3-D resistivity forward modeling and inversion using conjugate gradients. Geophysics, 60, 1313–1325.
Zhu, J. and Yeh, T.-C.J., 2005, Characterization of aquifer heterogeneity using transient hydraulic tomography. Water Resour. Res., 41, W07028, doi:10.1029/2004WR003790.
Zhu, J. and Yeh, T.-C.J., 2006, Analysis of hydraulic tomography using temporal moments of drawdown-recovery data. Water Resour. Res., 42, W02403, doi:10.1029/2005WR004309.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeh, TC.J., Lee, CH., Hsu, KC. et al. Fusion of hydrologic and geophysical tomographic surveys. Geosci J 12, 159–167 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-008-0017-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-008-0017-6