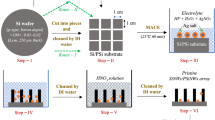
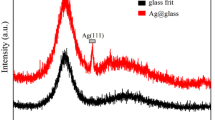
Abstract
Silver (Ag) paste is widely used in semiconductor metallization, especially in silicon solar cells. Ag powder is the material with the highest proportion in Ag paste. The morphology and structure of Ag powder are crucial which determine its characteristics, especially for the sintering activity. In this work, a simple method was developed to synthesize a type of microcrystalline spherical Ag particles (SP-A) with internal pores and the structural changes and sintering behavior were thoroughly studied by combining ultra-small-angle X-ray scattering (USAXS), small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS), in-situ heating X-ray diffraction (XRD), focused ion beam (FIB), and thermal analysis measurement. Due to the unique internal pores, the grain size of SP-A is smaller, and the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) is higher than that of traditional solid Ag particles. As a result, the sintering activity of SP-A is excellent, which can form a denser sintered body and form silver nanoparticles at the Ag–Si interface to improve silver silicon contact. Polycrystalline silicon solar cell built with SP-A obtained a low series resistance (Rs) and a high photoelectric conversion efficiency (PCE) of 19.26%. These fill a gap in Ag particle structure research, which is significant for the development of high-performance electronic Ag particles and efficient semiconductor devices.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Helveston, J. P.; He, G.; Davidson, M. R. Quantifying the cost savings of global solar photovoltaic supply chains. Nature 2022, 612, 83–87.
Buiting, A. G. M.; Thompson, J.; van der Keur, D.; Schmal-Bauer, W. C.; Bertina, R. M. Procoagulant activity of endocardial vegetations and blood monocytes in rabbits with streptococcus sanguis endocarditis. Thromb. Haemost. 1989, 62, 1029–1033.
Schubert, G.; Fischer, B.; Fath, P. Formation and nature of Ag thick film front contacts on crystalline silicon solar cells. Proc. 18th Eur. Photovoltaic Sol. Energy Conf., 2002, pp 343–346.
Yang, Y.; Seyedmohammadi, S.; Kumar, U.; Gnizak, D.; Graddy, E. D.; Shaikh, A. Screen printable silver paste for silicon solar cells with high sheet resistance emitters. Energy Procedia 2011, 8, 607–613.
Deng, W. W.; Ye, F.; Xiong, Z.; Chen, D. M.; Guo, W. W.; Chen, Y. F.; Yang, Y.; Altermatt, P. P.; Feng, Z. Q.; Verlinden, P. J. Development of high-efficiency industrial p-type multi-crystalline PERC solar cells with efficiency greater than 21%. Energy Procedia 2016, 92, 721–729.
Hang, K. W.; Wang, Y. L. Glass composition and its use in conductive silver paste. U. S. Patent 2, 013, 021, 114, November 14, 2013.
Fu, M.; Li, H. Y.; Wang, Y.; Fan, L.; Chen, D.; Feng, Z. Study on the synthesis and performances of ultrafine silver powder used as silicon solar cell front silver contacts. Mater. Sci. Forum 2016, 852, 378–384.
Fields, J. D.; Ahmad, M. I.; Pool, V. L.; Yu, J. F.; Van Campen, D. G.; Parilla, P. A.; Toney, M. F.; van Hest, M. F. A. M. The formation mechanism for printed silver-contacts for silicon solar cells. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11143.
Muchmore, P. Collections may depend on your own attitudes. Dent. Econ. 1982, 72, 51–54.
Li, W.; Yu, C. X.; Wang, Y. K.; Yao, Y.; Yu, X. L.; Zuo, C.; Yu, Y. Experimental investigation of effect of flake silver powder content on sintering structure and properties of front silver paste of silicon solar cell. Materials 2022, 15, 7142.
Zhang, X. F.; Liu, Z. G.; Shen, W.; Gurunathan, S. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, properties, applications, and therapeutic approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1534.
Shen, W. F.; Zhang, X. P.; Huang, Q. J.; Xu, Q. S.; Song, W. J. Preparation of solid silver nanoparticles for inkjet printed flexible electronics with high conductivity. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 1622–1628.
Sundaram, D.; Yang, V.; Yetter, R. A. Metal-based nanoenergetic materials: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2017, 61, 293–365.
Pasquino, R.; Grizzuti, N.; Maffettone, P. L.; Greco, F. Rheology of dilute and semidilute noncolloidal hard sphere suspensions. J. Rheol. 2008, 52, 1369–1384.
Avramović, L.; Pavlović, M. M.; Maksimović, V. M.; Vuković, M.; Stevanović, J. S.; Bugarin, M.; Nikolić, N. D. Comparative morphological and crystallographic analysis of electrochemically- and chemically-produced silver powder particles. Metals 2017, 7, 160.
Gebauer, J. S.; Treuel, L. Influence of individual ionic components on the agglomeration kinetics of silver nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 354, 546–554.
Sangsuk, S. Preparation of high surface area silver powder via Tollens process under sonication. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 775–777.
Jose, M.; Sakthivel, M. Synthesis and characterization of silver nanospheres in mixed surfactant solution. Mater. Lett. 2014, 117, 78–81.
Khanna, P. K.; Singh, N.; Kulkarni, D.; Deshmukh, S.; Charan, S.; Adhyapak, P. V. Water based simple synthesis of re-dispersible silver nano-particles. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 3366–3370.
Wang, Q. H.; Zhu, Y. X.; Xue, J.; Zhao, X. S.; Guo, Z. P.; Wang, C. General synthesis of porous mixed metal oxide hollow spheres with enhanced supercapacitive properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 17226–17232.
Liu, N.; Zhao, S. P.; Yang, Z. L.; Liu, B. Patchy templated synthesis of macroporous colloidal hollow spheres and their application as catalytic microreactors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 47008–47014.
Wu, P.; Du, N.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, C. X.; Yang, D. R. Self-templating synthesis of SnO2-carbon hybrid hollow spheres for superior reversible lithium ion storage. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 1946–1952.
Zhang, B.; Li, Y. S.; Chen, Y. J.; Chen, H. B.; Zhu, C.; Liu, J.; Lin, Y.; Pan, F. Interface tuning through the MoO3 additive in Al paste to enhance the performance of crystalline silicon solar cells. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2022, 5, 13254–13260.
Xu, J.; Zhu, X. Z.; Xu, L. H.; Kan, C. X.; Shi, D. N. Template-directed growth of Ag nanostructures: Soft templates versus hard templates. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 1687–1694.
Tuin, G.; Stein, H. N. Adsorption of ionic surfactant on polystyrene particles in the absence and presence of cosurfactant. Langmuir 1994, 10, 1054–1059.
Sarma, S.; Bora, M.; Dutta, R. K. Effects of alcohol on partition equilibrium of phenol red in micellar solutions and O/W microemulsions of anionic surfactants. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 256, 105–110.
Sarma, S.; Gohain, B.; Dutta, R. K. A visible spectroscopic study of microstructure of O/W microemulsions of anionic surfactants: Effect of cosurfactant. J. Dispersion Sci. Technol. 2006, 27, 899–905.
Ahsan, T.; Aveyard, R.; Binks, B. P. Winsor transitions and interfacial film compositions in systems containing sodium dodecylbenzene sulphonate and alkanols. Colloids Surf. 1991, 52, 339–352.
Giannini, C.; Ladisa, M.; Altamura, D.; Siliqi, D.; Sibillano, T.; De Caro, L. X-ray diffraction: A powerful technique for the multiple-length-scale structural analysis of nanomaterials. Crystals 2016, 6, 87.
Chen, Z. W.; Yang, M. L.; Chen, G. J.; Tang, G. X.; Huang, Z. Y.; Chu, M. H.; Qi, R.; Li, S. M.; Wang, R.; Wang, C. Q. et al. Triggering anionic redox activity in Fe/Mn-based layered oxide for high-performance sodium-ion batteries. Nano Energy 2022, 94, 106958.
Yan, X. S.; Lin, P.; Qi, X.; Yang, L. Finnis-sinclair potentials for fcc Au−Pd and Ag−Pt alloys. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2011, 102, 381–388.
Holzwarth, U.; Gibson, N. The Scherrer equation versus the ‘debyescherrer equation’. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 534.
Hammouda, B. Analysis of the beaucage model. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2010, 43, 1474–1478.
Hammouda, B. A new guinier-porod model. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2010, 43, 716–719.
Porod, G. Die Röntgenkleinwinkelstreuung von dichtgepackten kolloiden Systemen. II. Teil. Kolloid-Zeitschrift 1952, 125, 108–122.
Guinier, A.; Fournet, G. Small-Angle Scattering of X-Rays; Walker, C. B., trans. Wiley: New York, 1955.
Li, Z. H.; Gong, Y. J.; Wu, D.; Sun, Y. H.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Dong, B. Z. A negative deviation from Porod’s law in SAXS of organo-MSU-X. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2001, 46, 75–80.
Maruyama, I.; Sakamoto, N.; Matsui, K.; Igarashi, G. Microstructural changes in white Portland cement paste under the first drying process evaluated by WAXS, SAXS, and USAXS. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 91, 24–32.
Beaucage, G.; Kammler, H. K.; Pratsinis, S. E. Particle size distributions from small-angle scattering using global scattering functions. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2004, 37, 523–535.
Wang, W. S.; Zhen, L.; Xu, C. Y.; Yang, L.; Shao, W. Z. Controlled synthesis of calcium tungstate hollow microspheres via ostwald ripening and their photoluminescence property. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 19390–19398.
Möller, J.; Jacob, K. I.; Schmelzer, J. Ostwald ripening in porous viscoelastic materials. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1998, 59, 1097–1103.
Gill, P.; Moghadam, T. T.; Ranjbar, B. Differential scanning calorimetry techniques: Applications in biology and nanoscience. J. Biomol. Tech. 2010, 21, 167–193.
Rhodes, W. H. Agglomerate and particle size effects on sintering yttria-stabilized zirconia. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1981, 64, 19–22.
Exner, H. E. Role of interfaces in sintering. Metal Science 1982, 16, 451–456.
Edelson, L. H.; Glaeser, A. M. Role of particle substructure in the sintering of monosized titania. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1988, 71, 225–235.
Coble, R. L. Sintering crystalline solids. I. Intermediate and final state diffusion models. In Sintering Key Papers. Sōmiya, S.; Moriyoshi, Y., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, 1990; pp 55–67.
Chen, P.; Raghavan, P.; Yazzie, K.; Fei, H. Y. On the effective coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) of bilayer/trilayer in semiconductor package substrates. In 2015 IEEE 65th Electronic Components and Technology Conference, San Diego, USA, 2015, pp 1932–1937.
Kang, S. J. L. Sintering densification, grain growht, and microstructure. Int. J. Powder Metall. 2005, 41, 73–74.
Li, P.; Chen, S. Y.; Dai, H. F.; Yang, Z. M.; Chen, Z. Q.; Wang, Y. S.; Chen, Y. Q.; Peng, W. Q.; Shan, W. B.; Duan, H. G. Recent advances in focused ion beam nanofabrication for nanostructures and devices: Fundamentals and applications. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 1529–1565.
Li, M. Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Z. H.; Yu, J. Bimodal sintered silver nanoparticle paste with ultrahigh thermal conductivity and shear strength for high temperature thermal interface material applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 9157–9168.
Kim, H. S.; Cho, S. B.; Kim, H.; Kim, D.; Dovrat, M.; Eytan, G.; Huh, J. Y. Electrochemical nature of contact firing reactions for screen-printed silicon solar cells: Origin of “gray finger” phenomenon. Prog. Photovolt. 2016, 24, 1237–1250.
Schroder, D. K.; Meier, D. L. Solar-cell contact resistance—A review. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1984, 31, 637–647.
Wan, L.; Zhang, C. L.; Ge, K. P.; Yang, X. L.; Li, F.; Yan, W. S.; Xu, Z.; Yang, L.; Xu, Y.; Song, D. Y. et al. Conductive hole-selective passivating contacts for crystalline silicon solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 1903851.
Zhao, S. X.; Qiao, Q.; Zhang, S.; Ji, J. J.; Shi, Z. R.; Li, G. H. Rear passivation of commercial multi-crystalline PERC solar cell by PECVD Al2O3. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 290, 66–70.
Karpowich, L.; Mayberry, R. W.; Hörteis, M. Impact of glass chemistry on contact formation for silver metallization pastes. In 33rd European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference and Exhibition, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017, pp 617–621.
Eberstein, M.; Falk-Windisch, H.; Peschel, M.; Schilm, J.; Seuthe, T.; Wenzel, M.; Kretzschmar, C.; Partsch, U. Sintering and contact formation of glass containing silver pastes. Energy Procedia, 2012, 27, 522–530.
Keithley Instruments, Inc. Making Precision Low Voltage and Low Resistance Measurements [Online]. https://download.tek.com/document/LV_LR_e-hnbook_91113.pdf (accessed Aug 17, 2023).
Wu, W.; Chan, C.; Lewittes, M.; Zhang, L.; Roelofs, K. Study of carrier transport in silver paste metallized silicon solar cells. Energy Procedia 2016, 92, 984–989.
Kumar, P.; Aabdin, Z.; Pfeffer, M.; Eibl, O. High-efficiency, single-crystalline, p- and n-type Si solar cells: Microstructure and chemical analysis of the glass layer. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2018, 178, 52–64.
Li, W.; Wu, T.; Jiao, R. B.; Zhang, B. P.; Li, S. Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L. L. Effects of silver nanoparticles on the firing behavior of silver paste on crystalline silicon solar cells. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 466, 132–137.
Deng, D. Y.; Chen, Z. Y.; Hu, Y. L.; Tong, Y. G.; Liang, X. B. Preparation and post-treatment of silver powders for front contact pastes of silicon solar cells. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2021, 112, 457–464.
Hilali, M. M. The effect of Ag Powder surface topography on the viscoelastic behavior of thick-film Ag gridlines and solar cell performance. In 2018 IEEE 7th World Conference on Photovoltaic Energy Conversion (WCPEC) (A Joint Conference of 45th IEEE PVSC, 28th PVSEC & 34th EU PVSEC), Waikoloa, USA, 2018, pp 2663–2666.
Lan, F.; Bai, J. T.; Wang, H. The preparation of oleylamine modified micro-size sphere silver particles and its application in crystalline silicon solar cells. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 16866–16872.
Acknowledgments
The author would thank the support of the Soft Science Research Project of Guangdong Province (No. 2017B030301013), the Guangdong Innovative Team Program (No. 2013N080), and the Guangdong Province Major Talent Introducing Program (No. 2021QN020687). USAXS experiments supported by Dr. Feng Tian and BL10U1 beamline at SSRF are also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Chen, Z., Zhou, R. et al. Design of advanced porous silver powder with high-sintering activity to improve silicon solar cells. Nano Res. 17, 3189–3197 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6163-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6163-3