Abstract
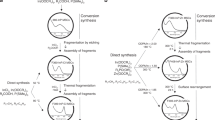
The formation pathway of colloidal semiconductor ZnSe magic-size clusters (MSCs) in a reaction that display an optical absorption doublet remains poorly understood. The reaction of Zn(OAc)2/OLA (made from zinc acetate and oleylamine) and tri-n-octylphosphine selenide (SeTOP) in OLA in the presence of diphenylphosphine (HPPh2) is studied, in which dMSC-345 displays a doublet peaking at 328/345 nm. We suggest that the development is from the clusters that form in the initial prenucleation stage of the reaction. The clusters are the precursor compound (PC-299) of MSC-299 (displaying an absorption singlet peaking at 299 nm). PC-299 transforms to PC-345 at a later stage. The presence of alcohol (such as methanol or ethylene glycol) promotes another pathway, which is the PC-299 to PC-320 transformation. PC-320 transforms to dMSC-320 (with a doublet at 305/320 nm), followed by dMSC-345 via PC-345. The present study provides additional evidence that clusters (PC-299) form and transform (such as to dMSC-345 via PC-345) in the prenucleation stage of ZnSe quantum dots (QDs).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wei, H. T.; Sun, H. Z.; Zhang, H.; Gao, C.; Yang, B. An effective method to prepare polymer/nanocrystal composites with tunable emission over the whole visible light range. Nano Res. 2010, 3, 496–505.
Chen, H. S.; Wang, S. J. J.; Lo, C. J.; Chi, J. Y. White-light emission from organics-capped ZnSe quantum dots and application in white-light-emitting diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 131905.
Li, Z. J.; Li, S. Y.; Davis, A. H.; Hofman, E.; Leem, G.; Zheng, W. W. Enhanced singlet oxygen generation by hybrid Mn-doped nanocomposites for selective photo-oxidation of benzylic alcohols. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 1668–1676.
Luo, W. N.; Jiu, T. G.; Kuang, C. Y.; Li, B. R.; Lu, F. S.; Fang, J. F. Dithiol treatments enhancing the efficiency of hybrid solar cells based on PTB7 and CdSe nanorods. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 3045–3053.
Zhu, Z. Z.; Li, X. X.; Qu, Y. T.; Zhou, F. Y.; Wang, Z. Y.; Wang, W. Y.; Zhao, C. M.; Wang, H. J.; Li, L. Q.; Yao, Y. G. et al. A hierarchical heterostructure of CdS QDs confined on 3D ZnIn2S4 with boosted charge transfer for photocatalytic CO2 reduction. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 81–90.
Sarkar, A.; Gracia-Espino, E.; Wågberg, T.; Shchukarev, A.; Mohl, M.; Rautio, A. R.; Pitkänen, O.; Sharifi, T.; Kordas, K.; Mikkola, J. P. Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 with H2O over modified TiO2 nanofibers: Understanding the reduction pathway. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 1956–1968.
Long, Z. W.; Liu, M. R.; Wu, X. G.; Gu, K.; Yang, G. L.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, R. H.; Zhong, H. Z. A reactivity-controlled epitaxial growth strategy for synthesizing large nanocrystals. Nat. Synth. 2023, 2, 296–304.
Yu, K.; Hrdina, A.; Zhang, X. G.; Ouyang, J. Y.; Leek, D. M.; Wu, X. H.; Gong, M. L.; Wilkinson, D.; Li, C. S. Highly-photoluminescent ZnSe nanocrystals via a non-injection-based approach with precursor reactivity elevated by a secondary phosphine. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 8811–8813.
Li, L. S.; Pradhan, N.; Wang, Y. J.; Peng, X. G. High quality ZnSe and ZnS nanocrystals formed by activating zinc carboxylate precursors. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 2261–2264.
Pang, Y. P.; Zhang, M. Y.; Chen, D. C.; Chen, W.; Wang, F.; Anwar, S. J.; Saunders, M.; Rowles, M. R.; Liu, L. H.; Liu, S. M. et al. Why do colloidal wurtzite semiconductor nanoplatelets have an atomically uniform thickness of eight monolayers. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 3465–3471.
Cunningham, P. D.; Coropceanu, I.; Mulloy, K.; Cho, W.; Talapin, D. V. Quantized reaction pathways for solution synthesis of colloidal ZnSe nanostructures: A connection between clusters, nanowires, and two-dimensional nanoplatelets. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 3847–3857.
Zhou, Y.; Jiang, R. D.; Wang, Y. Y.; Rohrs, H. W.; Rath, N. P.; Buhro, W. E. Isolation of amine derivatives of (ZnSe)34 and (CdTe)34. Spectroscopic comparisons of the (II–VI)13 and (II–VI)34 magic-size nanoclusters. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 1815–1825.
Wang, Y. Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Buhro, W. E. Magic-size II–VI nanoclusters as synthons for flat colloidal nanocrystals. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 1165–1177.
Park, H.; Chung, H.; Kim, W. Synthesis of ultrathin wurtzite ZnSe nanosheets. Mater. Lett. 2013, 99, 172–175.
Murray, C. B.; Norris, D. J.; Bawendi, M. G. Synthesis and characterization of nearly monodisperse CdE (E = sulfur, selenium, tellurium) semiconductor nanocrystallites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 8706–8715.
Peng, Z. A.; Peng, X. G. Nearly monodisperse and shape-controlled CdSe nanocrystals via alternative routes: Nucleation and growth. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 3343–3353.
Kasuya, A.; Sivamohan, R.; Barnakov, Y. A.; Dmitruk, I. M.; Nirasawa, T.; Romanyuk, V. R.; Kumar, V.; Mamykin, S. V.; Tohji, K.; Jeyadevan, B. et al. Ultra- stable nanoparticles of CdSe revealed from mass spectrometry. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 99–102.
Kudera, S.; Zanella, M.; Giannini, C.; Rizzo, A.; Li, Y.; Gigli, G.; Cingolani, R.; Ciccarella, G.; Spahl, W.; Parak, W. J. et al. Sequential growth of magic-size CdSe nanocrystals. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 548–552.
Liu, M. Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, L. X.; Han, S.; Fan, H. S.; Rowell, N.; Ripmeester, J. A.; Renoud, R.; Bian, F. G.; Zeng, J. R. et al. Probing intermediates of the induction period prior to nucleation and growth of semiconductor quantum dots. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15467.
Wang, L. X.; Hui, J.; Tang, J. B.; Rowell, N.; Zhang, B. W.; Zhu, T. T.; Zhang, M.; Hao, X. Y.; Fan, H. S.; Zeng, J. R. et al. Precursor self-assembly identified as a general pathway for colloidal semiconductor magic-size clusters. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1800632.
Zhang, J.; Hao, X. Y.; Rowell, N.; Kreouzis, T.; Han, S.; Fan, H. S.; Zhang, C. C.; Hu, C. W.; Zhang, M.; Yu, K. Individual pathways in the formation of magic-size clusters and conventional quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 3660–3666.
Li, Y.; Rowell, N.; Luan, C. R.; Zhang, M.; Chen, X. Q.; Yu, K. A two-pathway model for the evolution of colloidal compound semiconductor quantum dots and magic-size clusters. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2107940.
Whitesides, G. M.; Mathias, J. P.; Seto, C. T. Molecular self-assembly and nanochemistry: A chemical strategy for the synthesis of nanostructures. Science 1991, 254, 1312–1319.
Philp, D.; Stoddart, J. F. Self-assembly in natural and unnatural systems. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 1996, 35, 1154–1196.
Service, R. F. How far can we push chemical self-assembly. Science 2005, 309, 95–95.
Yang, X. X.; Zhang, M.; Shen, Q.; Li, Y.; Luan, C. R.; Yu, K. The precursor compound of two types of ZnSe magic-sized clusters. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 465–474.
Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; He, L.; Rowell, N.; Kreouzis, T.; Zhang, C. C.; Wang, S. L.; Luan, C. R.; Chen, X. Q.; Zhang, S. J. et al. Manipulating reaction intermediates to aqueous-phase ZnSe magic-size clusters and quantum dots at room temperature. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202209615.
Wang, T. H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S. L.; Chen, X. Q.; Luan, C. R.; Yu, K. Thermally-induced isomerization of prenucleation clusters during the prenucleation stage of CdTe quantum dots. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202310234.
Xu, R. K.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y. S.; Gu, C.; Luan, C. R.; Wang, S. L.; Chen, X. Q.; Yu, K. Formation and transformation of CdS clusters during the prenucleation stage and in a dilute dispersion at room temperature. Nano Lett. 2024, 24, 1294–1302.
Yang, Y. S.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, C. C.; Rowell, N.; Zhang, M.; Chen, X. Q.; Luan, C. R.; Yu, K. Direct and indirect pathways of CdTeSe magic-size cluster isomerization induced by surface ligands at room temperature. ACS Cent. Sci. 2023, 9, 519–530.
Yu, K.; Liu, X. Y.; Zeng, Q.; Leek, D. M.; Ouyang, J. Y.; Whitmore, K. M.; Ripmeester, J. A.; Tao, Y.; Yang, M. L. Effect of tertiary and secondary phosphines on low-temperature formation of quantum dots. Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 4923–4928.
Jackman, L. M.; Cotton F. A. Dynamic Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy; Academic Press: New York, 1975.
He, L.; Luan, C. R.; Liu, S. P.; Chen, M.; Rowell, N.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C. C.; Lu, J.; Zhang, M. et al. Transformations of magic-size clusters via precursor compound cation exchange at room temperature. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 19060–19069.
Justino, L. L. G.; Ramos, M. L.; Knaapila, M.; Marques, A. T.; Kudla, C. J.; Scherf, U.; Almásy, L.; Schweins, R.; Burrows, H. D.; Monkman, A. P. Gel formation and interpolymer alkyl chain interactions with poly (9,9-dioctylfluorene-2,7-diyl) (PFO) in toluene solution: Results from NMR, SANS, DFT, and semiempirical calculations and their implications for PFO β-phase formation. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 334–343.
Wang, D. Q.; Liu, Y. H.; Rowell, N.; Wang, S. L.; Zhang, C. C.; Zhang, M.; Luan, C. R.; Yu, K. Direct and indirect evolution of photoluminescent semiconductor CdS magic-size clusters through their precursor compounds. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202304329.
Liu, Y. Y.; Willis, M.; Rowell, N.; Luo, W. Z.; Fan, H. S.; Han, S.; Yu, K. Effect of small molecule additives in the prenucleation stage of semiconductor CdSe quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 6356–6363.
Liu, Y. Y.; Rowell, N.; Willis, M.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S. L.; Fan, H. S.; Huang, W.; Chen, X. Q.; Yu, K. Photoluminescent colloidal nanohelices self-assembled from CdSe magic-size clusters via nanoplatelets. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 2794–2801.
Zhu, J. M.; Cao, Z. P.; Zhu, Y. C.; Rowell, N.; Li, Y.; Wang, S. L.; Zhang, C. C.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, J. R. et al. Transformation pathway from CdSe magic-size clusters with absorption doublets at 373/393 nm to clusters at 434/460 nm. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 20358–20365.
Shen, J.; Luan, C. R.; Rowell, N.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, X. Q.; Yu, K. Size matters: Steric hindrance of precursor molecules controlling the evolution of CdSe magic-size clusters and quantum dots. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 8564–8572.
Cao, Z. P.; Zhu, J. M.; Peng, J.; Meng, N.; Bian, F. G.; Luan, C. R.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Yu, K.; Zeng, J. R. Transformation pathway from CdSe nanoplatelets with absorption doublets at 373/393 nm to nanoplatelets at 434/460 nm. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 3983–3989.
Wang, Z.; Zhang, C. C.; Wang, S. L.; Zhang, M.; Chen, X. Q.; Luan, C. R.; Yu, K. Formation and transformation of ZnTe and CdTe magic-size clusters assisted by their precursor compounds. Chem. Mater., in press, doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.3c03309.
Acknowledgements
K. Y. thanks the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22275126), the Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province (No. 2023NSFSC0634), and the Open Project of Key State Laboratory for Supramolecular Structures and Materials of Jilin University (No. SKLSSM 2023031). C. R. L. thanks the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22305162). We thank Dr. Li He and Dr. Meng Zhang for their assistance in the experimental design and manuscript preparation. For 1H NMR and TEM, we thank Analysis and Testing Center of Sichuan University (Dr. ChunChun Zhang and Dr. Shanling Wang). We are also grateful to Dr. Feng Yang (College of Chemistry, Sichuan University) for her invaluable patience for TEM. For LDI-TOF MS, we thank the comprehensive training platform of the Specialized Laboratory of College of Chemistry, Sichuan University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, D., Wang, S., Xue, J. et al. Formation of ZnSe magic-size clusters displaying optical absorption doublets from prenucleation clusters. Nano Res. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-024-6627-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-024-6627-0