Abstract
Background
Determining the indications for adjuvant chemotherapy (CT) in patients with hormone receptor (HR)-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer are difficult. The transcription factors GATA-binding protein 3 (GATA-3) and Forkhead-box protein A1 (FOXA1) are crucial for the hormone responsive phenotype of breast cancer. This study evaluated whether the expression of GATA-3 and FOXA1 is a prognostic and predictive marker of outcomes in patients with HR-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer.
Methods
The expression of GATA-3 and FOXA1 was analyzed immunohistochemically in 214 patients with invasive breast cancer to evaluate the association with the clinicopathological features and the prognosis.
Results
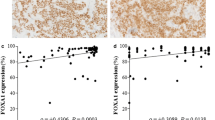
GATA-3 expression was positively correlated with FOXA1 expression (P < 0.0001). Both GATA-3 and FOXA1 were positively correlated with ER (P < 0.0001 each) and PR expression (P = 0.0001 and P = 0.0009, respectively), and inversely correlated with nuclear grade (P = 0.0002 and P = 0.0018, respectively) and Ki67 index (P = 0.0052 and P = 0.0049, respectively). Expression of GATA-3 and FOXA1 was associated with better prognosis. FOXA1 was an independent favorable prognostic marker in HR-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer. Disease-free survival rates were similar in patients with HR-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer and high FOXA1 expression given adjuvant hormone therapy (HT) alone and those given CT plus HT.
Conclusion
GATA-3 and FOXA1 are associated with a less aggressive phenotype and a better prognosis in patients with HR-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer. FOXA1 may be useful in identifying those patients who may not require adjuvant CT.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000;406:747–52.
Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, et al. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:10869–74.
Cheang MC, Chia SK, Voduc D, et al. Ki67 index, HER2 status, and prognosis of patients with luminal B breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009;101:736–50.
Hugh J, Hanson J, Cheang MC, et al. Breast cancer subtypes and response to docetaxel in node-positive breast cancer: use of an immunohistochemical definition in the BCIRG 001 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:1168–76.
Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Thurlimann B, Senn HJ. Strategies for subtypes–dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann Oncol. 2011;22:1736–47.
Kim C, Paik S. Gene-expression-based prognostic assays for breast cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2010;7:340–7.
Badve S, Nakshatri H. Oestrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer: towards bridging histopathological and molecular classifications. J Clin Pathol. 2009;62:6–12.
Lim KC, Lakshmanan G, Crawford SE, Gu Y, Grosveld F, Engel JD. GATA3 loss leads to embryonic lethality due to noradrenaline deficiency of the sympathetic nervous system. Nat Genet. 2000;25:209–12.
Kaufman CK, Zhou P, Pasolli HA, et al. GATA-3: an unexpected regulator of cell lineage determination in skin. Genes Dev. 2003;17:2108–22.
Ting CN, Olson MC, Barton KP, Leiden JM. Transcription factor GATA-3 is required for development of the T-cell lineage. Nature. 1996;384:474–8.
Kouros-Mehr H, Slorach EM, Sternlicht MD, Werb Z. GATA-3 maintains the differentiation of the luminal cell fate in the mammary gland. Cell. 2006;127:1041–55.
Asselin-Labat ML, Sutherland KD, Barker H, et al. GATA-3 is an essential regulator of mammary-gland morphogenesis and luminal-cell differentiation. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:201–9.
Mehra R, Varambally S, Ding L, et al. Identification of GATA3 as a breast cancer prognostic marker by global gene expression meta-analysis. Cancer Res. 2005;65:11259–64.
Carlsson P, Mahlapuu M. Forkhead transcription factors: key players in development and metabolism. Dev Biol. 2002;250:1–23.
Kaestner KH. The hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 (HNF3 or FOXA) family in metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2000;11:281–5.
Carroll JS, Brown M. Estrogen receptor target gene: an evolving concept. Mol Endocrinol. 2006;20:1707–14.
Laganiere J, Deblois G, Lefebvre C, Bataille AR, Robert F, Giguere V. From the Cover: location analysis of estrogen receptor alpha target promoters reveals that FOXA1 defines a domain of the estrogen response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:11651–6.
Hurtado A, Holmes KA, Ross-Innes CS, Schmidt D, Carroll JS. FOXA1 is a key determinant of estrogen receptor function and endocrine response. Nat Genet. 2011;43:27–33.
Badve S, Turbin D, Thorat MA, et al. FOXA1 expression in breast cancer–correlation with luminal subtype A and survival. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:4415–21.
Ijichi N, Shigekawa T, Ikeda K, et al. Association of double-positive FOXA1 and FOXP1 immunoreactivities with favorable prognosis of tamoxifen-treated breast cancer patients. Hormon Cancer. 2012;3:147–59.
Mehta RJ, Jain RK, Leung S, et al. FOXA1 is an independent prognostic marker for ER-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;131:881–90.
Hisamatsu Y, Tokunaga E, Yamashita N, et al. Impact of FOXA1 expression on the prognosis of patients with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:1145–52.
Hoch RV, Thompson DA, Baker RJ, Weigel RJ. GATA-3 is expressed in association with estrogen receptor in breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1999;84:122–8.
Parikh P, Palazzo JP, Rose LJ, Daskalakis C, Weigel RJ. GATA-3 expression as a predictor of hormone response in breast cancer. J Am Coll Surg. 2005;200:705–10.
Ademuyiwa FO, Thorat MA, Jain RK, Nakshatri H, Badve S. Expression of forkhead-box protein A1, a marker of luminal A type breast cancer, parallels low Oncotype DX 21-gene recurrence scores. Mod Pathol. 2010;23:270–5.
Bernardo GM, Lozada KL, Miedler JD, et al. FOXA1 is an essential determinant of ERα expression and mammary ductal morphogenesis. Development. 2010;137:2045–54.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports Science, and Technology of Japan (Grant No. 23591896). We are grateful to Ms. Yuko Kubota for her valuable technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Hisamatsu, Y., Tokunaga, E., Yamashita, N. et al. Impact of GATA-3 and FOXA1 expression in patients with hormone receptor-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer 22, 520–528 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-013-0515-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-013-0515-x