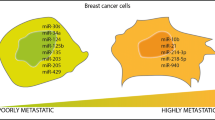
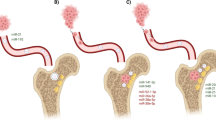
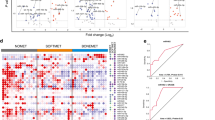
Abstract
Breast cancer (BC) bone metastasis is primarily osteolytic and has limited therapeutic options. Metastasized BC cells prime the secondary environment in bone by forming a tumor niche, which favors their homing and colonization. The tumor microenvironment (TME) is primarily generated by the cancer cells. Bone TME is an intricate network of multiple cells, including altered bone, tumor, stromal, and immune cells. Recent findings highlight the significance of small non-coding microRNAs (miRNAs) in influencing TME during tumor metastasis. MiRNAs from TME-resident cells facilitate the interaction between the tumor and its microenvironment, thereby regulating the biological processes of tumors. These miRNAs can serve as oncogenes or tumor suppressors. Hence, both miRNA inhibitors and mimics are extensively utilized in pre-clinical trials for modulating the phenotypes of tumor cells and associated stromal cells. This review briefly summarizes the recent developments on the functional role of miRNAs secreted directly or indirectly from the TME-resident cells in facilitating tumor growth, progression, and metastasis. This information would be beneficial in developing novel targeted therapies for BC.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BC:
-
Breast cancer
- BME:
-
Bone microenvironment
- TME:
-
Tumor microenvironment
- TAM:
-
Tumor-associated macrophages
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- EMT:
-
Epithelial mesenchymal transition
- CTC:
-
Circulating tumor cell
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- CAF:
-
Cancer-associated fibroblast
- MARCKS:
-
Myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics. CA: A Cancer J Clin. 2022;72(1):7–33.
Jiang X, Chen G, Sun L, Liu C, Zhang Y, Liu M, Liu C. Characteristics and survival in bone metastatic breast cancer patients with different hormone receptor status: A population-based cohort study. Front Oncol. 2022;12: 977226.
Farach-Carson MC, Lin SH, Nalty T, Satcher RL. Sex Differences and Bone Metastases of Breast, Lung, and Prostate Cancers: Do Bone Homing Cancers Favor Feminized Bone Marrow? Front Oncol. 2017;7:163.
Shao H, Varamini P. Breast Cancer Bone Metastasis: A Narrative Review of Emerging Targeted Drug Delivery Systems. Cells. 2022;11(3):388.
Xiao Y, Yu D. Tumor microenvironment as a therapeutic target in cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 2021;221: 107753.
Baghban R, Roshangar L, Jahanban-Esfahlan R, Seidi K, Ebrahimi-Kalan A, Jaymand M, Kolahian S, Javaheri T, Zare P. Tumor microenvironment complexity and therapeutic implications at a glance. Cell Commun Signal. 2020;18(1):59.
Mantovani A, Marchesi F, Malesci A, Laghi L, Allavena P. Tumour-associated macrophages as treatment targets in oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2017;14(7):399–416.
Pan Y, Yu Y, Wang X, Zhang T. Tumor-associated macrophages in tumor immunity. Front Immunol. 2020;11: 583084.
Feng Y, Ye Z, Song F, He Y, Liu J. The Role of TAMs in Tumor Microenvironment and New Research Progress. Stem Cells Int. 2022;15:5775696.
Wilson C, Brown H, Holen I. The endocrine influence on the bone microenvironment in early breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2016;23(12):R567–76.
Zarrer J, Haider MT, Smit DJ, Taipaleenmäki H. Pathological Crosstalk between Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells and the Bone Microenvironment. Biomolecules. 2020;10(2):337.
Kolb AD, Shupp AB, Mukhopadhyay D, Marini FC, Bussard KM. Osteoblasts are “educated” by crosstalk with metastatic breast cancer cells in the bone tumor microenvironment. Breast Cancer Res : BCR. 2019;21(1):31.
Haider MT, Smit DJ, Taipaleenmäki H. The Endosteal Niche in Breast Cancer Bone Metastasis. Front Oncol. 2020;10:335.
Wang WT, Han C, Sun YM, Chen TQ, Chen YQ. Noncoding RNAs in cancer therapy resistance and targeted drug development. J Hematol Oncol. 2019;12(1):55.
Dvorská D, Braný D, Ňachajová M, Halašová E, Danková Z. Breast Cancer and the Other Non-Coding RNAs. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(6):3280.
Prabhu KS, Raza A, Karedath T, Raza SS, Fathima H, Ahmed EI, Kuttikrishnan S, Therachiyil L, Kulinski M, Dermime S, Junejo K, Steinhoff M, Uddin S. Non-Coding RNAs as Regulators and Markers for Targeting of Breast Cancer and Cancer Stem Cells. Cancers. 2020;12(2):351.
Crudele F, Bianchi N, Reali E, Galasso M, Agnoletto C, Volinia S. The network of non-coding RNAs and their molecular targets in breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):61.
Najminejad H, Farhadihosseinabadi B, Dabaghian M, Dezhkam A, Rigi Yousofabadi E, Najminejad R, Abdollahpour-Alitappeh M, Karimi MH, Bagheri N, Mahi-Birjand M, Ghasemi N, Mazaheri M, Kalantar SM, Seifalian A, Sheikhha MH. Key Regulatory miRNAs and their Interplay with Mechanosensing and Mechanotransduction Signaling Pathways in Breast Cancer Progression. Mol Cancer Res: MCR. 2020;18(8):1113–28.
Mansoori B, Baradaran B, Nazari A, Gaballu FA, Cho WC, Mansoori B. MicroRNAs in the cancer cell-to-cell communication: An insight into biological vehicles. Biomed Pharmacother Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;153:113449.
Dai R, Liu M, Xiang X, Xi Z, Xu H. Osteoblasts and osteoclasts: an important switch of tumour cell dormancy during bone metastasis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res: CR. 2022;41(1):316.
Clézardin P, Coleman R, Puppo M, Ottewell P, Bonnelye E, Paycha F, Confavreux CB, Holen I. Bone metastasis: mechanisms, therapies, and biomarkers. Physiol Rev. 2021;101(3):797–855.
Taverna S, Giusti I, D’Ascenzo S, Pizzorno L, Dolo V. Breast Cancer Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Bone Metastasis Induction and Their Clinical Implications as Biomarkers. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(10):3573.
Liu T, Han C, Wang S, Fang P, Ma Z, Xu L, Yin R. Cancer-associated fibroblasts: an emerging target of anti-cancer immunotherapy. J Hematol Oncol. 2019;12(1):86.
Yin Z, Dong C, Jiang K, Xu Z, Li R, Guo K, Shao S, Wang L. Heterogeneity of cancer-associated fibroblasts and roles in the progression, prognosis, and therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hematol Oncol. 2019;12:101.
Mun JY, Leem SH, Lee JH, Kim HS. Dual Relationship Between Stromal Cells and Immune Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment. Front Immunol. 2022;13: 864739.
Hu D, Li Z, Zheng B, Lin X, Pan Y, Gong P, Zhuo W, Hu Y, Chen C, Chen L, Zhou J, Wang L. Cancer-associated fibroblasts in breast cancer: Challenges and opportunities. Cancer Commun. 2022;42(5):401–34.
Li Y, Wang C, Huang T, Yu X, Tian B. The role of cancer-associated fibroblasts in breast cancer metastasis. Front Oncol. 2023;13:1194835.
Tan Q, Xu L, Zhang J, Ning L, Jiang Y, He T, Luo J, Chen J, L v, Q., Yang, X., & Xie, H. Breast cancer cells interact with tumor-derived extracellular matrix in a molecular subtype-specific manner. Biomater Adv. 2023;146:213301.
Takai K, Le A, Weaver VM, Werb Z. Targeting the cancer-associated fibroblasts as a treatment in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7(50):82889–901.
Wang N, Liu W, Zheng Y, Wang S, Yang B, Li M, Song J, Zhang F, Zhang X, Wang Q, Wang Z. CXCL1 derived from tumor-associated macrophages promotes breast cancer metastasis via activating NF-κB/SOX4 signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(9):880.
Yang Q, Guo N, Zhou Y, Chen J, Wei Q, Han M. The role of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in tumor progression and relevant advance in targeted therapy. Acta pharmaceuticaSinica B. 2020;10(11):2156–70.
Wu K, Lin K, Li X, Yuan X, Xu P, Ni P, Xu D. Redefining Tumor-Associated Macrophage Subpopulations and Functions in the Tumor Microenvironment. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1731.
Riobo-Del Galdo NA, Lara Montero Á, Wertheimer EV. Role of Hedgehog Signaling in Breast Cancer: Pathogenesis and Therapeutics. Cells. 2019;8(4):375.
Hida K, Maishi N, Annan DA, Hida Y. Contribution of Tumor Endothelial Cells in Cancer Progression. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(5):1272.
Venetis K, Piciotti R, Sajjadi E, Invernizzi M, Morganti S, Criscitiello C, Fusco N. Breast Cancer with Bone Metastasis: Molecular Insights and Clinical Management. Cells. 2021;10(6):1377.
Akech J, Wixted JJ, Bedard K, van der Deen M, Hussain S, Guise TA, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Languino LR, Altieri DC, Pratap J, Keller E, Stein GS, Lian JB. Runx2 association with progression of prostate cancer in patients: mechanisms mediating bone osteolysis and osteoblastic metastatic lesions. Oncogene. 2010;29(6):811–21.
Shupp AB, Kolb AD, Mukhopadhyay D, Bussard KM. Cancer Metastases to Bone: Concepts, Mechanisms, and Interactions with Bone Osteoblasts. Cancers. 2018;10(6):182.
Göbel A, Dell’Endice S, Jaschke N, Pählig S, Shahid A, Hofbauer LC, Rachner TD. The Role of Inflammation in Breast and Prostate Cancer Metastasis to Bone. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(10):5078.
Xiang L, Gilkes DM. The Contribution of the Immune System in Bone Metastasis Pathogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(4):999.
Malla RR, Kiran P. Tumor microenvironment pathways: Cross regulation in breast cancer metastasis. Genes Dis. 2020;9(2):310–24.
Shinde AV, Humeres C, Frangogiannis NG. (2017) The role of α-smooth muscle actin in fibroblast-mediated matrix contraction and remodeling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1863;1:298–309.
Erdogan B, Webb DJ. Cancer-associated fibroblasts modulate growth factor signaling and extracellular matrix remodeling to regulate tumor metastasis. Biochem Soc Trans. 2017;45(1):229–36.
Takahashi H, Sakakura K, Kudo T, Toyoda M, Kaira K, Oyama T, Chikamatsu K. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote an immunosuppressive microenvironment through the induction and accumulation of protumoral macrophages. Oncotarget. 2017;8(5):8633–47.
Wei C, Yang C, Wang S, Shi D, Zhang C, Lin X, Liu Q, Dou R, Xiong B. Crosstalk between cancer cells and tumor associated macrophages is required for mesenchymal circulating tumor cell-mediated colorectal cancer metastasis. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):64.
Jiang M, Chen J, Zhang W, Zhang R, Ye Y, Liu P, Yu W, Wei F, Ren X, Yu J. Interleukin-6 Trans-Signaling Pathway Promotes Immunosuppressive Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells via Suppression of Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 3 in Breast Cancer. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1840.
Li F, Zhao Y, Wei L, Li S, Liu J. Tumor-infiltrating Treg, MDSC, and IDO expression associated with outcomes of neoadjuvant chemotherapy of breast cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2018;19(8):695–705.
Cole K, Pravoverov K, Talmadge JE. Role of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2021;40(2):391–411.
Russo E, Laffranchi M, Tomaipitinca L, Del Prete A, Santoni A, Sozzani S, Bernardini G. NK Cell Anti-Tumor Surveillance in a Myeloid Cell-Shaped Environment. Front Immunol. 2021;12: 787116.
Yan M, Zheng M, Niu R, Yang X, Tian S, Fan L, Li Y, Zhang S. Roles of tumor-associated neutrophils in tumor metastasis and its clinical applications. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10: 938289.
Rocamora-Reverte L, Melzer FL, Würzner R, Weinberger B. The Complex Role of Regulatory T Cells in Immunity and Aging. Front Immunol. 2021;11: 616949.
Sasidharan Nair V, Elkord E. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer therapy: a focus on T-regulatory cells. Immunol Cell Biol. 2018;96(1):21–33.
Huang Y, Wang H, Yue X, Li X. Bone serves as a transfer station for secondary dissemination of breast cancer. Bone Res. 2023;11(1):21.
Omokehinde T, Johnson RW. GP130 Cytokines in Breast Cancer and Bone. Cancers. 2020;12(2):326.
Sole C, Arnaiz E, Manterola L, Otaegui D, Lawrie CH. The circulating transcriptome as a source of cancer liquid biopsy biomarkers. Semin Cancer Biol. 2019;58:100–8.
Klinge CM. Non-Coding RNAs in Breast Cancer: Intracellular and Intercellular Communication. Non-coding RNA. 2018;4(4):40.
Zografos E, Zagouri F, Kalapanida D, Zakopoulou R, Kyriazoglou A, Apostolidou K, Gazouli M, Dimopoulos MA. Prognostic role of microRNAs in breast cancer: A systematic review. Oncotarget. 2019;10(67):7156–78.
Ghafouri-Fard S, KhanbabapourSasi A, Abak A, Shoorei H, Khoshkar A, Taheri M. Contribution of miRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Breast Cancer. Front Oncol. 2021;11: 768949.
Adinew GM, Taka E, Mendonca P, Messeha SS, Soliman KFA. The Anticancer Effects of Flavonoids through miRNAs Modulations in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Nutrients. 2021;13(4):1212.
Wieder R. Awakening of Dormant Breast Cancer Cells in the Bone Marrow. Cancers. 2023;15(11):3021.
Peng Y, Wang X, Guo Y, Peng F, Zheng N, He B, Ge H, Tao L, Wang Q. Pattern of cell-to-cell transfer of microRNA by gap junction and its effect on the proliferation of glioma cells. Cancer Sci. 2019;110(6):1947–58.
Zarzynska, J. M. (2017) The Role of Stem Cells in Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer - From Biology to Medicine. In Tech
Corcoran KE, Malhotra A, Molina CA, Rameshwar P. Stromal-derived factor-1alpha induces a non-canonical pathway to activate the endocrine-linked Tac1 gene in non-tumorigenic breast cells. J Mol Endocrinol. 2008;40(3):113–23.
Reddy BY, Greco SJ, Patel PS, Trzaska KA, Rameshwar P. RE-1-silencing transcription factor shows tumor-suppressor functions and negatively regulates the oncogenic TAC1 in breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106(11):4408–13.
Lim PK, Bliss SA, Patel SA, Taborga M, Dave MA, Gregory LA, Greco SJ, Bryan M, Patel PS, Rameshwar P. Gap junction-mediated import of microRNA from bone marrow stromal cells can elicit cell cycle quiescence in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2011;71(5):1550–60.
Bliss SA, Sinha G, Sandiford OA, Williams LM, Engelberth DJ, Guiro K, Isenalumhe LL, Greco SJ, Ayer S, Bryan M, Kumar R, Ponzio NM, Rameshwar P. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Stimulate Cycling Quiescence and Early Breast Cancer Dormancy in Bone Marrow. Cancer Res. 2016;76(19):5832–44.
Kogure A, Kosaka N, Ochiya T. Cross-talk between cancer cells and their neighbors via miRNA in extracellular vesicles: an emerging player in cancer metastasis. J Biomed Sci. 2019;26(1):7.
Liu Q, Peng F, Chen J. The Role of Exosomal MicroRNAs in the Tumor Microenvironment of Breast Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(16):3884.
Asgarpour K, Shojaei Z, Amiri F, Ai J, Mahjoubin-Tehran M, Ghasemi F, ArefNezhad R, Hamblin MR, Mirzaei H. Exosomal microRNAs derived from mesenchymal stem cells: cell-to-cell messages. Cell Commun Signal. 2020;18(1):149. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-020-00650-6.
Shu L, Wang Z, Wang Q, Wang Y, Zhang X. Signature miRNAs in peripheral blood monocytes of patients with gastric or breast cancers. Open Biol. 2018;8(10):180051.
Tavakoli F, Sartakhti JS, Manshaei MH, Basanta D. Cancer immunoediting: A game theoretical approach. In Silico Biol. 2021;14(1–2):1–12.
Kim SK, Cho SW. The evasion mechanisms of cancer immunity and drug intervention in the tumor microenvironment. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13: 868695.
Xing Y, Wang Z, Lu Z, Xia J, Xie Z, Jiao M, Liu R, Chu Y. MicroRNAs: immune modulators in cancer immunotherapy. Immunother Adv. 2021;1(1):ltab006.
He Z, Zhang S. Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Their Functional Transformation in the Hypoxic Tumor Microenvironment. Front Immunol. 2021;12: 741305.
Gao J, Liang Y, Wang L. Shaping Polarization Of Tumor-Associated Macrophages In Cancer Immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 2022;13: 888713.
Petty AJ, Yang Y. Tumor-associated macrophages: implications in cancer immunotherapy. Immunotherapy. 2017;9(3):289–302.
Chatterjee B, Saha P, Bose S, Shukla D, Chatterjee N, Kumar S, Tripathi PP, Srivastava AK. MicroRNAs: As Critical Regulators of Tumor- Associated Macrophages. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(19):7117.
Boutilier AJ, Elsawa SF. Macrophage Polarization States in the Tumor Microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(13):6995.
Yang J, Zhang Z, Chen C, Liu Y, Si Q, Chuang TH, Li N, Gomez-Cabrero A, Reisfeld RA, Xiang R, Luo Y. MicroRNA-19a-3p inhibits breast cancer progression and metastasis by inducing macrophage polarization through downregulated expression of Fra-1 proto-oncogene. Oncogene. 2014;33(23):3014–23.
Hong BS, Ryu HS, Kim N, Kim J, Lee E, Moon H, Kim KH, Jin MS, Kwon NH, Kim S, Kim D, Chung DH, Jeong K, Kim K, Kim KY, Lee HB, Han W, Yun J, Kim JI, Noh DY, Moon HG. Tumor Suppressor miRNA-204-5p Regulates Growth, Metastasis, and Immune Microenvironment Remodeling in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2019;79(7):1520–34.
Ma S, Liu M, Xu Z, Li Y, Guo H, Ge Y, Liu Y, Zheng D, Shi J. A double feedback loop mediated by microRNA-23a/27a/24–2 regulates M1 versus M2 macrophage polarization and thus regulates cancer progression. Oncotarget. 2016;7(12):13502–19.
Zonari E, Pucci F, Saini M, Mazzieri R, Politi LS, Gentner B, Naldini L. A role for miR-155 in enabling tumor-infiltrating innate immune cells to mount effective antitumor responses in mice. Blood. 2013;122(2):243–52.
Kwon Y, Kim M, Kim Y, Jung HS, Jeoung D. Exosomal MicroRNAs as Mediators of Cellular Interactions Between Cancer Cells and Macrophages. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1167.
Chen X, Song E. Turning foes to friends: targeting cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2019;18(2):99–115.
Ziani L, Chouaib S, Thiery J. Alteration of the Antitumor Immune Response by Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Front Immunol. 2018;9:414.
Shah SH, Miller P, Garcia-Contreras M, Ao Z, Machlin L, Issa E, El-Ashry D. Hierarchical paracrine interaction of breast cancer associated fibroblasts with cancer cells via hMAPK-microRNAs to drive ER-negative breast cancer phenotype. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(11):1671–81.
Chatterjee A, Jana S, Chatterjee S, Wastall LM, Mandal G, Nargis N, Roy H, Hughes TA, Bhattacharyya A. MicroRNA-222 reprogrammed cancer-associated fibroblasts enhance growth and metastasis of breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2019;121(8):679–89.
Donnarumma E, Fiore D, Nappa M, Roscigno G, Adamo A, Iaboni M, Russo V, Affinito A, Puoti I, Quintavalle C, Rienzo A, Piscuoglio S, Thomas R, Condorelli G. Cancer-associated fibroblasts release exosomal microRNAs that dictate an aggressive phenotype in breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(12):19592–608.
Al-Ansari MM, Aboussekhra A. miR-146b-5p mediates p16-dependent repression of IL-6 and suppresses paracrine procarcinogenic effects of breast stromal fibroblasts. Oncotarget. 2015;6(30):30006–16.
Tang X, Hou Y, Yang G, Wang X, Tang S, Du YE, Yang L, Yu T, Zhang H, Zhou M, Wen S, Xu L, Liu M. Stromal miR-200s contribute to breast cancer cell invasion through CAF activation and ECM remodeling. Cell Death Differ. 2016;23(1):132–45.
Dysthe M, Parihar R. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1224:117–40.
Deng Z, Rong Y, Teng Y, Zhuang X, Samykutty A, Mu J, Zhang L, Cao P, Yan J, Miller D, Zhang HG. Exosomes miR-126a released from MDSC induced by DOX treatment promotes lung metastasis. Oncogene. 2017;36(5):639–51.
Song L, Dong G, Guo L, Graves DT. The function of dendritic cells in modulating the host response. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2018;33(1):13–21.
Del Prete A, Salvi V, Soriani A, Laffranchi M, Sozio F, Bosisio D, Sozzani S. Dendritic cell subsets in cancer immunity and tumor antigen sensing. Cell Mol Immunol. 2023;20(5):432–47.
Lee SS, Cheah YK. The Interplay between MicroRNAs and Cellular Components of Tumour Microenvironment (TME) on Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Progression. J Immunol Res. 2019;2019:3046379.
Scalavino V, Liso M, Serino G. Role of microRNAs in the Regulation of Dendritic Cell Generation and Function. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(4):1319.
Liang X, Liu Y, Mei S, Zhang M, Xin J, Zhang Y, Yang R. MicroRNA-22 impairs anti-tumor ability of dendritic cells by targeting p38. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(3): e0121510.
Zhang M, Shi Y, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Alotaibi F, Qiu L, Wang H, Peng S, Liu Y, Li Q, Gao D, Wang Z, Yuan K, Dou FF, Koropatnick J, Xiong J, Min W. miRNA-5119 regulates immune checkpoints in dendritic cells to enhance breast cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol, Immunother: CII. 2020;69(6):951–67.
De Sanctis F, Ugel S, Facciponte J, Facciabene A. The dark side of tumor-associated endothelial cells. Semin Immunol. 2018;35:35–47.
Maishi N, Annan DA, Kikuchi H, Hida Y, Hida K. Tumor Endothelial Heterogeneity in Cancer Progression. Cancers. 2019;11(10):1511.
Soheilifar MH, Masoudi-Khoram N, Madadi S, Nobari S, Maadi H, Keshmiri Neghab H, Amini R, Pishnamazi M. Angioregulatory microRNAs in breast cancer: Molecular mechanistic basis and implications for therapeutic strategies. J Adv Res. 2021;37:235–53.
Zhu N, Zhang D, Xie H, Zhou Z, Chen H, Hu T, Bai Y, Shen Y, Yuan W, Jing Q, Qin Y. Endothelial-specific intron-derived miR-126 is down-regulated in human breast cancer and targets both VEGFA and PIK3R2. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011;351(1–2):157–64.
Okeke EB, Uzonna JE. The Pivotal Role of Regulatory T Cells in the Regulation of Innate Immune Cells. Front Immunol. 2019;10:680.
Shan F, Somasundaram A, Bruno TC, Workman CJ, Vignali DAA. Therapeutic targeting of regulatory T cells in cancer. Trends Cancer. 2022;8(11):944–61.
Kos K, de Visser KE. The Multifaceted Role of Regulatory T Cells in Breast Cancer. Annu Rev Cancer Biol. 2021;5:291–310.
Soheilifar MH, Vaseghi H, Seif F, Ariana M, Ghorbanifar S, Habibi N, Papari Barjasteh F, Pornour M. Concomitant overexpression of mir-182-5p and mir-182-3p raises the possibility of IL-17-producing Treg formation in breast cancer by targeting CD3d, ITK, FOXO1, and NFATs: A meta-analysis and experimental study. Cancer Sci. 2021;112(2):589–603.
Pei X, Wang X, Li H. LncRNA SNHG1 regulates the differentiation of Treg cells and affects the immune escape of breast cancer via regulating miR-448/IDO. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;118(Pt A):24–30.
Rodríguez-Galán A, Fernández-Messina L, Sánchez-Madrid F. Control of Immunoregulatory Molecules by miRNAs in T Cell Activation. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2148.
Hippen KL, Loschi M, Nicholls J, MacDonald KPA, Blazar BR. Effects of MicroRNA on Regulatory T Cells and Implications for Adoptive Cellular Therapy to Ameliorate Graft-versus-Host Disease. Front Immunol. 2018;9:57.
Hu Y, Wang C, Li Y, Zhao J, Chen C, Zhou Y, Tao Y, Guo M, Qin N, Ren T, Wen Z, Xu L. MiR-21 controls in situ expansion of CCR6+ regulatory T cells through PTEN/AKT pathway in breast cancer. Immunol Cell Biol. 2015;93(8):753–64.
Xuan X, Tian C, Zhao M, Sun Y, Huang C. Mesenchymal stem cells in cancer progression and anticancer therapeutic resistance. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21(1):595.
Li X, Fan Q, Peng X, Yang S, Wei S, Liu J, Yang L, Li H. Mesenchymal/stromal stem cells: necessary factors in tumour progression. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8(1):333.
Wang N, Pei B, Yuan X, Yi C, Wiredu Ocansey DK, Qian H, Mao F. Emerging roles of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in gastrointestinal cancers. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:1019459.
Pakravan K, Babashah S, Sadeghizadeh M, Mowla SJ, Mossahebi-Mohammadi M, Ataei F, Dana N, Javan M. MicroRNA-100 shuttled by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes suppresses in vitro angiogenesis through modulating the mTOR/HIF-1α/VEGF signaling axis in breast cancer cells. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2017;40(5):457–70.
Hughes AM, Kolb AD, Shupp AB, Shine KM, Bussard KM. Printing the Pathway Forward in Bone Metastatic Cancer Research: Applications of 3D Engineered Models and Bioprinted Scaffolds to Recapitulate the Bone-Tumor Niche. Cancers. 2021;13(3):507.
Back J, Nguyen MN, Li L, Lee S, Lee I, Chen F, Gillinov L, Chung YH, Alder KD, Kwon HK, Yu KE, Dussik CM, Hao Z, Flores MJ, Kim Y, Ibe IK, Munger AM, Seo SW, Lee FY. Inflammatory conversion of quiescent osteoblasts by metastatic breast cancer cells through pERK1/2 aggravates cancer-induced bone destruction. Bone Res. 2021;9(1):43.
Haider MT, Smit DJ, Taipaleenmäki H. MicroRNAs: Emerging Regulators of Metastatic Bone Disease in Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2022;14(3):729.
Liu X, Cao M, Palomares M, Wu X, Li A, Yan W, Fong MY, Chan WC, Wang SE. Metastatic breast cancer cells overexpress and secrete miR-218 to regulate type I collagen deposition by osteoblasts. Breast Cancer Res: BCR. 2018;20(1):127.
Marini, F., Chifman, J., Tooze, J., Gomez-Manzano, C., & Bussard, K. M. Osteoblasts are educated into a tumor-associated stromal cell by disseminated breast cancer cells and mediate breast cancer cell proliferation in the bone microenvironment [abstract]. In: Proceedings of the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2017; 2017 Apr 1–5; Washington, DC. Philadelphia (PA): AACR; Cancer Res 2017; 77(13 Suppl): Abstract nr 5890.
Puppo M, Taipaleenmäki H, Hesse E, Clézardin P. Non-coding RNAs in bone remodelling and bone metastasis: Mechanisms of action and translational relevance. Br J Pharmacol. 2021;178(9):1936–54.
Liu J, Dang L, Wu X, Li D, Ren Q, Lu A, Zhang G. microRNA-Mediated Regulation of Bone Remodeling: A Brief Review. JBMR plus. 2019;3(9): e10213.
Li D, Liu J, Guo B, Liang C, Dang L, Lu C, He X, Cheung HY, Xu L, Lu C, He B, Liu B, Shaikh AB, Li F, Wang L, Yang Z, Au DW, Peng S, Zhang Z, Zhang BT, Pan X, Qian A, Shang P, Xiao L, Wong CK, Xu J, Bian Z, Liang Z, Guo DA, Zhu H, Tan W, Lu A, Zhang G. Osteoclast-derived exosomal miR-214-3p inhibits osteoblastic bone formation. Nat Commun. 2016;7:10872.
Orso F, Quirico L, Virga F, Penna E, Dettori D, Cimino D, Coppo R, Grassi E, Elia AR, Brusa D, Deaglio S, Brizzi MF, Stadler MB, Provero P, Caselle M, Taverna D. miR-214 and miR-148b Targeting Inhibits Dissemination of Melanoma and Breast Cancer. Can Res. 2016;76(17):5151–62.
Wang W, Liu Y, Guo J, He H, Mi X, Chen C, Xie J, Wang S, Wu P, Cao F, Bai L, Si Q, Xiang R, Luo Y. miR-100 maintains phenotype of tumor-associated macrophages by targeting mTOR to promote tumor metastasis via Stat5a/IL-1ra pathway in mouse breast cancer. Oncogenesis. 2018;7(12):97.
Zhong Y, Yi C. MicroRNA-720 suppresses M2 macrophage polarization by targeting GATA3. Biosci Rep. 2016;36(4): e00363.
Li Y, Zhao L, Shi B, Ma S, Xu Z, Ge Y, Liu Y, Zheng D, Shi J. Functions of miR-146a and miR-222 in Tumor-associated Macrophages in Breast Cancer. Sci Rep. 2015;5:18648.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Indian Council of Medical Research, India [No.5/13/05/2019/NCD-III to N.S.] and the Department of Science &Technology [DST/INSPIRE Fellowships: 2019/IF190170 to R. L. A. and 2021/IF210073 to I. S.].
Funding
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced the work reported in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RLA wrote the manuscript. IS helped in preparing the figures. NS designed and reviewed the content and secured funding for this research.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Akshaya, R.L., Saranya, I. & Selvamurugan, N. MicroRNAs mediated interaction of tumor microenvironment cells with breast cancer cells during bone metastasis. Breast Cancer 30, 910–925 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-023-01491-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-023-01491-0