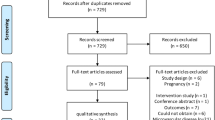
Abstract
Altered vascular function and pathological angiogenesis are important factors common to the development of obesity and obesity-associated diseases. Most human studies relating obesity and angiogenesis have compared levels of angiogenic factors in obesity without looking at the serum angiogenic capacity which reflects the balance between the effects of angiogenic and angiostatic factors. Therefore, in this cross-sectional study, the serum angiogenic potential and levels of angiogenic factors in serum of obese (BMI > 25 kg/m2) and lean subjects (BMI < 23 kg/m2), with no history of obesity associated co-morbidities, were assessed. Serum angiogenic potential was significantly higher (p < 0.0001) in both male (n = 67) and female (n = 35) obese subjects and showed a positive correlation (r = 0.4, p < 0.0001) with BMI. Serum levels of the angiogenic factors, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and angiopoietin were significantly higher in obese subjects. Levels of angiostatic factors such as angiostatin, endostatin were not altered in obese male subjects but were elevated in female obese subjects. Angiogenic potential and levels of VEGF did not vary in obese subjects with high HOMA-IR compared to obese subjects with low HOMA-IR. These results suggest that the angiogenic potential of serum was elevated in obesity and that insulin resistance may not contribute to the increased angiogenic potential in obesity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao Y. Angiogenesis modulates adipogenesis and obesity. J Clin Invest. 2007;117:2362–8.
Chung AS, Ferrara N. Developmental and pathological angiogenesis. Ann Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2011;27:563–84.
Lijnen HR. Angiogenesis and obesity. Cardiovasc Res. 2008;78:286–93.
Tinahones FJ, Coín-Aragüez L, Mayas MD, Garcia-Fuentes E, Hurtado-del-Pozo C, Vendrell J, et al. Obesity-associated insulin resistance is correlated to adipose tissue vascular endothelial growth factors and metalloproteinase levels. BMC Physiol. 2012;12:4.
Gealekman O, Gusevan N, Hartigan C, Apotheker S, Gorgoglione M, Gurav K, et al. Depot specific differences and insufficient subcutaneous adipose tissue angiogenesis in human obesity. Circulation. 2011;123:186–94.
Michaildou Z, Turban S, Miller E, Zou X, Schrader J, Ratcliffe PJ, et al. Increased angiogenesis protects against adipose hypoxia and fibrosis in metabolic disease resistant 11-β hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (HSD 1) deficient mice. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:4188–97.
Wree A, Mayer A, Westphal S, Beilfuss A, Canbay A, Schick RR, et al. Adipokine expression in brown and white adipocyte in response to hypoxia. J Endocrinol Invest. 2012;35:522–7.
Sung HK, Doh KO, Son JE, Park JG, Bae Y, Choi S, et al. Adipose VEGF regulates metabolic homeostasis through angiogenesis. Cell Metab. 2013;17:61–72.
Silha JV, Krsek M, Sucharda P, Murphy LJ. Angiogenic factors are elevated in overweight and obese individuals. Int J Obes. 2005;29:1308–14.
Bell LN, Ward JL, Degawa-Yamauchi M, Bovenkerk JE, Jones R, Cacucci BM, et al. Adipose tissue production of hepatocyte growth factor contributes to elevated serum HGF in obesity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006;291:843–8.
Bouloumie A, Drexler HC, Lafontan M, Busse R. Leptin, the product of Ob gene, promotes angiogenesis. Circ Res. 1998;83:1059–66.
Brakenhielm E, Veitonmaki N, Cao R, Kihara S, Matsuzawa Y, Zhivotovsky B, et al. Adiponectin-induced anti-angiogenesis and anti-tumour activity involve caspase-mediated endothelial cell apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:2476–81.
Matsubara M, Maruoka S, Katayose S. Inverse relationship between plasma adiponectin and leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese women. Eur J Endocrinol. 2002;147:173–80.
Kahn BB, Flier JS. Obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 2000;106:473–81.
Ribatti D, Gualandris A, Bastaki M, Vacca A, Iurlaro M, Roncali L, et al. New model for the study of angiogenesis and anti-angiogenesis in the chick embryo chorio-allantoic membrane: the gelatin sponge/chorio-allantoic membrane assay. J Vasc Res. 1997;34:455–63.
Kumar VBS, Viji RI, Kiran MS, Sudhakaran PR. Endothelial cell response to lactate: implication of PAR modification of VEGF. J Cell Physiol. 2007;211:477–85.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985;28:412–9.
Nizamuddin S, Govindaraj P, Saxena S, Kashyap M, Mishra A, Singh S, et al. A novel gene THSD7A is associated with obesity. Int J of Obesity. 2015;39:1662–5.
Sudhakar M, Silambanan S, Chandran AS, Prabhakaran AA, Ramakrishnan R. C-reactive protein (crp) and leptin receptor in obesity: binding of monomeric crp to leptin receptor. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1167. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.01167.
Chen K, Li F, Li J, Cai H, Strom S, Bisello A, et al. Induction of leptin resistance through direct interaction of C-reactive protein with leptin. Nat Med. 2006;12:25–32.
Seida A, Wada J, Kunitomi M, Tsuchiyama Y, Miyatake N, Fujii M, et al. Serum β-FGF levels are reduced in Japanese overweight men and restored by a 6-month exercise education. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2003;27:1325–31.
Garufi G, Seyhan AA, Pascarica M. Elevated secreted frizzled-related protein-4 in obesity: a potential role in adipose tissue dysfunction. Obesity. 2015;23:24–7.
Loebig M, Klement J, Schmoller A, Betz S, Heuck N, Schweiger U, et al. Evidence for a relationship between VEGF and BMI independent of insulin sensitivity by glucose clamp procedure in a homogenous group healthy young men. PLoS One. 2010;7:5(9):e12610. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0012610.
Tsuji T, Kelly NJ, Takahashi S, Leme AS, Houghton AM, Shapiro SD. Macrophage elastase suppresses white adipose tissue expansion with cigarette smoking. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014;51:822–9.
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by financial assistance in the form of a TSS fellowship from ICMR, New Delhi to MS. Support from the Medical superintendent and staff of Sri Ramachandra Medical college hospital in collection of samples is gratefully acknowledged.
Funding
The study was supported by financial assistance in the form of a TSS fellowship from Indian Council for Medical Research, New Delhi to Manu Sudhakar.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors Manu Sudhakar, Santhi Silambanan, Athira. A. Prabhakaran, and Ramya Ramakrishnan declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sudhakar, M., Silambanan, S., Prabhakaran, A.A. et al. Angiogenic Potential, Circulating Angiogenic Factors and Insulin Resistance in Subjects with Obesity. Ind J Clin Biochem 36, 43–50 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-019-0816-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-019-0816-8