Abstract
Background
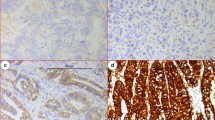
In patients with luminal-type breast cancer (positive for ER and/or PgR), a complete consensus on the threshold indication for a combination of chemotherapy and endocrine therapy has not been achieved, especially for patients with HER2-negative luminal type (HNLT). Girdin, an actin-binding Akt substrate, plays a crucial role in the migration of cancer cells. This study examined the expression of Girdin in relation to clinicopathological features and other immunohistochemical markers (HER2, Ki-67), especially in patients with HNLT breast cancer.
Methods
One hundred one breast cancer patients who underwent surgery were evaluated. Immunohistochemical staining was performed for Girdin and other biomarkers, such as ER, PgR, HER2, and Ki-67.
Results
Positive expression of Girdin was observed in 26 patients. The expression of Girdin was significantly associated with the incidence of lymph node metastases (p = 0.001). Among the other examined biomarkers, positive expression of Ki-67 also showed a significant association with the incidence of lymph node metastases (p = 0.04). In the HNLT breast cancer patients (n = 73), the 5-year recurrence-free survival rate was significantly lower (57 %) in patients with positive expression of both Girdin and Ki-67 than the rate in other patients (92 %) (p = 0.002).
Conclusion
This study demonstrated that the expression of Girdin in invasive breast cancer is strongly associated with lymph node metastasis. The expression status of Girdin and Ki-67 can be a useful biomarker in stratifying patients with HNLT breast cancer into those with high risk of recurrence and the need for additional chemotherapy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Thurlimann B, Senn HJ. Strategies for subtypes—dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St. Gallen international expert consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2011. Ann Oncol. 2011;22(8):1736–47.
Urruticoechea A, Smith IE, Dowsett M. Proliferation marker Ki-67 in early breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(28):7212–20.
Colozza M, Azambuja E, Cardoso F, Sotiriou C, Larsimont D, Piccart MJ. Proliferative markers as prognostic and predictive tools in early breast cancer: where are we now? Ann Oncol. 2005;16(11):1723–39.
Vivanco I, Sawyers CL. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Can. 2002;2(7):489–501.
Kane LP, Shapiro VS, Stokoe D, Weiss A. Induction of NF-kappaB by the Akt/PKB kinase. Curr Biol CB. 1999;9(11):601–4.
Kops GJ, de Ruiter ND, De Vries-Smits AM, Powell DR, Bos JL, Burgering BM. Direct control of the Fork head transcription factor AFX by protein kinase B. Nature. 1999;398(6728):630–4.
Hutchinson J, Jin J, Cardiff RD, Woodgett JR, Muller WJ. Activation of Akt (protein kinase B) in mammary epithelium provides a critical cell survival signal required for tumor progression. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21(6):2203–12.
Enomoto A, Murakami H, Asai N, Morone N, Watanabe T, Kawai K, et al. Akt/PKB regulates actin organization and cell motility via Girdin/APE. Dev Cell. 2005;9(3):389–402.
Jiang P, Enomoto A, Jijiwa M, Kato T, Hasegawa T, Ishida M, et al. An actin-binding protein Girdin regulates the motility of breast cancer cells. Can Res. 2008;68(5):1310–8.
Liu C, Zhang Y, Xu H, Zhang R, Li H, Lu P, et al. Girdin protein: a new potential distant metastasis predictor of breast cancer. Med Oncol. 2012;29(3):1554–60.
Ling Y, Jiang P, Cui SP, Ren YL, Zhu SN, Yang JP, et al. Clinical implications for girdin protein expression in breast cancer. Can Inv. 2011;29(6):405–10.
Dowsett M, Nielsen TO, A’Hern R, Bartlett J, Coombes RC, Cuzick J, et al. Assessment of Ki67 in breast cancer: recommendations from the International Ki67 in Breast Cancer Working Group. J Natl Can Inst. 2011;103(22):1656–64.
Cheang MC, Chia SK, Voduc D, Gao D, Leung S, Snider J, et al. Ki67 index, HER2 status, and prognosis of patients with luminal B breast cancer. J Natl Can Inst. 2009;101(10):736–50.
Allred DC, Harvey JM, Berardo M, Clark GM. Prognostic and predictive factors in breast cancer by immunohistochemical analysis. Mod Pathol. 1998;11(2):155–68.
Badve S, Nakshatri H. Oestrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer: towards bridging histopathological and molecular classifications. J Clin Pathol. 2009;62(1):6–12.
Kroger N, Milde-Langosch K, Riethdorf S, Schmoor C, Schumacher M, Zander AR, et al. Prognostic and predictive effects of immunohistochemical factors in high-risk primary breast cancer patients. Clin Can Res. 2006;12(1):159–68.
Soerjomataram I, Louwman MW, Ribot JG, Roukema JA, Coebergh JW. An overview of prognostic factors for long-term survivors of breast cancer. Breast Can Res Treat. 2008;107(3):309–30.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Nishimae, K., Tsunoda, N., Yokoyama, Y. et al. The impact of Girdin expression on recurrence-free survival in patients with luminal-type breast cancer. Breast Cancer 22, 445–451 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-013-0501-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-013-0501-3