Abstract
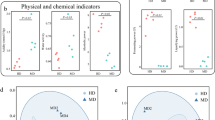
The microbial community is one of the most important factors in shaping the characteristics of fermented food. Nuodeng ham, traditionally produced and subjected to 1–4 years of fermentation, is a dry fermented food product with cultural and economic significance to locals in southwestern China. In this study, we aimed to characterize the microbiota and physicochemical profiles of Nuodeng ham across different stages of fermentation. Ham samples from each of the four years were analyzed by sequencing bacterial 16S rRNA gene and fungal internal transcribed spacer sequence, in order to characterize the diversity and composition of their microflora. A total of 2,679,483 bacterial and 2,983,234 fungal sequences of high quality were obtained and assigned to 514 and 57 genera, respectively. Among these microbes, Staphylococcus and Candida were the most abundant genera observed in the ham samples, though samples from different years showed differences in their microbial abundance. Results of physicochemical properties (pH, water, amino acid, NaCl, nitrate and nitrite contents, and the composition of volatile compounds) revealed differences among the ham samples in the composition of volatile compounds, especially in the third year samples, in which no nitrite was detected. These results suggest that the structure and diversity of microbial communities significantly differed across different stages of fermentation. Moreover, the third year hams exhibits a unique and balanced microbial community, which might contribute to the special flavor in the green and safe food products. Thus, our study lends insights into the production of high quality Nuodeng ham.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrade, M.J., Córdoba, J.J., Sánchez, B., Casado, E.M., and Rodríguez, M. 2009. Evaluation and selection of yeasts isolated from dry-cured Iberian ham by their volatile compound production. Food Chem. 113, 457–463.
Andrade, M.J., Thorsen, L., Rodríguez, A., Córdoba, J.J., and Jespersen, L. 2014. Inhibition of ochratoxigenic moulds by Debaryomyces hansenii strains for biopreservation of dry-cured meat products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 170, 70–77.
Bosse, R., Gibis, M., Schmidt, H., and Weiss, J. 2016. Nitrate reductase activity of Staphylococcus carnosus affecting the color formation in cured raw ham. Food Res. Int. 85, 113–120.
Caporaso, J.G., Kuczynski, J., Stombaugh, J., Bittinger, K., Bushman, F.D., Costello, E.K., Fierer, N., Peña, A.G., Goodrich, J.K., Gordon, J.I., et al. 2010. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 7, 335–336.
Caporaso, J.G., Lauber, C.L., Walters, W.A., Berg-Lyons, D., Lozupone, C.A., Turnbaugh, P.J., Fierer, N., and Knight, R. 2011. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, 4516–4522.
Cordero, M.R. and Zumalacárregui, J.M. 2000. Characterization of Micrococcaceae isolated from salt used for Spanish dry-cured ham. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 31, 303–306.
Edgar, R.C. 2004. MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, 1792–1797.
Edgar, R.C. 2013. UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 10, 996–998.
Edgar, R.C., Haas, B.J., Clemente, J.C., Quince, C., and Knight, R. 2011. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27, 2194–2200.
Fadda, S., López, C., and Vignolo, G. 2010. Role of lactic acid bacteria during meat conditioning and fermentation: Peptides generated as sensorial and hygienic biomarkers. Meat Sci. 86, 66–79.
Fulladosa, E., Garriga, M., Martín, B., Guàrdia, M.D., García-Regueiro, J.A., and Arnau, J. 2010. Volatile profile and microbiological characterization of hollow defect in dry-cured ham. Meat Sci. 86, 801–807.
Ge, Q., Gu, Y., Zhang, W., Yin, Y., Yu, H., Wu, M., Wang, Z., and Zhou, G. 2017. Comparison of microbial communities from different Jinhua ham factories. AMB Expr. 7, 37.
Geeraerts, W., Pothakos, V., DeVuyst, L., and Leroy, F. 2017. Diversity of the dominant bacterial species on sliced cooked pork products at expiration date in the Belgian retail. Food Microbiol. 65, 236–243.
Haas, B.J., Gevers, D., Earl, A.M., Feldgarden, M., Ward, D.V., Giannoukos, G., Ciulla, D., Tabbaa, D., Highlander, S.K., Sodergren, E., et al. 2011. Chimeric 16S rRNA sequence formation and detection in Sanger and 454-pyrosequenced PCR amplicons. Genome Res. 21, 494–504.
Huang, Z.R., Hong, J.L., Xu, J.X., Li, L., Guo, W.L., Pan, Y.Y., Chen, S.J., Bai, W.D., Rao, P.F., Ni, L., et al. 2018. Exploring core functional microbiota responsible for the production of volatile flavour during the traditional brewing of Wuyi Hong Qu glutinous rice wine. Food Microbiol. 76, 487–496.
Kaban, G. 2013. Sucuk and pastirma: microbiological changes and formation of volatile compounds. Meat Sci. 95, 912–918.
Magoč, T. and Salzberg, S.L. 2011. FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27, 2957–2963.
Martín, A., Colín, B., Aranda, E., Benito, M.J., and Córdoba, M.G. 2007. Characterization of Micrococcaceae isolated from Iberian dry-cured sausages. Meat Sci. 75, 696–708.
Martín, A., Córdoba, J.J., Aranda, E., Córdoba, M.G., and Asensio, M.A. 2006. Contribution of a selected fungal population to the volatile compounds on dry-cured ham. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 110, 8–18.
Martínez-Onandi, N., Castioni, A., Martín, E.S., Rivas-Cañedo, A., Nuñez, M., Torriani, S., and Picon, A. 2017. Microbiota of high-pressure-processed Serrano ham investigated by culture-dependent and culture-independent methods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 241, 298–307.
Martínez-Onandi, N., Rivas-Cañedo, A., Nuñez, M., and Picon, A. 2016. Effect of chemical composition and high pressure processing on the volatile fraction of Serrano dry-cured ham. Meat Sci. 111, 130–138.
Martínez-Onandi, N., Sánchez, C., Nuñez, M., and Picon, A. 2019. Microbiota of Iberian dry-cured ham as influenced by chemical composition, high pressure processing and prolonged refrigerated storage. Food Microbiol. 80, 62–69.
Nychas, G.J.E. and Arkoudelos, J.S. 1990. Staphylococci: their role in fermented sausages. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 69, 167S–188S.
Oberhardt, M.A., Zarecki, R., Gronow, S., Lang, E., Klenk, H.P., Gophna, U., and Ruppin, E. 2015. Harnessing the landscape of microbial culture media to predict new organism-media pairings. Nat. Commun. 6, 8493.
Orgiazzi, A., Lumini, E., Nilsson, R.H., Girlanda, M., Vizzini, A., Bonfante, P., and Bianciotto, V. 2012. Unravelling soil fungal communities from different mediterranean land-use backgrounds. PLoS ONE 7, e34847.
Papamanoli, E., Kotzekidou, P., Tzanetakis, N., and Litopoulou-Tzanetaki, E. 2002. Characterization of Micrococcaceae isolated from dry fermented sausage. Food Microbiol. 19, 441–449.
Peromingo, B., Núñez, F., Rodríguez, A., Alía, A., and Andrade, M.J. 2018. Potential of yeasts isolated from dry-cured ham to control ochratoxin A production in meat models. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 268, 73–80.
Petrova, I., Aasen, I.M., Rustad, T., and Eikevik, T.M. 2015. Manufacture of dry-cured ham: a review. Part 1. Biochemical changes during the technological process. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 241, 587–599.
Połka, J., Rebecchi, A., Pisacane, V., Morelli, L., and Puglisi, E. 2015. Bacterial diversity in typical Italian salami at different ripening stages as revealed by high-throughput sequencing of 16S rRNA amplicons. Food Microbiol. 46, 342–356.
Purrinos, L., Carballo, J., and Lorenzo, J.M. 2013. The influence of Debaryomyces hansenii, Candida deformans and Candida zeylanoides on the aroma formation of dry-cured “lacón”. Meat Sci. 93, 344–350.
Quast, C., Pruesse, E., Yilmaz, P., Gerken, J., Schweer, T., Yarza, P., Peplies, J., and Glöckner, F.O. 2013. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 41, D590–D596.
Rebecchi, A., Pisacane, V., Miragoli, F., Polka, J., Falasconi, I., Morelli, L., and Puglisi, E. 2015. High-throughput assessment of bacterial ecology in hog, cow and ovine casings used in sausages production. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 212, 49–59.
Rodríguez, M., Núñez, F., Córdoba, J.J., Bermúdez, M.E., and Asensio, M.A. 1998. Evaluation of proteolytic activity of microorganisms isolated from dry cured ham. J. Appl. Microbiol. 85, 905–912.
Simoncini, N., Rotelli, D., Virgili, R., and Quintavalla, S. 2007. Dynamics and characterization of yeasts during ripening of typical Italian dry-cured ham. Food Microbiol. 24, 577–584.
Song, Z., Du, H., Zhang, Y., and Xu, Y. 2017. Unraveling core functional microbiota in traditional solid-state fermentation by high-throughput amplicons and metatranscriptomics sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 8, 1294.
Stavropoulou, D.A., VanReckem, E., DeSmet, S., DeVuyst, L., and Leroy, F. 2018. The narrowing down of inoculated communities of coagulase-negative staphylococci in fermented meat models is modulated by temperature and pH. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 274, 52–59.
Ventanas, S., Estevez, M., Andrés, A.I., and Ruiz, J. 2008. Analysis of volatile compounds of Iberian dry-cured loins with different intramuscular fat contents using SPME-DED. Meat Sci. 79, 172–180.
Wang, Q., Garrity, G.M., Tiedje, J.M., and Cole, J.R. 2007. Naïve bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73, 5261–5267.
Wang, Z.M., Lu, Z.M., Shi, J.S., and Xu, Z.H. 2016. Exploring flavour-producing core microbiota in multispecies solid-state fermentation of traditional Chinese vinegar. Sci. Rep. 6, 26818.
Wang, X., Ma, P., Jiang, D.F., Peng, Q., and Yang, H.Y. 2006. The natural microflora of Xuanwei ham and the no-mouldy ham production. J. Food Eng. 77, 103–111.
White, T.J., Bruns, T., Lee, S., and Taylor, J. 1990. 38-Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., and White, T.J. (eds.), PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. pp. 315–322. Academic Press, Caimbridge, Messachusetts, USA.
Wolfe, B.E., Button, J.E., Santarelli, M., and Dutton, R.J. 2014. Cheese rind communities provide tractable systems for in situ and in vitro studies of microbial diversity. Cell 158, 422–433.
Xiao, X., Dong, Y., Zhu, Y., and Cui, H.L. 2013. Bacterial diversity analysis of Zhenjiang Yao meat during refrigerated and vacuum-packed storage by 454 pyrosequencing. Curr. Microbiol. 66, 398–405.
Zhang, J., Zhen, Z., Zhang, W., Zeng, T., and Zhou, G. 2009. Effect of intensifying high-temperature ripening on proteolysis, lipolysis and flavor of Jinhua ham. J. Sci. Food Agr. 89, 834–842.
Zhao, F., Zhou, G., Ye, K., Wang, S., Xu, X., and Li, C. 2015. Microbial changes in vacuum-packed chilled pork during storage. Meat Sci. 100, 145–149.
Zhou, G.H. and Zhao, G.M. 2007. Biochemical changes during processing of traditional Jinhua ham. Meat Sci. 77, 114–120.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the project of Yunnan University Service Yunnan Action Plan (N0. KS161020), the Top Young Talents of Ten Thousand Program in Yunnan Province, and the expert base workstation of Yunnan Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://www.springerlink.com/content/120956.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Xm., Dang, Xj., Wang, Yb. et al. Diversity and composition of microbiota during fermentation of traditional Nuodeng ham. J Microbiol. 59, 20–28 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-021-0219-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-021-0219-4