Abstract
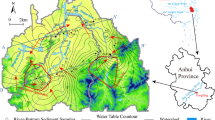
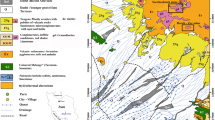
The U.S. Geological Survey, in cooperation with the New Mexico Environment Department and supported by Molycorp, Inc (currently Chevron Minerals), has completed a 5-year investigation (2001–2006) to determine the pre-mining groundwater quality at Molycorp’s Questa molybdenum mine in northern New Mexico. Current mine-site ground waters are often contaminated with mine-waste leachates and no data exists on pre-mining ground-water quality so that pre-mining conditions must be inferred. Ground-water quality undisturbed by mining is often worse than New Mexico standards and data are needed to help establish closure requirements. The key to determining pre-mining conditions was to study the hydrogeochemistry of a proximal natural analog site, the Straight Creek catchment. Main rock types exposed to weathering include a Tertiary andesite and the Tertiary Amalia tuff (rhyolitic composition), both hydrothermally altered to various degrees. Two types of ground water are common in mineralized areas, acidic ground waters in alluvial debris fans with pH 3–4 and bedrock ground waters with pH 6–8. Siderite, ferrihydrite, rhodochrosite, amorphous to microcrystalline Al(OH)3, calcite, gypsum, barite, and amorphous silica mineral solubilities control concentrations of Fe(II), Fe(III), Mn(II), Al, Ca, Ba, and SiO2, depending on pH and solution composition. Concentrations at low pH are governed by element abundance and mineral weathering rates. Concentrations of Zn and Cd range from detection up to about 10 and 0.05 mg/L, respectively, and are derived primarily from sphalerite dissolution. Concentrations of Ni and Co range from detection up to 1 and 0.4 mg/L, respectively, and are derived primarily from pyrite dissolution. Concentrations of Ca and SO4 are derived from secondary gypsum dissolution and weathering of calcite and pyrite. Metal:sulfate concentration ratios are relatively constant for acidic waters, suggesting consistent weathering rates, independent of catchment. These trends, combined with lithology, mineralogy, and mineral solubility controls, provide useful constraints on pre-mining ground-water quality for the mine site where the lithology is known.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpers, C.N. and Nordstrom, D.K., 2000, Estimation of pre-mining conditions for trace metal mobility in mineralized areas. In Proc. Fifth Inter. Conf. Acid Rock Drainage, ICARD 2000, v. 1, Society for Mining, Metallurgy, and Exploration, Littleton, Colo., 463–472.
Ball, J.W., Runkel, R.L., and Nordstrom, D.K., 2005, Questa baseline and pre-mining ground-water quality investigation. 12. Geochemical and reactive-transport modeling based on low-flow and snowmelt tracer studies for the Red River, New Mexico. U.S. Geol. Survey Sci. Invest. Report 2005-5149.
Caine, J.S., 2003, Questa baseline and pre-mining ground-water quality investigation. Preliminary brittle structure geologic data, Questa mining district, southern Sangre de Cristo Mountains, New Mexico. U.S. Geol. Survey Open-File Report 03-280.
Caine, J.S., 2006, Questa baseline and pre-mining ground-water quality investigation. 18. Characterization of brittle structures in the Questa Caldera and their potential influence on bedrock ground-water flow, Red River Valley, New Mexico. U.S. Geol. Survey Professional Paper1729.
Church, S.E., Fey, D.L., and Marot, M.E., 2005, Questa baseline and pre-mining ground-water quality investigation. 8. Lake-sediment geochemical record from 1960 to 2002, Eagle Rock and Fawn Lakes, Taos County, New Mexico. U.S. Geol. Survey Open-File Report 2005-5006.
Dietzel, M., 2000, Dissolution of silicates and the stability of polysilicic acid. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64, 3275–3281.
Fleischer, M., 1955, Minor elements in some sulfide minerals. In Bateman, A.M., ed., Econ. Geol., Fiftieth Anniversary Volume, 1905–1955,Part II, Lancaster Press, Lancaster, Penn., 970–1024.
Icopini, G.A., Brantley, S.L., and Heaney, P.J., 2005, Kinetics of silica oligomerization and noncolloid formation as function of pH and ionic strength at 25 °C. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 69, 293–303.
Kimball, B.A., Nordstrom, D.K., Runkel, R.L., Vincent, K.R., and Verplanck, PL., 2006, Questa baseline and pre-mining ground-water quality investigation. 23. Quantification of mass loading from mined and unmined areas along the red River, New Mexico. U.S. Geol. Survey Sci. Invest. Report 2006-5004.
Livo, K.E. and Clark, R. N., 2002, Mapped Minerals at Questa, New Mexico, Using Airbourne Visible-Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (AVIRIS) Data—preliminary report. U.S. Geol. Survey Open-File Report 02-0026.
Lovetere, S.H., Nordstrom, D.K., Maest, A.S., and Naus, C.A., 2004, Questa baseline and pre-mining ground-water quality investigation. 3. Historical ground-water quality for the Red River Valley, New Mexico. U.S. Geol. Survey Water-Resour. Invest. Report 03-4186.
Ludington, S., Plumlee, G.S., Caine, J.S., Bove, D., Holloway, J.M., and Livo, K.E., 2004, Questa baseline and pre-mining groundwater quality investigation. 10. Geologic influences on ground and surface waters in the lower Red River watershed, New Mexico. U.S. Geol. Survey Sci. Invest. Report 2004-5245.
Maest, A.S., Nordstrom, D.K., and Lovetere, S.H., 2004, Questa baseline and pre-mining ground-water quality investigation. 4. Historical surface-water quality for the Red River Valley, New Mexico. U.S. Geol. Survey Sci. Invest. Report 2004-5063.
McCleskey, R.B., Nordstrom, D.K., Steiger, J.I., Kimball, B.A., and Verplanck, P.L., 2003, Questa baseline and pre-mining groundwater quality investigation. 2. Low-flow (2001) and snowmelt (2002) synoptic/tracer water chemistry for the Red River, New Mexico. U.S. Geol. Survey Open-File Report 03-148.
McCleskey, R.B. Nordstrom, D.K., and Naus, C.A., 2004, Questa baseline and pre-mining ground-water quality investigation. 16. Quality assurance and quality control of water analyses. U.S. Geol. Survey Open-File Report 2004-1341.
Meyer, J. and Leonardson, R., 1990, Tectonic, hydrothermal and geomorphic controls on alteration scar formation near Questa, New Mexico. In New Mexico Geol. Soc. Guidebook, 41st Field Conference, Southern Sangre de Cristo Mountains, 417–422.
Naus, C.A., McAda, D.P., and Myers, N.C., 2006, Questa baseline and pre-mining ground-water quality investigation. 21. Hydrology and water balance of the Red River Basin, New Mexico 1930–2004. U.S. Geol. Survey Sci. Invest. Report 2006-5040.
Naus, C.A., McCleskey, R.B., Nordstrom, D.K., Donohoe, L.C., Hunt. A.G., Paillet, F., Morin, R.H., and Verplanck, P.L., 2005, Questa baseline and pre-mining ground-water quality investigation. 5. Well installation, water-level Data, and surface-and groundwater geochemistry in the Straight Creek Drainage Basin, Red River Valley, New Mexico, 2001–03. U.S. Geol. Survey Sci. Invest. Report 2005-5088.
Nordstrom, D.K., 2008, Questa baseline and pre-mining groundwater quality investigation. 25. Summary of results and baseline and pre-mining ground-water geochemistry, Red River Valley, Taos County, New Mexico, 2001–2005. U.S. Geol. Survey Professional Paper 1728.
Nordstrom, D.K., and Ball, J.W., 1986, The geochemical behavior of aluminum in acidified surface waters: Science, 232, 54–56.
Nordstrom, D.K., McCleskey, R.B., Hunt, A.G., and Naus, C.A., 2005, Questa baseline and pre-mining ground-water quality investigation. 14. Interpretation of ground-water geochemistry in catchments other than the Straight Creek catchment, Red River Valley, Taos County, New Mexico, 2002–2003. U.S. Geol. Survey Sci. Invest. Report 2005-5050.
Plumlee, G.S., Lowers, H.A., Ludington, S.D., Koening, A.E., and Briggs, P.H., 2005, Questa baseline and pre-mining ground-water quality investigation. 13. Mineral microscopy and chemistry of mined and unmined porphyry molybdenum mineralization along the Red River, New Mexico — Implications for ground-and surface-water quality. U.S. Geol. Survey Sci. Invest. Report 2005-1442.
Powers, M.H. and Burton, B.L., 2004, Questa baseline and pre-mining ground-water quality investigation. 1. Depth to bedrock determinations using shallow seismic data acquired in the Straight Creek Drainage near Red River, New Mexico. U.S. Geol. Survey Open-File Report 2004-1236.
Questa, 2005, Questa baseline and pre-mining ground-water quality investigation, Red River Valley Basin, New Mexico, available on the World Wide Web, accessed December 19, 2005, at URL http://wwwbrr.cr.usgs.gov/projects/GWC_chemtherm/questa.htm
Runnells, D.D., Shepard, T.A., and Angino, E.E., 1992, Metals in water-Determining natural background concentrations in mineralized areas. Env. Sci. Technol., 26, 2316–2322.
Smith, K.S., Hageman, P.L., Briggs, P.H., Sutley, S.J., McCleskey, R.B., Livo, K.E., Verplanck, P.L., Adams, M.G., and Gemery-Hill, P.A., 2006, Questa baseline and pre-mining ground-water quality investigation. 19. Leaching characteristics of composited materials from mine waste-rock piles and naturally altered areas near Questa, New Mexico, U.S. Geol. Survey Sci. Invest. Report 2006-5165.
To, T.B., Nordstrom, D.K., Cunningham, K.M., Ball, J.W., and McCleskey, R.B., 1999, New method for the direct determination of dissolved Fe(III) concentration in acid mine waters. Env. Sci. Technol., 33, 807–813.
Vincent, K.R., 2008, Questa baseline and pre-mining ground-water quality investigation. 17. Geomorphology of the Red River Valley, Taos County, New Mexico, with emphasis on the shallow alluvial aquifer. U.S. Geol. Survey Sci. Invest. Report 2006-5156.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nordstrom, D.K. What was the groundwater quality before mining in a mineralized region? Lessons from the Questa project. Geosci J 12, 139–149 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-008-0015-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-008-0015-8