Abstract
Background
Recent studies have indicated that the response to chemotherapy and the prognostic impact of a pathological complete response (pCR) after neoadjuvant chemotherapy differ among breast cancer subtypes. Predictors of response to chemotherapy and prognostic factors for survival might be different in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer.
Methods
Women with Stage II to III ER-positive HER2-negative breast cancer treated with anthracycline and taxane-containing neoadjuvant chemotherapy between 2003 and 2011 were retrospectively analyzed. Expression of forkhead box A1 (FOXA1), B cell lymphoma 2 (BCL2) and microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) as well as ER, progesterone receptor, HER2 and Ki67 was examined by immunohistochemistry in pre- and post-treatment specimens. Factors predictive of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy and distant disease-free survival were analyzed.
Results
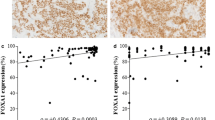
Tumor grade was positively correlated with Ki67 expression. Expression levels of ER were positively correlated with expression levels of HER2, BCL2, FOXA1 and MAPT in pre-treatment tumors. The Ki67 labeling index was the only factor that was significantly associated with clinical response measured by the reduction of tumor volume and pCR. Lymph node status, expression of ER before neoadjuvant chemotherapy and expression of FOXA1 after neoadjuvant chemotherapy were significantly associated with distant disease-free survival, both by univariate and multivariate analyses.
Conclusions
Patients with ER-positive HER2-negative breast cancer should be selected for neoadjuvant chemotherapy. FOXA1 expression could be a prognostic marker in ER-positive breast cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
- PgR:
-
Progesterone receptor
- HER2:
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- Ki67 LI:
-
Ki67 labeling index
- BCL2:
-
B-cell lymphoma 2
- FOXA1:
-
Forkhead box A1
- MAPT:
-
Microtubule-associated protein tau
- pCR:
-
Pathological complete response
References
Kaufmann M, von Minckwitz G, Mamounas EP, Cameron D, Carey LA, Cristofanilli M, et al. Recommendations from an international consensus conference on the current status and future of neoadjuvant systemic therapy in primary breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:1508–16.
Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Thurlimann B, Senn HJ. Strategies for subtypes–dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann Oncol. 2011;22:1736–47.
von Minckwitz G. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer-insights from the German experience. Breast Cancer. 2012;19:282–8.
Houssami N, Macaskill P, von Minckwitz G, Marinovich ML, Mamounas E. Meta-analysis of the association of breast cancer subtype and pathologic complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Eur J Cancer. 2012;48:3342–54.
Jones RL, Salter J, A’Hern R, Nerurkar A, Parton M, Reis-Filho JS, et al. Relationship between oestrogen receptor status and proliferation in predicting response and long-term outcome to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010;119:315–23.
Lips EH, Mulder L, de Ronde JJ, Mandjes IA, Vincent A, Vrancken Peeters MT, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in ER+ HER2− breast cancer: response prediction based on immunohistochemical and molecular characteristics. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;131:827–36.
Burcombe R, Wilson GD, Dowsett M, Khan I, Richman PI, Daley F, et al. Evaluation of Ki-67 proliferation and apoptotic index before, during and after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2006;8:R31.
Jones RL, Salter J, A’Hern R, Nerurkar A, Parton M, Reis-Filho JS, et al. The prognostic significance of Ki67 before and after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009;116:53–68.
Fasching PA, Heusinger K, Haeberle L, Niklos M, Hein A, Bayer CM, et al. Ki67, chemotherapy response, and prognosis in breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant treatment. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:486.
Matsubara N, Mukai H, Fujii S, Wada N. Different prognostic significance of Ki-67 change between pre- and post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy in various subtypes of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013;137:203–12.
Montagna E, Bagnardi V, Rotmensz N, Viale G, Pruneri G, Veronesi P, et al. Pathological complete response after preoperative systemic therapy and outcome: relevance of clinical and biologic baseline features. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010;124:689–99.
Badve S, Turbin D, Thorat MA, Morimiya A, Nielsen TO, Perou CM, et al. FOXA1 expression in breast cancer—correlation with luminal subtype A and survival. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2007;13:4415–21.
Habashy HO, Powe DG, Rakha EA, Ball G, Paish C, Gee J, et al. Forkhead-box A1 (FOXA1) expression in breast cancer and its prognostic significance. Eur J Cancer. 2008;44:1541–51.
Mehta RJ, Jain RK, Leung S, Choo J, Nielsen T, Huntsman D, et al. FOXA1 is an independent prognostic marker for ER-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;131:881–90.
Hisamatsu Y, Tokunaga E, Yamashita N, Akiyoshi S, Okada S, Nakashima Y, et al. Impact of FOXA1 expression on the prognosis of patients with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:1145–52.
Callagy GM, Webber MJ, Pharoah PD, Caldas C. Meta-analysis confirms BCL2 is an independent prognostic marker in breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:153.
Dawson SJ, Makretsov N, Blows FM, Driver KE, Provenzano E, Le Quesne J, et al. BCL2 in breast cancer: a favourable prognostic marker across molecular subtypes and independent of adjuvant therapy received. Br J Cancer. 2010;103:668–75.
Rouzier R, Rajan R, Wagner P, Hess KR, Gold DL, Stec J, et al. Microtubule-associated protein tau: a marker of paclitaxel sensitivity in breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:8315–20.
Smoter M, Bodnar L, Duchnowska R, Stec R, Grala B, Szczylik C. The role of Tau protein in resistance to paclitaxel. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011;68:553–7.
Baquero MT, Lostritto K, Gustavson MD, Bassi KA, Appia F, Camp RL, et al. Evaluation of prognostic and predictive value of microtubule associated protein tau in two independent cohorts. Breast Cancer Res. 2011;13:R85.
Pusztai L, Jeong JH, Gong Y, Ross JS, Kim C, Paik S, et al. Evaluation of microtubule-associated protein-Tau expression as a prognostic and predictive marker in the NSABP-B 28 randomized clinical trial. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:4287–92.
Kurosumi M, Akashi-Tanaka S, Akiyama F, Komoike Y, Mukai H, Nakamura S, et al. Histopathological criteria for assessment of therapeutic response in breast cancer (2007 version). Breast Cancer. 2008;15:5–7.
von Minckwitz G, Untch M, Blohmer JU, Costa SD, Eidtmann H, Fasching PA, et al. Definition and impact of pathologic complete response on prognosis after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in various intrinsic breast cancer subtypes. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:1796–804.
Yamashita H, Takahashi S, Ito Y, Yamashita T, Ando Y, Toyama T, et al. Predictors of response to exemestane as primary endocrine therapy in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 2009;100:2028–33.
Allred DC, Harvey JM, Berardo M, Clark GM. Prognostic and predictive factors in breast cancer by immunohistochemical analysis. Modern Pathol Off J US Can Acad Pathol. 1998;11:155–68.
Endo Y, Toyama T, Takahashi S, Yoshimoto N, Iwasa M, Asano T, et al. miR-1290 and its potential targets are associated with characteristics of estrogen receptor alpha-positive breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2013;20:91–102.
Piccart-Gebhart MJ. New developments in hormone receptor-positive disease. Oncologist. 2010;15(Suppl 5):18–28.
Endo Y, Toyama T, Takahashi S, Sugiura H, Yoshimoto N, Iwasa M, et al. High estrogen receptor expression and low Ki67 expression are associated with improved time to progression during first-line endocrine therapy with aromatase inhibitors in breast cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 2011;16:512–8.
Viale G, Regan MM, Mastropasqua MG, Maffini F, Maiorano E, Colleoni M, et al. Predictive value of tumor Ki-67 expression in two randomized trials of adjuvant chemoendocrine therapy for node-negative breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100:207–12.
Hugh J, Hanson J, Cheang MC, Nielsen TO, Perou CM, Dumontet C, et al. Breast cancer subtypes and response to docetaxel in node-positive breast cancer: use of an immunohistochemical definition in the BCIRG 001 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:1168–76.
Penault-Llorca F, Andre F, Sagan C, Lacroix-Triki M, Denoux Y, Verriele V, et al. Ki67 expression and docetaxel efficacy in patients with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:2809–15.
Hurtado A, Holmes KA, Ross-Innes CS, Schmidt D, Carroll JS. FOXA1 is a key determinant of estrogen receptor function and endocrine response. Nat Genet. 2011;43:27–33.
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kawase, M., Toyama, T., Takahashi, S. et al. FOXA1 expression after neoadjuvant chemotherapy is a prognostic marker in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer 22, 308–316 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-013-0482-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-013-0482-2