Abstract
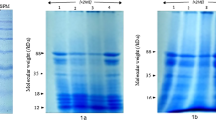
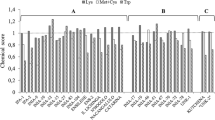
Twenty one genotypes and two check varieties viz. CS-88 and V-240 of cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp. ] were screened for total proteins. The total protein content ranged from 22.4 (HC-3) to 27.9 % (HC-98-64) in 21 genotypes whereas in check varieties it was 25.6 (V-240) and 26.0 % (CS-88). Seven genotypes viz. HC-6, HC-5, CP-21, LST-II-C-12, CP-16, COVU-702 and HC-98-64 having high protein content (26.7 to 27.9 %) were selected for further characterization of their seed storage proteins. Globulins were the major protein fraction ranging from 55.6 (LST-II-C-12) to 58.8 % (CP-16 and HC-6) of total protein. Glutelins was the second major fraction ranging from 14.4 to 15.6 % followed by albumins (8.2 to 11.9 %) and prolamins (2.3 to 5.0 %). Content of free amino acids also showed variations amongst genotypes with COVU-702 having maximum and LST-II-C-12 having minimum content. Essential amino acid analysis revealed that S-amino acids (cysteine and methionine) were the first limiting amino acids followed by tryptophan. From the results presented here it could be suggested that two genotypes viz. LST-II-C-12 and HC-5 be used in breeding programmes aimed at developing high protein moth bean varieties with good quality.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen DJ (1983). The Pathology of Tropical Food Legumes. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester.
AOAC (1984). Official Methods of Analysis, 14th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Washington, DC.
Awolumate EO (1983). Accumulation and quality of storage protein in developing cowpea, mungbean and soybean seeds. J. Sci. Food Agric. 34: 1351–1357.
Bala A, Satija DR and Gupta VP (1994). Variation and association analysis among protein quality traits in chickpea. Indian J. Genet. Pl. Breed. 54: 105–109.
Dhawan K, Malhotra S, Dahiya BS and Singh D (1991). Seed protein fractions and amino acid composition in gram (Cicer arietinum). Plant Fd. Human Nutr. 41: 225–232.
Dionex Corporation. Determination of the amino acid content of peptides by AAA-Direct. Technical Note 50. Sunnyvale, CA.
Gonzalez ON, Banzon EA, Liggayu RG and Quinitio PH (1964). Isolation and chemical composition of mungbean (Phaseolus aureus Roxb.) protein. Philip. J. Sci. 93: 47–56.
Gupta VP and Kapoor AC (1979). Chemical evaluation of protein quality of various grain legumes. Indian J. agric. Sci. 50: 393–398.
Horax R, Hettiarachchy NS, Chen P and Jalaluddin M (2004). Preparation and characterization of protein isolate from cow pea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) walp). J. Fd. Sci. 69: 114–118.
Hussain MA and Basahy AY (1998). Nutrient composition and amino acid pattern of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp, Fabaceae) grown in the Gizan area of Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Fd Sci. Nutr. 49: 117–124.
Kapoor AC and Gupta YP (1977). Chemical evaluation and electrophoretic pattern of soya protein. J. Fd. Sci. Agric. 42: 1558–1561.
Leverton RM (1967). Soybean protein in mixed foods. In: Proc. Int. Conf. Soybean protein foods, U. S. Dept. Agric., pp. 75–80.
Mahajan R, Malhotra SP and Singh R (1988). Characterization of seed storage proteins of urdbean (Vigna mingo). Plant Fd. Human Nutr. 38: 163–173.
Mendoza EMT, Adachi M, Bernardo AEN and Utsumi S (2001). Mung bean (Vigna radiate (L.) Wilczek) globulins: purification and characterization. J. Agric. Food Chem. 49: 1152–1158.
Nie NH, Hull CH and Bent DH (1970). Statistical Package for the Social Sciences. McGraw-Hill. Eds 1 & 2 1970, 1975. New York.
Nielsen S, Ohler T, Mitchell C (1997). Cowpea leaves for human consumption: production, utilization, and nutrient composition. In: Advances in cowpea research (Ed. Singh, B.; Mohan Raj, D.; Dashiell K. and Jackai L.), Intr. Inst. Trop. Agric. (IITA) and Japan Intr. Res. Center Agric. Sci. (JIRCASS), Ibadan, Nigeria, pp 326–332.
Oluwatosin OB (1997). Genetic and environmental variation for seed yield, lipid and amino acid composition in cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp]. J. Sci. Fd Agric. 74: 107–116.
Osborne TB (1924). The vegetable proteins. Longmans, Green and Co, London. Padhye VW and Salunkhe DK (1979). Biochemical studies on black gram (Phaseolus mungo L.) seeds. Amino acid composition and subunit constitution of fractions of the proteins. J. Fd. Sci. 44: 606–610.
Quass CF (1995). Guidelines for the Production of Cowpeas. National Department of Agriculture, Pretoria.
Rachie KO (1985). Introduction. In: Cowpea Researches, Production and Utilization (Ed. Singh, S.R and Rachie, K.O.), Wiley, New York. pp. 108.
Rosario RRD, Lozano Y and Neol MG (1981). The chemical and biochemical composition of legume seeds. 2. Cowpea. Philippine-Agriculturist. 64: 49–57.
Singh SP, Misra BK, Sikka KC, Chandel KP and Pant KC (1985). Studies on some nutritional aspects of ricebean (Vigna umbellate). J. Fd. Sci. Tech. 22: 180–185.
Turkova V and Klozova E (1985). Comparison of seed proteins in some representatives of the genus Vigna. Biol. Plant. 27: 70–73.
Wang N and Daun JK (2004). Effect of variety and crude protein content on nutrients and certain antinutrients in field peas (Pisum sativum). J. Sci. Fd Agric. 84: 1021–1029.
Yemm EW and Cocking EC (1955). The determination of amino acids with ninhydrin. Analyst. 80: 209–213.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, P., Singh, R., Malhotra, S. et al. Characterization of seed storage proteins in high protein genotypes of cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.]. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 16, 53–58 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-010-0007-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-010-0007-9