Abstract
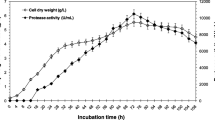
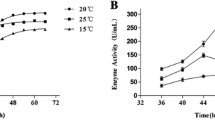
Unbranched heterocytous cyanobacteria produce a number of serine peptidases. We have characterized several peptidases in the cell-free extracts of a true-branched N2-fixing cyanobacterium, Westiellopsis ramosa sp. nov. Upon substrate-gel zymography of intact filaments and heterocytes, five peptidase bands were resolved, whereas in vegetative cells, a single band was discernible. No band was detected in \({\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - } /{\text{NH}}_{4}^{ + }\)-grown cultures suggesting that the peptidases were present under diazotrophic conditions with much of them confined to heterocytes. Using salt precipitation and chromatography, a caseinolytic peptidase, called Wrp49, was purified which also demonstrated fibrinolytic activity. In SDS-PAGE, the purified peptidase was resolved into 17 and 27 kDa fragments. The enzyme in its native state exhibited Mr ≈ 49 kDa, and digested gelatin in a substrate gel at a corresponding position. The enzyme showed amidolytic activity on a plasmin specific substrate, D-Val-Leu-Lys p-nitroanilide. Moreover, a trypsin specific substrate, N-benzoyl-DL-Arg p-nitroanilide was hydrolyzed at an apparent Km = 0.195 mM and Vmax = 5 × 10−7 M s−1. The enzyme was stable in a wide pH and temperature range. While Ca2+ stimulated the activity; phenylmethane sulfonyl fluoride, leupeptin, EDTA and chelants were inhibitory. The activity of the EDTA-inactivated enzyme was completely restored upon adding Ca2+, suggesting that both compounds competed with each other in modulating the enzyme activity. The enzyme showed similarities with a Ca2+ stimulated subtilisin-like serine peptidase of Anabaena variabilis ATCC 29413, but also presented several unique features of metallopeptidases, such as the chelant’s response. Moreover, the N-terminal sequence (MTVENLARTGVGPGWR) did not match with any of the known peptidases.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal MK, Zitt A, Bagchi D, Weckesser J (2005) Characterization of proteases in gut of Daphnia magna and their inhibition by Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806. Environ Toxicol 20:314–322. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.20123
Andrews P (1965) The gel filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J 96:595–606
Baier K, Nicklisch S, Lockau W (1996) Evidence for propeptide-assisted folding of the calcium-dependent protease of the cyanobacterium Anabaena. Eur J Biochem 241:750–755
Banerjee S, Prasanna R, Bagchi SN (2013) Purification and characterization of a fibrino(geno)lytic protease from cultured natural isolate of a cyanobacterium, Anabaena fertilissima. J Appl Phycol 25:1111–1122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-012-9946-6
Burnat M, Herrero A, Flores E (2014) Compartmentalized cyanophycin metabolism in the diazotrophic filaments of a heterocyst forming cyanobacterium. PNAS 111:3823–3828. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1318564111
Christie-Oleza JA, Armengaud J, Guerin P, Scanlan DJ (2015) Functional distinctness in the exoproteomes of marine Synechococcus. Environ Microbiol 17(10):3781–3794. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.12822
Datta G, Dong A, Witt J, Tu AT (1995) Biochemical-characterization of basilase, a fibrinolytic protease from Crotalus basiliscus basiliscus. Arch Biochem Biophys 317:365–373. https://doi.org/10.1006/abbi.1995.1176
Ghosh SK, Bagchi D, Bagchi SN (2008) Proteolytic activity in Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806 is inhibited by a trypsin inhibitory cyanobacterial peptide with a partial structure of microviridin. J Appl Phycol 20:1045–1052. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-007-9304-2
Kim SH, Choi NS, Lee WY (1998) Fibrin zymography: a direct analysis of fibrinolytic enzymes on gels. Anal Biochem 263:115–116. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1998.2816
Kristjánsson MM (1991) Purification and characterization of trypsin from the pyloric caeca of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J Agric Food Chem 39:1738–1742. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf00010a009
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Leikoski N, Fewer DP, Jokela J, Wahlsten M (2010) Highly diverse cyanobactins in strains of the genus Anabaena. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(3):701–709. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01061-09
Lockau W, Massalsky B, Dirmeier A (1988) Purification and partial characterization of a calcium-stimulated protease from the cyanobacterium, Anabaena variabilis. Eur J Biochem 172:433–438. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13906.x
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mackinney G (1941) Absorption of light by chlorophyll solution. J Biol Chem 140:315–322
Maldener I, Lockau W, Cai Y, Wolk CP (1991) Calcium-dependent protease of the cyanobacterium Anabaena: molecular cloning and expression of the gene in Escherichia coli, sequencing and site-directed mutagenesis. Mol Gen Genet 225:113–120
Martinez-Rosales C, Marizcurrena JJ, Iriarte A, Fullana N (2015) Characterizing proteases in an Antarctic Janthinobacterium sp. isolate: evidence of a protease horizontal gene transfer event. Adv Polar Sci 26:88–95. https://doi.org/10.13679/j.advps.2015.1.00088
Nürnberg DJ, Mariscal V, Bornikoel J, Nieves-Morion M (2015) Intercellular diffusion of a fluorescent sucrose analog via the septal junctions in a filamentous cyanobacterium. M Bio 6(2):e02109–e02114. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.02109-14
Oliveira P, Martins NM, Santos M, Couto NAS (2015) The Anabaena sp. PCC 7120 exoproteome: taking a peek outside the box. Life 5(1):130–163. https://doi.org/10.3390/life5010130
Park JJ, Lechno-Yossef S, Wolk CP, Vieille C (2013) Cell-specific gene expression in Anabaena variabilis grown phototrophically, mixotrophically, and heterotrophically. BMC Genomics 14(1):759. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-759
Pernil R, Picossi S, Herrero A, Flores E (2015) Amino acid transporters and release of hydrophobic amino acids in the heterocyst-forming cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. Life 5:1282–1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/life5021282
Richter R, Hejazi M, Kraft R, Ziegler K, Lockau W (1999) Cyanophycinase, a peptidase degrading the cyanobacterial reserve material multi-l-arginyl-poly-l-aspartic acid (cyanophycin): molecular cloning of the gene of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803, expression in Escherichia coli, and biochemical characterization of the purified enzyme. Eur J Biochem 263(1):163–169. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00479.x
Rippka R, Deruelles J, Waterbury JB, Herdman M, Stanier RY (1979) Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure culture of cyanobacteria. J Gen Microbiol 111:1–61
Singh P, Dubey N, Bagchi SN (2017) Westiellopsis ramosa sp. nov., intensely branched species of Westiellopsis (cyanobacteria) isolated from Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh, India. Plant Syst Evol 303:1239–1249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-017-1434-7
Strohmeier U, Gerdes C, Lockau W (1994) Proteolysis in heterocyst-forming cyanobacteria: characterization of a further enzyme with trypsin-like specificity, and of a prolyl endopeptidase from Anabaena variabilis. Z Naturforsch 49:70–78
Thomas J, Meeks JC, Wolk CP, Shaffer PW, Austin SM (1977) Formation of glutamine from [13N] ammonia, [13N] dinitrogen, and [14C] glutamate by heterocysts isolated from Anabaena cylindrica. J Bacteriol 129:1545–1555
Tork SE, Shahein YE, El-Hakim AE, Abdel-Aty AM (2013) Production and characterization of thermostable metallo-keratinase from newly isolated Bacillus subtilis NRC 3. Int J Biol Macromol 55:169–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.01.002
Vilhauer L, Jervis J, Ray WK, Helm RF (2014) The exo-proteome and exo-metabolome of Nostoc punctiforme (cyanobacteria) in the presence and absence of nitrate. Arch Microbiol 196:357–367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-014-0974-2
Wu B, Wu L, Chen D, Yang Z (2009) Purification and characterization of a novel fibrinolytic protease from Fusarium sp. CPCC 480097. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36(3):451–459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-008-0516-5
Zhou R, Wei X, Jiang N, Li H (1998) Evidence that HetR protein is an unusual serine-type protease. PNAS 95:4959–4963
Acknowledgment
The authors wish to thank the Head of the Department of Biological Science, Rani Durgavati University, Jabalpur, for providing lab facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SNB and PS designed the experiments. ND and PS performed the experiments.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
12298_2017_497_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary material Fig. S1 Photomicrographs of (a) NH4Cl supplemented culture showing no heterocytes, poor growth with retracted cytoplasmic content visible inside the cells and branching (b) Culture supplemented with NaNO3 showing better growth than (a) along with the presence of branching; no heterocytes are visible, and (c) culture without external supplementation of nitrogen showing the presence of heterocytes (arrows). Scale bar = 5 µm (TIFF 594 kb)
12298_2017_497_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary material Fig. S2 Demonstration of casein dissolution activity. (a) Sonicated cells and (b) culture filtrate equivalent to 10 and 20 µg protein in 30 µL, and (c) buffer were applied to dry filter paper discs (diameter, 5 mm) and placed on surface of casein plates prepared by hardening 1% casein in 20 mM Tris–HCl, pH 8.0 with 1.5% agar. After overnight incubation at 37 °C, plates were overlaid with 5% (w/v) TCA to observe clearing zones (TIFF 225 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dubey, N., Singh, P. & Bagchi, S.N. A calcium-stimulated serine peptidase from a true-branching cyanobacterium, Westiellopsis ramosa sp. nov.. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 24, 261–273 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-017-0497-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-017-0497-9