Abstract
Background
The antituberculosis drugs (ATDs), isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide and ethambutol prompt extreme hepatic and renal damage during treatment of tuberculosis. The present study aimed to investigate protective potential of naringenin against ATDs induced hepato-renal injury.
Methods
Rats were administered with ATDs (pyrazinamide; 210, ethambutol; 170, isoniazid; 85, rifampicin; 65 mg/kg b.wt) orally for 8 weeks (3 days/week) followed by naringenin at three different doses (10, 20 and 40 mg/kg b.wt) conjointly for 8 weeks (3 days/week alternately to ATDs administration) and silymarin (50 mg/kg b.wt) as positive control.
Results
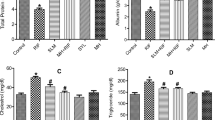
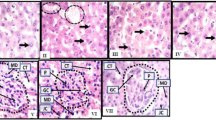
Exposure to ATDs caused significant increase in interleukin-6 (IL-6), triglycerides, cholesterol, bilirubin whereas depletion in insulin like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), albumin and glucose in serum. Endogenous antioxidant enzymes glutathione reductase (GR), glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase (G-6-PDH) were diminished in liver and kidney tissues with parallel increase in triglycerides, cholesterol, microsomal LPO and aniline hydroxylase (CYP2E1 enzyme). Ultra-structural observations of liver and kidney showed marked deviation in plasma membranes of various cellular and sub-cellular organelles after 8 weeks of exposure to ATDs.
Conclusions
Conjoint treatment of naringenin counteracted ATDs induced toxic manifestations by regulating IL-6, IGF-1, CYP2E1, biochemical and ultra-structural integrity in a dose dependent manner. Naringenin has excellent potential to protect ATDs induced hepato-renal injury by altering oxidative stress, modulation of antioxidant enzymes, serum cytokines and ultra-structural changes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
WHO (2020) Global tuberculosis report 2020: executive summary.
Arbex MA, Varella Mde C, Siqueira HR, Mello FA (2010) Antituberculosis drugs: drug interactions, adverse effects, and use in special situations. Part 1: first-line drugs. J Bras Pneumol 36(5):626–640
Tostmann A, Boeree MJ, Aarnoutse RE, de Lange WC, van der Ven AJ, Dekhuijzen R (2008) Antituberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity: concise up-to-date review. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 23(2):192–202
Shehu AI, Ma X, Venkataramanan R (2017) Mechanisms of Drug-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Clin Liver Dis 21(1):35–54
Chang CH, Chen YF, Wu VC, Shu CC, Lee CH, Wang JY et al (2014) Acute kidney injury due to anti-tuberculosis drugs: a five-year experience in an aging population. BMC Infect Dis 14:23
Biswas A, Santra S, Bishnu D, Dhali GK, Chowdhury A, Santra A (2020) Isoniazid and Rifampicin Produce Hepatic Fibrosis through an Oxidative Stress-Dependent Mechanism. Int J Hepatol 2020:6987295
Lock EA, Reed CJ (1998) Xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes of the kidney. Toxicol Pathol 26(1):18–25
Attia SM (2010) Deleterious effects of reactive metabolites. Oxid Med Cell Longev 3(4):238–253
Palma-Duran SA, Caire-Juvera G, Robles-Burgeño Mdel R, Ortega-Vélez MI, Gutiérrez-Coronado Mde L, Almada Mdel C et al (2015) Serum levels of phytoestrogens as biomarkers of intake in Mexican women. Int J Food Sci Nutr 66(7):819–825
Tripoli E, La Guardia M, Giammanco S, Di Majo D, Giammanco M (2007) Citrus flavonoids: Molecular structure, biological activity and nutritional properties: A review. Food Chem 104(2):466–479
Yoshida H, Watanabe W, Oomagari H, Tsuruta E, Shida M, Kurokawa M (2013) Citrus flavonoid naringenin inhibits TLR2 expression in adipocytes. J Nutr Biochem 24(7):1276–1284
Renugadevi J, Prabu SM (2009) Naringenin protects against cadmium-induced oxidative renal dysfunction in rats. Toxicology 256(1–2):128–134
Mershiba SD, Dassprakash MV, Saraswathy SD (2013) Protective effect of naringenin on hepatic and renal dysfunction and oxidative stress in arsenic intoxicated rats. Mol Biol Rep 40(5):3681–3691
Yilma AN, Singh SR, Morici L, Dennis VA (2013) Flavonoid naringenin: a potential immunomodulator for Chlamydia trachomatis inflammation. Mediators Inflamm 2013:102457
Sahu N, Mishra G, Chandra HK, Nirala SK, Bhadauria M (2020) Naringenin mitigates antituberculosis drugs induced hepatic and renal injury in rats. J Tradit Complement Med 10(1):26–35
Wang J, Chen R, Tang S, Lv X, Wu S, Zhang Y et al (2015) Analysis of IL-6, STAT3 and HSPA1L gene polymorphisms in anti-tuberculosis drug-induced hepatitis in a nested case-control study. PLoS ONE 10(3):e0118862
Freireich EJ, Gehan EA, Rall DP, Schmidt LH, Skipper HE (1966) Quantitative comparison of toxicity of anticancer agents in mouse, rat, hamster, dog, monkey, and man. Cancer Chemother Rep 50(4):219–244
Arifin WN, Zahiruddin WM (2017) Sample Size Calculation in Animal Studies Using Resource Equation Approach. Malays J Med Sci 24(5):101–105
Kato R, Gillette JR (1965) Sex differences in the effects of abnormal physiological states on the metabolism of drugs by rat liver microsomes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 150(2):285–291
Sharma SK, Krishna Murti CR (1968) Production of lipid peroxides by brain. J Neurochem 15(2):147–149
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275
Zlatkis A, Zak B, Boyle AJ (1953) A new method for the direct determination of serum cholesterol. J Lab Clin Med 41(3):486–492
Neri BP, Frings CS (1973) Improved method for determination of triglycerides in serum. Clin Chem 19(10):1201–1202
Paglia DE, Valentine WN (1967) Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70(1):158–169
Tayarani I, Cloëz I, Clément M, Bourre JM (1989) Antioxidant enzymes and related trace elements in aging brain capillaries and choroid plexus. J Neurochem 53(3):817–824
Askar MA, Sumathy K, Baquer NZ (1996) Regulation and properties of purified glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from rat brain. Indian J Biochem Biophys 33(6):512–518
Sahu N, Mishra G, Chandra HK, Nirala SK, Bhadauria M (2018) Propolis modulates cellular biochemistry, antioxidants, cytokine profile, histological and ultra-morphological status against antituberculosis drugs induced hepatic injury. Asian Pac J Trop Med 11(11):609
Snedecor GW, Cochran WG (1980) Statistical methods. Iowa state university press. Ames Iowa
Rakshit S, Shukla P, Verma A, Kumar Nirala S, Bhadauria M (2021) Protective role of rutin against combined exposure to lipopolysaccharide and D-galactosamine-induced dysfunctions in liver, kidney, and brain: Hematological, biochemical, and histological evidences. J Food Biochem 45(2):e13605
Cavia-Saiz M, Busto MD, Pilar-Izquierdo MC, Ortega N, Perez-Mateos M, Muñiz P (2010) Antioxidant properties, radical scavenging activity and biomolecule protection capacity of flavonoid naringenin and its glycoside naringin: a comparative study. J Sci Food Agric 90(7):1238–1244
Martinez RM, Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Steffen VS, Caviglione CV, Vignoli JA, Barbosa DS et al (2015) Naringenin Inhibits UVB Irradiation-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in the Skin of Hairless Mice. J Nat Prod 78(7):1647–1655
Pandit A, Sachdeva T, Bafna P (2012) Drug-induced hepatotoxicity: a review. J Appl Pharm Sci 2(5):233–243
Rakshit S, Nirala SK, Bhadauria M (2020) Gallic Acid Protects from Acute Multiorgan Injury Induced by Lipopolysaccharide and D-galactosamine. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 21(14):1489–1504
He X, Song Y, Wang L, Xu J (2020) Protective effect of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate on isoniazid/rifampicin–induced liver injury in rats. Mol Med Rep 21(1):463–469
Bais B, Saiju P (2014) Ameliorative effect of Leucas cephalotes extract on isoniazid and rifampicin induced hepatotoxicity. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 4:S633–S8
Upadhyay G, Kumar A, Singh MP (2007) Effect of silymarin on pyrogallol- and rifampicin-induced hepatotoxicity in mouse. Eur J Pharmacol 565(1–3):190–201
van Acker FA, Hulshof JW, Haenen GR, Menge WM, van der Vijgh WJ, Bast A (2001) New synthetic flavonoids as potent protectors against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Free Radic Biol Med 31(1):31–37
Young IS, Woodside JV (2001) Antioxidants in health and disease. J Clin Pathol 54(3):176–186
Hernández-Aquino E, Muriel P (2018) Beneficial effects of naringenin in liver diseases: Molecular mechanisms. World J Gastroenterol 24(16):1679–1707
Rashmi R, Bojan Magesh S, Mohanram Ramkumar K, Suryanarayanan S, Venkata SubbaRao M (2018) Antioxidant Potential of Naringenin Helps to Protect Liver Tissue from Streptozotocin-Induced Damage. Rep Biochem Mol Biol 7(1):76–84
Ozkaya A, Sahin Z, Dag U, Ozkaraca M (2016) Effects of Naringenin on Oxidative Stress and Histopathological Changes in the Liver of Lead Acetate Administered Rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 30(5):243–248
Wieckowska A, Papouchado BG, Li Z, Lopez R, Zein NN, Feldstein AE (2008) Increased hepatic and circulating interleukin-6 levels in human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 103(6):1372–1379
Kineman RD, Del Rio-Moreno M, Sarmento-Cabral A (2018) 40 YEARS of IGF1: Understanding the tissue-specific roles of IGF1/IGF1R in regulating metabolism using the Cre/loxP system. J Mol Endocrinol 61(1):T187–t98
Wit JM, Camacho-Hübner C (2011) Endocrine regulation of longitudinal bone growth. Endocr Dev 21:30–41
Yakar S, Rosen CJ, Beamer WG, Ackert-Bicknell CL, Wu Y, Liu JL et al (2002) Circulating levels of IGF-1 directly regulate bone growth and density. J Clin Invest 110(6):771–781
Tseng YT, Hsu HT, Lee TY, Chang WH, Lo YC (2021) Naringenin, a dietary flavanone, enhances insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor-mediated antioxidant defense and attenuates methylglyoxal-induced neurite damage and apoptotic death. Nutr Neurosci 24(1):71–81
Zheng YR, Suntharalingam K, Johnstone TC, Yoo H, Lin W, Brooks JG et al (2014) Pt(IV) prodrugs designed to bind non-covalently to human serum albumin for drug delivery. J Am Chem Soc 136(24):8790–8798
Byrne JA, Strautnieks SS, Mieli-Vergani G, Higgins CF, Linton KJ, Thompson RJ (2002) The human bile salt export pump: characterization of substrate specificity and identification of inhibitors. Gastroenterology 123(5):1649–1658
Mishra G, Chandra HK, Sahu N, Nirala SK, Bhadauria M (2018) Ameliorative effect of Pergularia daemia (Forssk.) Chiov. leaves extract against anti-tuberculosis drugs induced liver injury in rats. Asian Pac J Trop Med 11(9):518
Reddy GJ, Reddy VP, Sreepavani M, Rajaram C, Kumar SN, Kanhere RS (2013) Evaluation of hepatoprotective potential of ethanolic extract of Ixora pavetta against isoniazid and rifampicin induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Drug Invent Today 5(3):201–206
Santhosh S, Sini TK, Anandan R, Mathew PT (2006) Effect of chitosan supplementation on antitubercular drugs-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Toxicology 219(1–3):53–59
Priscilla DH, Jayakumar M, Thirumurugan K (2015) Flavanone naringenin: An effective antihyperglycemic and antihyperlipidemic nutraceutical agent on high fat diet fed streptozotocin induced type 2 diabetic rats. J Funct Foods 14:363–373
Zaverucha-do-Valle C, Monteiro SP, El-Jaick KB, Rosadas LA, Costa MJ, Quintana MS et al (2014) The role of cigarette smoking and liver enzymes polymorphisms in anti-tuberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity in Brazilian patients. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 94(3):299–305
Huang YS, Chern HD, Su WJ, Wu JC, Chang SC, Chiang CH et al (2003) Cytochrome P450 2E1 genotype and the susceptibility to antituberculosis drug-induced hepatitis. Hepatology 37(4):924–930
Bhadauria M, Nirala SK, Shukla S (2007) Propolis protects CYP 2E1 enzymatic activity and oxidative stress induced by carbon tetrachloride. Mol Cell Biochem 302(1–2):215–224
Jaswal A, Sinha N, Bhadauria M, Shrivastava S, Shukla S (2013) Therapeutic potential of thymoquinone against anti-tuberculosis drugs induced liver damage. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 36(3):779–786
Hunt NJ, Kang SWS, Lockwood GP, Le Couteur DG, Cogger VC (2019) Hallmarks of Aging in the Liver. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 17:1151–1161
Acknowledgements
Chhattisgarh Institute of Medical Sciences (CIMS), Bilaspur generously provided antituberculosis drugs for conducting experiments. Technical support was extended from All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi for electron microscopy.
Funding
The research work was financially supported by University Grants Commission, New Delhi [(F42-520/2013(SR) dated 23-03-2013] sanctioned to Dr. Monika Bhadauria.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors hold no conflict of interest on any issue from this study.
Ethical approval:
All the experiments were held in accordance with the rules set by the Committee for the Purpose of Control and Supervision of Experiments on Animals (CPCSEA) India. All the protocols of present study were approved by institutional animal ethics committee (994/Ere/Go/06/CPCSEA).
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sahu, N., Rakshit, S., Nirala, S.K. et al. Naringenin protects hepato-renal tissues against antituberculosis drugs induced toxic manifestations by modulating interleukin-6, insulin like growth factor-1, biochemical and ultra-structural integrity. Mol Biol Rep 50, 1019–1031 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07799-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07799-y