Abstract
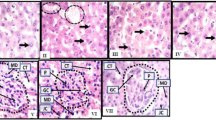
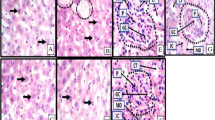
Tuberculosis (TB) is a challenging public health issue, particularly in poor and developing countries. Rifampicin (RIF) is one of the most common first-line anti-TB drugs but it is known for its adverse effects on the hepato-renal system. The present study investigated the efficacy of morin hydrate (MH) in protecting hepato-renal damage inflicted by RIF in rats. RIF (50 mg/kg), and a combination of RIF (50 mg/kg) and MH (50 mg/kg) were administered orally for 4 weeks in rats. Silymarin (50 mg/kg) was used as a positive control. Increased levels of serological parameters such as AST, ALT, ALP, LDH, GGT, bilirubin, triglyceride, total cholesterol, urea, uric acid, creatinine, TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-6 along with the decreased level of IL-10, total protein and albumin were used as markers of hepatic and renal injury. Oxidative damage in the tissues was measured by the increase in lipid peroxidation and decline in GSH, SOD and catalase activities. Histopathology of liver slices was used to study hepatic architecture. Four-week RIF treatment produced altered serological parameters with an increase in pro-inflammatory cytokines in serum suggesting hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity. The antioxidant status of the liver and kidney (increased lipid peroxidation and decline in GSH, SOD and catalase) was compromised. Cellular damage and necrosis were observed in liver slices. MH supplementation with RIF improved hepato-renal functions by restoring the serum and tissue markers towards normal values. Histological observations authenticated the results. MH supplementation also reduced the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Thus, the results revealed that MH provides protection against RIF-induced hepato-renal injury.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nwidu LL, Teme RE. Hot aqueous leaf extract of Lasianthera africana (Icacinaceae) attenuates rifampicin-isoniazid-induced hepatotoxicity. J Integrative Med. 2018;16:263–72.
WHO, Global tuberculosis report 2021. https://www.who.int/publications/digital/global-tuberculosis-report-2021/tb-diagnosis-treatment/drug-resistant-treatment
Campbell EA, Korzheva N, Mustaev A, Murakami K, Nair S, Goldfarb A, et al. Structural Mechanism for Rifampicin Inhibition of Bacterial RNA Polymerase. Cell. 2001;104:901–12.
Dubiwak AD, Gerema U, Abdisa D, Tofik E, Reta W. Amelioration of Nephrotoxicity in Mice Induced by Antituberculosis Drugs Using Ensete ventricosum (Welw.) Cheesman Corm Extract. Int J Nephrol. 2022;2022:6941509.
Thuawaini MM, Al-Farhaan MBG, Abbas F, K,. Hepatoprotective and nephroprotective effects of the aqueous extract of turmeric (Curcuma longa) in rifampicin and isoniazid-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in rats. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2019;1:293–8.
Kim J-H, Nam W, Kim S, Kwon O, Seung E, Jo J, et al. Mechanism investigation of rifampicin-induced liver injury using comparative Toxico-proteomics in Mice. IJMS. 2017;18:1417.
Lee KM, Lee Y, Chun HJ, Kim AH, Kim JY, Lee JY, et al. Neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of morin in a murine model of Parkinson’s disease: Morin Alleviates Neurotoxicity in PD. J Neurosci Res. 2016;94:865–78.
Caselli A, Cirri P, Santi A, Paoli P. Morin: a promising natural drug. Curr Med Chem. 2016;23:774–91.
Gendy A, Elnagar MR, Soubh A, Al-Mokaddem A, El-Haddad A, El-Sayed MK. Morin alleviates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion-induced mischief: In-vivo and in-silico contribution of Nrf2, TLR4, and NLRP3. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;138: 111539.
Li X, Yao Q, Huang J, Jin Q, Xu B, Chen F, et al. Morin hydrate inhibits TREM-1/TLR4-Mediated inflammatory response in macrophages and protects against carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury in mice. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:1089.
Gupta A, Pandey AK. Aceclofenac-induced hepatotoxicity: AN ameliorative effect of Terminalia bellirica fruit and ellagic acid. World J Hepatol. 2020;12:949–64.
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951;193:265–75.
Niehaus WG, Samuelsson B. Formation of Malonaldehyde from Phospholipid Arachidonate during Microsomal Lipid Peroxidation. Eur J Biochem. 1968;6:126–30.
Marklund S, Marklund G. Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem. 1974;47:469–74.
Beers RF, Sizer IW. A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J Biol Chem. 1952;195:133–40.
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Featherstone RM. A new and rapid colourimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1961;7:88–95.
Cardiff RD, Miller CH, Munn RJ. Manual Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining of Mouse Tissue Sections. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2014; 2014:pdb.prot073411.
Gupta A, Kumar R, Ganguly R, Singh AK, Rana HK, Pandey AK. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective activities of Terminalia bellirica and its bioactive component ellagic acid against diclofenac induced oxidative stress and hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Rep. 2021;8:44–52.
Chen X, Xu J, Zhang C, Yu T, Wang H, Zhao M, et al. The protective effects of ursodeoxycholic acid on isoniazid plus rifampicin induced liver injury in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011;659:53–60.
Kumar S, Kumar R, Dwivedi A, Pandey AK. In vitro antioxidant, antibacterial, and cytotoxic activity and in vivo effect of Syngonium podophyllum and Eichhornia crassipes leaf extracts on isoniazid induced oxidative stress and hepatic markers. BioMed Res Int. 2014;2014:459452. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/459452.
Anderson MS, Cote J, Liu Y, Stypinski D, Auger P, Hohnstein A, et al. Effects of Rifampin, a potent inducer of drug-metabolizing enzymes and an inhibitor of OATP1B1/3 transport, on the single dose pharmacokinetics of anacetrapib. J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;53:746–52.
Shehu AI, Li G, Xie W, Ma X. The pregnane X receptor in tuberculosis therapeutics. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2016;12:21–30.
Dong Y, Huang J, Lin X, Zhang S, Jiao Y, Liang T, et al. Hepatoprotective effects of Yulangsan polysaccharide against isoniazid and rifampicin-induced liver injury in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;152:201–6.
Kumar S, Pandey AK. Chemistry and biological activities of flavonoids: an overview. Sci World J. 2013;10: 162750.
Ganguly R, Gupta A, Pandey AK. Role of baicalin as a potential therapeutic agent in hepatobiliary and gastrointestinal disorders: a review. World J Gastroenterol. 2022;28(26):3047–62.
Kapoor R, Kakkar P. Protective role of morin, a flavonoid, against high glucose induced oxidative stress mediated apoptosis in primary rat hepatocytes. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e41663.
Folorunso IM, Lawal AO, Elekofehinti OO, Iwaloye O. Hepatoprotective effect of morin hydrate in type 2 diabetic Wistar rats exposed to diesel exhaust particles. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04366-4. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36708492.
Wu T-W, Zeng LH, Wu J, Fung KP. Morin hydrate is a plant-derived and antioxidant-based hepatoprotector. Life Sci. 1993; 53:PL213–8.
Martin SJ, Sabina EP. Amelioration of anti-tuberculosis drug-induced oxidative stress in kidneys by Spirulina fusiformis in a rat model. Ren Fail. 2016;38:1115–21.
Prince SE, Martin SJ, Lavinya BU, Selvanathan K, Geetha A. Anti-tuberculosis drug-induced oxidative stress in kidneys: role of brahmi as an antioxidant supplement. Pharmacogn Magazani. 2019;15(62):12–6.
Saravana MMG, Ramakrishnan T, Mani V, Achary A. Protective effect of crude sulphated polysaccharide from turbinaria ornata on isoniazid rifampicin induced hepatotoxicity and oxidative stress in the liver, kidney and brain of adult swiss albino rats. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 2018;55(8):237–44.
Jyothi B, Mahalakshmi S, Anitha K. Protective effect of Mirabilis jalapa leaves on anti-tubercular drugs induced hepatotoxicity. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2013;6(3):221–4.
Abd El-Reheem AMA, Abdel-Wahhab KG, AbdelWahhab MM, Morsy FA, Soliman SME, Abdel-Tawab MA. Protective effect of some natural extracts against isoniazid-induced hepatotoxicity in adult male rats. Curr Sci Int. 2015;4(3):409–22.
Pal R, Rana SV, Vaiphei K, Singh K. Isoniazid-rifampicin induced lipid changes in rats. Clin Chim Acta. 2008;389:55–60.
Ichikawa T, Liang J, Kitajima S, Koike T, Wang X, Sun H, et al. Macrophage-derived lipoprotein lipase increases aortic atherosclerosis in cholesterol-fed Tg rabbits. Atherosclerosis. 2005;179:87–95.
Fakhruddin S, Alanazi W, Jackson KE. Diabetes-induced reactive oxygen species: mechanism of their generation and role in renal injury. J Diabetes Res. 2017;2017:1–30.
Singaravelu A, Venkatachalam K, Jayaraj RL, Jayabalan P, Nadanam S. Morin treatment for acute ethanol exposure in rats. Biotech Histochem. 2021;96:230–41.
Messarah M, Saoudi M, Boumendjel A, Kadeche L, Boulakoud MS, Feki AE. Green tea extract alleviates arsenic-induced biochemical toxicity and lipid peroxidation in rats. Toxicol Ind Health. 2013;29:349–59.
Sharma UK, Kumar R, Gupta A, Ganguly R, Pandey AK. Renoprotective effect of cinnamaldehyde in food colour-induced toxicity. 3 Biotech. 2018; 8:212.
Ganguly R, Kumar R, Pandey AK. Baicalin provides protection against fluoxetine-induced hepatotoxicity by modulation of oxidative stress and inflammation. World J Hepatol. 2022;14:729–43.
Steuerwald NM, Foureau DM, Norton HJ, Zhou J, Parsons JC, Chalasani N, et al. Profiles of serum cytokines in acute drug-induced liver injury and their prognostic significance. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(12):81974.
Avitsur R, Hunzeker J, Sheridan JF. Role of early stress in the individual differences in host response to viral infection. Brain Behav Immun. 2006;20:339–48.
Baskaran UL, Sabina EP. The food supplement coenzyme Q10 and suppression of antitubercular drug-induced hepatic injury in rats: the role of antioxidant defence system, anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2015;31(4–5):211–9.
Hong DG, Lee S, Kim J, Yang S, Lee M, Ahn J, Lee H, Chang SC, Ha NC, Lee J. Anti-Inflammatory and neuroprotective effects of morin in an MPTP-induced Parkinson’s Disease model. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(18):10578.
Acknowledgements
HKR acknowledges UGC, New Delhi for CRET fellowship. AKS acknowledges the CSIR, India for JRF and SRF. All authors also acknowledge UGC-SAP and DST-FIST facilities of the Biochemistry Department, University of Allahabad, Prayagraj, India.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: AKP; Experiments: HKR, AKS; data analysis: HKR, AKS, AKP; first draft: HKR; critically reviewed and supervised: AKP; all authors: read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
The in-vivo study was performed in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals as approved by the University of Allahabad, Prayagraj.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rana, H.K., Singh, A.K. & Pandey, A.K. Therapeutic Potential of Morin Hydrate Against Rifampicin Induced Hepato and Renotoxicity in Albino Wistar Rats: Modulation of Organ Function, Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response. Ind J Clin Biochem 39, 197–206 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-023-01145-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-023-01145-0