Abstract
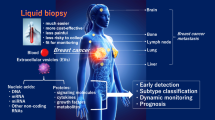
This article examines liquid biopsy using non-coding RNAs and extracellular vesicles in detail. Liquid biopsy is emerging as a prominent non-invasive diagnostic tool in the treatment of breast cancer. We will elucidate the roles of these molecules in early detection, monitoring treatment effectiveness, and prognostic assessment of breast cancer. Additionally, the clinical significance of these molecules will be discussed. We aim to delve into the distinct characteristics of these molecules and their possible roles in breast cancer management, with an anticipation of their contribution to future diagnostic and therapeutic advancements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shyamala K, Girish HC, Murgod S. Risk of tumor cell seeding through biopsy and aspiration cytology. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2014;4:5–11.
Alix-Panabières C, Pantel K. Liquid biopsy: from Discovery to clinical application. Cancer Discov. 2021;11:858–73.
Nikanjam M, Kato S, Kurzrock R. Liquid biopsy: current technology and clinical applications. J Hematol Oncol. 2022;15:131.
Zhang Z, Zhang J, Diao L, Han L. Small non-coding RNAs in human cancer: function, clinical utility, and characterization. Oncogene. 2021;40:1570–7.
Peng Y, Croce CM. The role of microRNAs in human cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2016;1:15004.
Miska EA. How microRNAs control cell division, differentiation and death. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2005;15:563–8.
miRBase. 2023.
Ling L, Aldoghachi AF, Chong ZX, Ho WY, Yeap SK, Chin RJ, et al. Addressing the clinical feasibility of adopting circulating miRNA for breast cancer detection, monitoring and management with artificial intelligence and machine learning platforms. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:15382.
Li R, Qu H, Wang S, Chater JM, Wang X, Cui Y, et al. CancerMIRNome: an interactive analysis and visualization database for miRNome profiles of human cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50:D1139–46.
Baldasici O, Pileczki V, Cruceriu D, Gavrilas LI, Tudoran O, Balacescu L, et al. Breast cancer-delivered exosomal miRNA as liquid biopsy biomarkers for metastasis prediction: a focus on translational research with clinical applicability. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:9371.
Cortez MA, Anfossi S, Ramapriyan R, Menon H, Atalar SC, Aliru M, et al. Role of miRNAs in immune responses and immunotherapy in cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2019;58:244–53.
Chen Y, Gao DY, Huang L. In vivo delivery of miRNAs for cancer therapy: challenges and strategies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;81:128–41.
Zangouei AS, Zangoue M, Taghehchian N, Zangooie A, Rahimi HR, Saburi E, et al. Cell cycle related long non-coding RNAs as the critical regulators of breast cancer progression and metastasis. Biol Res. 2023;56:1.
Zhou W, Ye XL, Xu J, Cao MG, Fang ZY, Li LY, et al. The lncRNA H19 mediates breast cancer cell plasticity during EMT and MET plasticity by differentially sponging miR-200b/c and let-7b. Sci Signal. 2017;10:eaak9557.
Hu Q, Ye Y, Chan LC, Li Y, Liang K, Lin A, et al. Oncogenic lncRNA downregulates cancer cell antigen presentation and intrinsic tumor suppression. Nat Immunol. 2019;20:835–51.
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings HM, Wong DJ, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature. 2010;464:1071–6.
Wang YL, Liu LC, Hung Y, Chen CJ, Lin YZ, Wu WR, Wang SC. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR in circulatory exosomes is correlated with ErbB2/HER2 positivity in breast cancer. Breast. 2019;46:64–9.
Mitobe Y, Ikeda K, Suzuki T, Takagi K, Kawabata H, Horie-Inoue K, Inoue S. ESR1-stabilizing long noncoding RNA TMPO-AS1 promotes hormone-refractory breast cancer progression. Mol Cell Biol. 2019;39:e00261-19.
Xia E, Shen Y, Bhandari A, Zhou X, Wang Y, Yang F, Wang O. Long non-coding RNA LINC00673 promotes breast cancer proliferation and metastasis through regulating B7–H6 and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Am J Cancer Res. 2018;8:1273–87.
Li S, Zhou J, Wang Z, Wang P, Gao X, Wang Y. Long noncoding RNA GAS5 suppresses triple negative breast cancer progression through inhibition of proliferation and invasion by competitively binding miR-196a-5p. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;104:451–7.
Deng C, Zhang B, Zhang Y, Xu X, Xiong D, Chen X, Wu J. A long non-coding RNA OLBC15 promotes triple-negative breast cancer progression via enhancing ZNF326 degradation. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020;34: e23304.
Jeck WR, Sharpless NE. Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32:453–61.
Li Y, Zheng Q, Bao C, Li S, Guo W, Zhao J, et al. Circular RNA is enriched and stable in exosomes: a promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Cell Res. 2015;25:981–4.
Tang X, Ren H, Guo M, Qian J, Yang Y, Gu C. Review on circular RNAs and new insights into their roles in cancer. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021;19:910–28.
Wang J, Zhang Q, Zhou S, Xu H, Wang D, Feng J, et al. Circular RNA expression in exosomes derived from breast cancer cells and patients. Epigenomics. 2019;11:411–21.
Chen X, Liang H, Zhang J, Zen K, Zhang CY. Horizontal transfer of microRNAs: molecular mechanisms and clinical applications. Protein Cell. 2012;3:28–37.
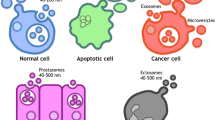
Théry C, Witwer KW, Aikawa E, Alcaraz MJ, Anderson JD, Andriantsitohaina R, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7:1535750.
Lee Y, Ni J, Beretov J, Wasinger VC, Graham P, Li Y. Recent advances of small extracellular vesicle biomarkers in breast cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Mol Cancer. 2023;22:33.
Shefer A, Yalovaya A, Tamkovich S. Exosomes in breast cancer: involvement in tumor dissemination and prospects for liquid biopsy. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:8845.
Xu R, Rai A, Chen M, Suwakulsiri W, Greening DW, Simpson RJ. Extracellular vesicles in cancer—implications for future improvements in cancer care. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018;15:617–38.
Jung HH, Kim JY, Cho EY, Oh JM, Lee JE, Kim SW, et al. Elevated level of nerve growth factor (NGF) in Serum-derived exosomes predicts poor survival in patients with breast cancer undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Cancers. 2021;13:5260.
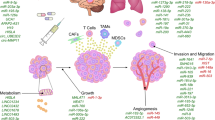
Tan Y, Luo X, Lv W, Hu W, Zhao C, Xiong M, et al. Tumor-derived exosomal components: the multifaceted roles and mechanisms in breast cancer metastasis. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12:547.
Chen WX, Cai YQ, Lv MM, Chen L, Zhong SL, Ma TF, et al. Exosomes from docetaxel-resistant breast cancer cells alter chemosensitivity by delivering microRNAs. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:9649–59.
Yang SS, Ma S, Dou H, Liu F, Zhang SY, Jiang C, et al. Breast cancer-derived exosomes regulate cell invasion and metastasis in breast cancer via miR-146a to activate cancer associated fibroblasts in tumor microenvironment. Exp Cell Res. 2020;391: 111983.
Chen B, Sang Y, Song X, Zhang D, Wang L, Zhao W, et al. Exosomal miR-500a-5p derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and metastasis through targeting USP28. Theranostics. 2021;11:3932–47.
Encarnación-Medina J, Godoy L, Matta J, Ortiz-Sánchez C. Identification of exo-miRNAs: a summary of the efforts in translational studies involving triple-negative breast cancer. Cells. 2023;12:1339.
Yu W, Hurley J, Roberts D, Chakrabortty SK, Enderle D, Noerholm M, et al. Exosome-based liquid biopsies in cancer: opportunities and challenges. Ann Oncol. 2021;32:466–77.
Curtaz CJ, Reifschläger L, Strähle L, Feldheim J, Feldheim JJ, Schmitt C, et al. Analysis of microRNAs in exosomes of breast cancer patients in search of molecular prognostic factors in brain metastases. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:3683.
Luo T, Kang Y, Liu Y, Li J, Li J. Small extracellular vesicles in breast cancer brain metastasis and the prospect of clinical application. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1162089.
Hoshino A, Kim HS, Bojmar L, Gyan KE, Cioffi M, Hernandez J, et al. Extracellular vesicle and particle biomarkers define multiple human cancers. Cell. 2020;182:1044-1061.e18.
Chanteloup G, Cordonnier M, Isambert N, Bertaut A, Hervieu A, Hennequin A, et al. Monitoring HSP70 exosomes in cancer patients’ follow up: a clinical prospective pilot study. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020;9:1766192.
Shimomura A, Shiino S, Kawauchi J, Takizawa S, Sakamoto H, Matsuzaki J, et al. Novel combination of serum microRNA for detecting breast cancer in the early stage. Cancer Sci. 2016;107:326–34.
Hannafon BN, Trigoso YD, Calloway CL, Zhao YD, Lum DH, Welm AL, et al. Plasma exosome microRNAs are indicative of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2016;18:90.
Yoshikawa M, Iinuma H, Umemoto Y, Yanagisawa T, Matsumoto A, Jinno H. Exosome-encapsulated microRNA-223-3p as a minimally invasive biomarker for the early detection of invasive breast cancer. Oncol Lett. 2018;15:9584–92.
Hirschfeld M, Rucker G, Weiss D, Berner K, Ritter A, Jager M, Erbes T. Urinary Exosomal microRNAs as potential non-invasive biomarkers in breast cancer detection. Mol Diagn Ther. 2020;24:215–32.
Zhang L, Xiao H, Karlan S, Zhou H, Gross J, Elashoff D, et al. Discovery and preclinical validation of salivary transcriptomic and proteomic biomarkers for the non-invasive detection of breast cancer. PLoS ONE. 2010;5: e15573.
Inubushi S, Kawaguchi H, Mizumoto S, Kunihisa T, Baba M, Kitayama Y, et al. Oncogenic miRNAs identified in tear exosomes from metastatic breast cancer patients. Anticancer Res. 2020;40:3091–6.
Zhong G, Wang K, Li J, Xiao S, Wei W, Liu J. Determination of serum exosomal H19 as a noninvasive biomarker for breast cancer diagnosis. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:2563–71.
Zhang K, Luo Z, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Wu L, Liu L, et al. Circulating lncRNA H19 in plasma as a novel biomarker for breast cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2016;17:187–94.
Chu M, Fang Y, Jin Y. CircRNAs as promising biomarker in diagnosis of breast cancer: an updated meta-analysis. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021;35: e23934.
Yu Y, Zheng W, Ji C, Wang X, Chen M, Hua K, et al. Tumor-derived circRNAs as circulating biomarkers for breast cancer. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13: 811856.
Yin WB, Yan MG, Fang X, Guo JJ, Xiong W, Zhang RP. Circulating circular RNA hsa_circ_0001785 acts as a diagnostic biomarker for breast cancer detection. Clin Chim Acta. 2018;487:363–8.
Hosseinpour Z, Rezaei Tavirani M, Akbari ME. Stage analysis of breast cancer metabolomics: a system biology approach. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023;24:1571–82.
Sueta A, Yamamoto Y, Tomiguchi M, Takeshita T, Yamamoto-Ibusuki M, Iwase H. Differential expression of exosomal miRNAs between breast cancer patients with and without recurrence. Oncotarget. 2017;8:69934–44.
Souza KCB, Evangelista AF, Leal LF, Souza CP, Vieira RA, Causin RL, et al. Identification of cell-free circulating microRNAs for the detection of early breast cancer and molecular subtyping. J Oncol. 2019;2019:8393769.
Stevic I, Muller V, Weber K, Fasching PA, Karn T, Marme F, et al. Specific microRNA signatures in exosomes of triple-negative and HER2-positive breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant therapy within the GeparSixto trial. BMC Med. 2018;16:179.
Hong F, Li N, Feng Z, Zheng Y, Zhu C, Zhang F. Exosomal microRNAs as novel diagnostic biomarkers in breast cancer: a systematic evaluation and meta-analysis. Asian J Surg. 2023;46:4727–36.
Zhang Z, Zhang L, Yu G, Sun Z, Wang T, Tian X, et al. Exosomal miR-1246 and miR-155 as predictive and prognostic biomarkers for trastuzumab-based therapy resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2020;86:761–72.
Long F, Ma H, Hao Y, Tian L, Li Y, Li B, et al. A novel exosome-derived prognostic signature and risk stratification for breast cancer based on multi-omics and systematic biological heterogeneity. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023;21:3010–23.
Bao S, Hu T, Liu J, Su J, Sun J, Ming Y, et al. Genomic instability-derived plasma extracellular vesicle-microRNA signature as a minimally invasive predictor of risk and unfavorable prognosis in breast cancer. J Nanobiotechnol. 2021;19:22.
Hammond SM. An overview of microRNAs. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;87:3–14.
To NH, Nguyen HQ, Thiolat A, Liu B, Cohen J, Radosevic-Robin N, Belkacemi Y. Radiation therapy for triple-negative breast cancer: emerging role of microRNAs as biomarkers and radiosensitivity modifiers. A systematic review. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2022;193:265–79.
Han X, Li M, Xu J, Fu J, Wang X, Wang J, et al. miR-1275 targets MDK/AKT signaling to inhibit breast cancer chemoresistance by lessening the properties of cancer stem cells. Int J Biol Sci. 2023;19:89–103.
Todorova VK, Byrum SD, Gies AJ, Haynie C, Smith H, Reyna NS, Makhoul I. Circulating exosomal microRNAs as predictive biomarkers of neoadjuvant chemotherapy response in breast cancer. Curr Oncol. 2022;29:613–30.
Salvador-Coloma C, Santaballa A, Sanmartin E, Calvo D, Garcia A, Hervas D, et al. Immunosuppressive profiles in liquid biopsy at diagnosis predict response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2020;139:119–34.
Di Cosimo S, Appierto V, Pizzamiglio S, Silvestri M, Baselga J, Piccart M, et al. Early modulation of circulating microRNAs levels in HER2-positive breast cancer patients treated with trastuzumab-based neoadjuvant therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:1386.
Sadovska L, Zayakin P, Eglītis K, Endzeliņš E, Radoviča-Spalviņa I, Avotiņa E, et al. Comprehensive characterization of RNA cargo of extracellular vesicles in breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Front Oncol. 2022;12:1005812.
Mitobe Y, Ikeda K, Sato W, Kodama Y, Naito M, Gotoh N, et al. Proliferation-associated long noncoding RNA, TMPO-AS1, is a potential therapeutic target for triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 2020;111:2440–50.
Rezaie J, Feghhi M, Etemadi T. A review on exosomes application in clinical trials: perspective, questions, and challenges. Cell Commun Signal. 2022;20:145.
Bunggulawa EJ, Wang W, Yin T, Wang N, Durkan C, Wang Y, Wang G. Recent advancements in the use of exosomes as drug delivery systems. J Nanobiotechnol. 2018;16:81.
Xu Z, Zeng S, Gong Z, Yan Y. Exosome-based immunotherapy: a promising approach for cancer treatment. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:160.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Ms. Masayo Kawamura for her kind assistance and administrative support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. The material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by KH. The first draft of the manuscript was written by KH and all authors commented on previous versions. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. Shimomura reports grants from Chugai Pharmaceutical, Taiho Pharmaceutical, AstraZeneca, Mochida Pharmaceutical, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, and Gilead Sciences outside the submitted work, and lecture fees from Chugai Pharmaceutical, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli-Lilly, Kyowa Kirin, AstraZeneca, MSD, Gilead Sciences, Pfizer, Exact Science, and Nihon Medi-Physics outside the submitted work. The other authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Hashimoto, K., Ochiya, T. & Shimomura, A. Liquid biopsy using non-coding RNAs and extracellular vesicles for breast cancer management. Breast Cancer (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-024-01562-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-024-01562-w