Abstract
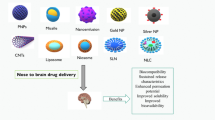
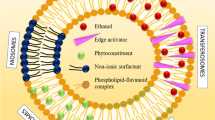
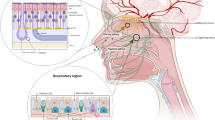
The existence of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) restricts the entry of drugs from the circulation into the central nervous system (CNS), which severely affects the treatment of neurological diseases, including glioblastoma, Parkinson’s disease (PD), and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). With the advantage of bypassing the BBB and avoiding systemic distribution, intranasal administration has emerged as an alternative method of delivering drugs to the brain. Drug delivery directly to the brain using intranasal nanosystems represents a new paradigm for neurological disease treatment because of its advantages in improving drug solubility and stability in vivo, enabling targeted drug delivery and controlled release, and reducing non-specific toxicity. And it has shown efficacy in animal models and clinical applications. Herein, this review describes the mechanisms of intranasal delivery of brain-targeted drugs, the properties of nanosystems for intranasal administration (e.g., liposomes, nanoemulsions, and micelles), and strategies for intranasal drug delivery to enhance brain-targeted drug delivery. Recent applications of nanosystems in intranasal drug delivery and disease treatment have been comprehensively reviewed. Although encouraging results have been reported, significant challenges still need to be overcome to translate these nanosystems into clinics. Therefore, the future prospects of intranasal drug delivery nanosystems are discussed in depth, expecting to provide useful insights and guidance for effective neurological disease treatment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
D’Souza, A.; Dave, K. M.; Stetler, R. A.; Manickam, D. S. Targeting the blood-brain barrier for the delivery of stroke therapies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 171, 332–351.
Sweeney, M. D.; Zhao, Z.; Montagne, A.; Nelson, A. R.; Zlokovic, B. V. Blood-brain barrier: From physiology to disease and back. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 21–78.
Banks, W. A. From blood-brain barrier to blood-brain interface: New opportunities for CNS drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 275–292.
Zhan, W. B.; Wang, C. H. Convection enhanced delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs into brain tumour. J. Control. Release 2018, 271, 74–87.
Bellat, V.; Alcaina, Y.; Tung, C. H.; Ting, R.; Michel, A. O.; Souweidane, M.; Law, B. A combined approach of convection-enhanced delivery of peptide nanofiber reservoir to prolong local DM1 retention for diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma treatment. Neuro Oncol. 2020, 22, 1495–1504.
Mangraviti, A.; Gullotti, D.; Tyler, B.; Brem, H. Nanobiotechnology-based delivery strategies: New frontiers in brain tumor targeted therapies. J. Control. Release 2016, 240, 443–453.
Tang, W.; Fan, W. P.; Lau, J.; Deng, L. M.; Shen, Z. Y.; Chen, X. Y. Emerging blood-brain-barrier-crossing nanotechnology for brain cancer theranostics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2967–3014.
Correa, D.; Scheuber, M. I.; Shan, H. M.; Weinmann, O. W.; Baumgartner, Y. A.; Harten, A.; Wahl, A. S.; Skaar, K. L.; Schwab, M. E. Intranasal delivery of full-length anti-nogo-A antibody: A potential alternative route for therapeutic antibodies to central nervous system targets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2200057120.
Terstappen, G. C.; Meyer, A. H.; Bell, R. D.; Zhang, W. D. Strategies for delivering therapeutics across the blood-brain barrier. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 362–383.
Padmakumar, S.; Jones, G.; Pawar, G.; Khorkova, O.; Hsiao, J.; Kim, J.; Amiji, M. M.; Bleier, B. S. Minimally invasive nasal depot (MIND) technique for direct BDNF AntagoNAT delivery to the brain. J. Control. Release 2021, 331, 176–186.
Kou, D. D.; Gao, Y.; Li, C.; Zhou, D. D.; Lu, K.; Wang, N.; Zhang, R. R.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, L. et al. Intranasal pathway for nanoparticles to enter the central nervous system. Nano Lett. 2023, 23, 5381–5390.
Chen, W. L.; Yao, S.; Wan, J.; Tian, Y.; Huang, L.; Wang, S. S.; Akter, F.; Wu, Y. Q.; Yao, Y. Z.; Zhang, X. C. BBB-crossing adeno-associated virus vector:An excellent gene delivery tool for CNS disease treatment. J. Control. Release 2021, 333, 129–138.
Agrawal, M.; Saraf, S.; Saraf, S.; Antimisiaris, S. G.; Chougule, M. B.; Shoyele, S. A.; Alexander, A. Nose-to-brain drug delivery: An update on clinical challenges and progress towards approval of anti-Alzheimer drugs. J. Control. Release 2018, 281, 139–177.
Meirinho, S.; Rodrigues, M.; Santos, A. O.; Falcão, A.; Alves, G. Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems: An alternative approach to improve brain bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs through intranasal administration. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1487.
Kozlovskaya, L.; Abou-Kaoud, M.; Stepensky, D. Quantitative analysis of drug delivery to the brain via nasal route. J. Control. Release 2014, 189, 133–140.
Xie, J. B.; Shen, Z. Y.; Anraku, Y.; Kataoka, K.; Chen, X. Y. Nanomaterial-based blood-brain-barrier (BBB) crossing strategies. Biomaterials 2019, 224, 119491.
Ruigrok, M. J. R.; De Lange, E. C. M. Emerging insights for translational pharmacokinetic and pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic studies: Towards prediction of nose-to-brain transport in humans. Aaps. J. 2015, 17, 493–505.
Costa, C. P.; Moreira, J. N.; Lobo, J. M. S.; Silva, A. C. Intranasal delivery of nanostructured lipid carriers, solid lipid nanoparticles and nanoemulsions: A current overview of in vivo studies. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 925–940.
Battaglia, L.; Panciani, P. P.; Muntoni, E.; Capucchio, M. T.; Biasibetti, E.; De Bonis, P.; Mioletti, S.; Fontanella, M.; Swaminathan, S. Lipid nanoparticles for intranasal administration: Application to nose-to-brain delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 369–378.
Pires, P. C.; Santos, A. O. Nanosystems in nose-to-brain drug delivery: A review of non-clinical brain targeting studies. J. Control. Release 2018, 270, 89–100.
Kumar, N. N.; Lochhead, J. J.; Pizzo, M. E.; Nehra, G.; Boroumand, S.; Greene, G.; Thorne, R. G. Delivery of immunoglobulin G antibodies to the rat nervous system following intranasal administration: Distribution, dose-response, and mechanisms of delivery. J. Control. Release 2018, 286, 467–484.
Lee, M. R.; Shnitko, T. A.; Blue, S. W.; Kaucher, A. V.; Winchell, A. J.; Erikson, D. W.; Grant, K. A.; Leggio, L. Labeled oxytocin administered via the intranasal route reaches the brain in rhesus macaques. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2783.
Veronesi, M. C.; Graner, B. D.; Cheng, S. H.; Zamora, M.; Zarrinmayeh, H.; Chen, C. T.; Das, S. K.; Vannier, M. W. Aerosolized in vivo 3D localization of nose-to-brain nanocarrier delivery using multimodality neuroimaging in a rat model-protocol development. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 391.
Van De Bittner, G. C.; Van De Bittner, K. C.; Wey, H. Y.; Rowe, W.; Dharanipragada, R.; Ying, X. Y.; Hurst, W.; Giovanni, A.; Alving, K.; Gupta, A. et al. Positron emission tomography assessment of the intranasal delivery route for orexin a. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 358–368.
Wang, K.; Kumar, U. S.; Sadeghipour, N.; Massoud, T. F.; Paulmurugan, R. A microfluidics-based scalable approach to generate extracellular vesicles with enhanced therapeutic microrna loading for intranasal delivery to mouse glioblastomas. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 18327–18346.
Grassin-Delyle, S.; Buenestado, A.; Naline, E.; Faisy, C.; Blouquit-Laye, S.; Couderc, L. J.; Le Guen, M.; Fischler, M.; Devillier, P. Intranasal drug delivery: An efficient and non-invasive route for systemic administration: Focus on opioids. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 134, 366–379.
Torrens, A.; Ruiz, C. M.; Martinez, M. X.; Tagne, A. M.; Roy, P.; Grimes, D.; Ahmed, F.; Lallai, V.; Inshishian, V.; Bautista, M. et al. Nasal accumulation and metabolism of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol following aerosol (“vaping”) administration in an adolescent rat model. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 187, 106600.
Chatterjee, B.; Gorain, B.; Mohananaidu, K.; Sengupta, P.; Mandal, U. K.; Choudhury, H. Targeted drug delivery to the brain via intranasal nanoemulsion: Available proof of concept and existing challenges. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 565, 258–268.
Hemmat, A.; Ghassami, E.; Minaiyan, M.; Varshosaz, J. Magnetophoretic intranasal drug-loaded magnetic nano-aggregates as a platform for drug delivery in status epilepticus. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2023, 11, 155–166.
Shringarpure, M.; Gharat, S.; Momin, M.; Omri, A. Management of epileptic disorders using nanotechnology-based strategies for nose-to-brain drug delivery. Exp. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 169–185.
Djupesland, P. G.; Messina, J. C.; Mahmoud, R. A. The nasal approach to delivering treatment for brain diseases: An anatomic, physiologic, and delivery technology overview. Ther. Deliv. 2014, 5, 709–733.
Pardeshi, C. V.; Belgamwar, V. S. Direct nose to brain drug delivery via integrated nerve pathways bypassing the blood-brain barrier: An excellent platform for brain targeting. Exp. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 957–972.
Gänger, S.; Schindowski, K. Tailoring formulations for intranasal nose-to-brain delivery: A review on architecture, physico-chemical characteristics and mucociliary clearance of the nasal olfactory mucosa. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 116.
Ogawa, K.; Uchida, M.; Yamaki, T.; Matsuzaki, H.; Kimura, M.; Okazaki, M.; Uchida, H.; Natsume, H. Delivery of acetaminophen to the central nervous system and the pharmacological effect after intranasal administration with a mucoadhesive agent and absorption enhancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 594, 120046.
Jiang, Y. J.; Li, Y.; Liu, X. F. Intranasal delivery: Circumventing the iron curtain to treat neurological disorders. Exp. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 1717–1725.
Priester, M. I.; Ten Hagen, T. L. M. Image-guided drug delivery in nanosystem-based cancer therapies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 192, 114621.
Large, D. E.; Abdelmessih, R. G.; Fink, E. A.; Auguste, D. T. Liposome composition in drug delivery design, synthesis, characterization, and clinical application. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 176, 113851.
Filipczak, N.; Pan, J. Y.; Yalamarty, S. S. K.; Torchilin, V. P. Recent advancements in liposome technology. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 156, 4–22.
Almeida, B.; Nag, O. K.; Rogers, K. E.; Delehanty, J. B. Recent progress in bioconjugation strategies for liposome-mediated drug delivery. Molecules 2020, 25, 5672.
Allen, T. M.; Cullis, P. R. Liposomal drug delivery systems: From concept to clinical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 36–48.
Singh, Y.; Meher, J. G.; Raval, K.; Khan, F. A.; Chaurasia, M.; Jain, N. K.; Chourasia, M. K. Nanoemulsion: Concepts, development and applications in drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2017, 252, 28–49.
Bozzato, E.; Bastiancich, C.; Préat, V. Nanomedicine: A useful tool against glioma stem cells. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 13, 9.
Saka, R.; Chella, N.; Khan, W. Development of imatinib mesylate-loaded liposomes for nose to brain delivery: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Aaps PharmSciTech 2021, 22, 192.
Rideau, E.; Dimova, R.; Schwille, P.; Wurm, F. R.; Landfester, K. Liposomes and polymersomes: A comparative review towards cell mimicking. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8572–8610.
Machut-Binkowski, C.; Hapiot, F.; Cecchelli, R.; Martin, P.; Monflier, E. A versatile liposome/cyclodextrin supramolecular carrier for drug delivery through the blood-brain barrier. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2007, 57, 567–572.
Kurano, T.; Kanazawa, T.; Ooba, A.; Masuyama, Y.; Maruhana, N.; Yamada, M.; Iioka, S.; Ibaraki, H.; Kosuge, Y.; Kondo, H. et al. Nose-to-brain/spinal cord delivery kinetics of liposomes with different surface properties. J. Control. Release 2022, 344, 225–234.
Pashirova, T. N.; Zueva, I. V.; Petrov, K. A.; Lukashenko, S. S.; Nizameev, I. R.; Kulik, N. V.; Voloshina, A. D.; Almasy, L.; Kadirov, M. K.; Masson, P. et al. Mixed cationic liposomes for brain delivery of drugs by the intranasal route: The acetylcholinesterase reactivator 2-PAM as encapsulated drug model. Colloids Surf. Biointerf. 2018, 171, 358–367.
Dhaval, M.; Vaghela, P.; Patel, K.; Sojitra, K.; Patel, M.; Patel, S.; Dudhat, K.; Shah, S.; Manek, R.; Parmar, R. Lipid-based emulsion drug delivery systems—A comprehensive review. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 1616–1639.
Dhaliwal, H. K.; Fan, Y. F.; Kim, J.; Amiji, M. M. Intranasal delivery and transfection of mRNA therapeutics in the brain using cationic liposomes. Mol. Pharmaceutics 2020, 17, 1996–2005.
Jojo, G. M.; Kuppusamy, G.; De, A.; Karri, V. V. S. N. R. Formulation and optimization of intranasal nanolipid carriers of pioglitazone for the repurposing in Alzheimer’s disease using Box-Behnken design. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 1061–1072.
Guo, X. L.; Zheng, H.; Guo, Y. T.; Wang, Y.; Anderson, G. J.; Ci, Y.; Yu, P.; Geng, L. N.; Chang, Y. Z. Nasal delivery of nanoliposome-encapsulated ferric ammonium citrate can increase the iron content of rat brain. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 15, 42.
Azambuja, J. H.; Schuh, R. S.; Michels, L. R.; Gelsleichter, N. E.; Beckenkamp, L. R.; Iser, I. C.; Lenz, G. S.; De Oliveira, F. H.; Venturin, G.; Greggio, S. et al. Nasal administration of cationic nanoemulsions as CD73-siRNA delivery system for glioblastoma treatment: A new therapeutical approach. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 635–649.
Kaur, A.; Nigam, K.; Srivastava, S.; Tyagi, A.; Dang, S. Memantine nanoemulsion: A new approach to treat Alzheimer’s disease. J. Microencapsul. 2020, 37, 355–365.
Fachel, F. N. S.; Medeiros-Neves, B.; Dal Prá, M.; Schuh, R. S.; Veras, K. S.; Bassani, V. L.; Koester, L. S.; Henriques, A. T.; Braganhol, E.; Teixeira, H. F. Box-Behnken design optimization of mucoadhesive chitosan-coated nanoemulsions for rosmarinic acid nasal delivery—In vitro studies. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 199, 572–582.
Sarheed, O.; Shouqair, D.; Ramesh, K. V. R. N. S.; Khaleel, T.; Amin, M.; Boateng, J.; Drechsler, M. Formation of stable nanoemulsions by ultrasound-assisted two-step emulsification process for topical drug delivery: Effect of oil phase composition and surfactant concentration and loratadine as ripening inhibitor. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 576, 118952.
Kanazawa, T.; Akiyama, F.; Kakizaki, S.; Takashima, Y.; Seta, Y. Delivery of siRNA to the brain using a combination of nose-to-brain delivery and cell-penetrating peptide-modified nano-micelles. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 9220–9226.
Nour, S. A.; Abdelmalak, N. S.; Naguib, M. J.; Rashed, H. M.; Ibrahim, A. B. Intranasal brain-targeted clonazepam polymeric micelles for immediate control of status epilepticus: In vitro optimization, ex vivo determination of cytotoxicity, in vivo biodistribution and pharmacodynamics studies. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 3681–3695.
Liu, S. S.; Yang, S. L.; Ho, P. C. Intranasal administration of carbamazepine-loaded carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles for drug delivery to the brain. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 72–81.
Ahmed, T. A.; El-Say, K. M.; Ahmed, O. A. A.; Aljaeid, B. M. Superiority of TPGS-loaded micelles in the brain delivery of vinpocetine via administration of thermosensitive intranasal gel. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 5555–5567.
Zhang, L.; Yang, S. L.; Wong, L. R.; Xie, H.; Ho, P. C. L. In vitro and in vivo comparison of curcumin-encapsulated chitosan-coated poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles and curcumin/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes administered intranasally as therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Pharmaceutics 2020, 17, 4256–4269.
Zameer, S.; Ali, J.; Vohora, D.; Najmi, A. K.; Akhtar, M. Development, optimisation and evaluation of chitosan nanoparticles of alendronate against Alzheimer’s disease in intracerebroventricular streptozotocin model for brain delivery. J. Drug Target. 2021, 29, 199–216.
Burilova, E. A.; Pashirova, T. N.; Zueva, I. V.; Gibadullina, E. M.; Lushchekina, S. V.; Sapunova, A. S.; Kayumova, R. M.; Rogov, A. M.; Evtjugin, V. G.; Sudakov, I. A. et al. Bi-functional sterically hindered phenol lipid-based delivery systems as potential multi-target agents against Alzheimer’s disease via an intranasal route. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 13757–13770.
Muntimadugu, E.; Dhommati, R.; Jain, A.; Challa, V. G. S.; Shaheen, M.; Khan, W. Intranasal delivery of nanoparticle encapsulated tarenflurbil: A potential brain targeting strategy for Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 92, 224–234.
Samaridou, E.; Walgrave, H.; Salta, E.; Álvarez, D. M.; Castro-López, V.; Loza, M.; Alonso, M. J. Nose-to-brain delivery of enveloped RNA-cell permeating peptide nanocomplexes for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Biomaterials 2020, 230, 119657.
Yang, H.; Mu, W. H.; Wei, D. H.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, Y.; Gao, J. X.; Gong, X. Q.; Wang, H. J.; Wu, X. L.; Tao, H. et al. A novel targeted and high-efficiency nanosystem for combinational therapy for Alzheimer’s disease. Adv. Sci. (Weinh.) 2020, 7, 1902906.
Sukumar, U. K.; Bose, R. J. C.; Malhotra, M.; Babikir, H. A.; Afjei, R.; Robinson, E.; Zeng, Y. T.; Chang, E.; Habte, F.; Sinclair, R. et al. Intranasal delivery of targeted polyfunctional gold-iron oxide nanoparticles loaded with therapeutic microRNAs for combined theranostic multimodality imaging and presensitization of glioblastoma to temozolomide. Biomaterials 2019, 218, 119342.
Sousa, F.; Dhaliwal, H. K.; Gattacceca, F.; Sarmento, B.; Amiji, M. M. Enhanced anti-angiogenic effects of bevacizumab in glioblastoma treatment upon intranasal administration in polymeric nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2019, 309, 37–47.
Shah, B. Microemulsion as a promising carrier for nose to brain delivery: Journey since last decade. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 611–634.
Iqbal, R.; Ahmed, S.; Jain, G. K.; Vohora, D. Design and development of letrozole nanoemulsion: A comparative evaluation of brain targeted nanoemulsion with free letrozole against status epilepticus and neurodegeneration in mice. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 565, 20–32.
Wik, J.; Bansal, K. K.; Assmuth, T.; Rosling, A.; Rosenholm, J. M. Facile methodology of nanoemulsion preparation using oily polymer for the delivery of poorly soluble drugs. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 1228–1240.
Roy, A.; Nishchaya, K.; Rai, V. K. Nanoemulsion-based dosage forms for the transdermal drug delivery applications: A review of recent advances. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 303–319.
Handa, M.; Tiwari, S.; Yadav, A. K.; Almalki, W. H.; Alghamdi, S.; Alharbi, K. S.; Shukla, R.; Beg, S. Therapeutic potential of nanoemulsions as feasible wagons for targeting Alzheimer’s disease. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 2881–2888.
Ozogul, Y.; Karsli, G. T.; Durmuş, M.; Yazgan, H.; Oztop, H. M.; McClements, D. J.; Ozogul, F. Recent developments in industrial applications of nanoemulsions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 304, 102685.
Richa, R.; Roy Choudhury, A. Exploration of polysaccharide based nanoemulsions for stabilization and entrapment of curcumin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 1287–1296.
Cheng, L. C.; Hashemnejad, S. M.; Zarket, B.; Muthukrishnan, S.; Doyle, P. S. Thermally and pH-responsive gelation of nanoemulsions stabilized by weak acid surfactants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 563, 229–240.
Carpenter, J.; Saharan, V. K. Ultrasonic assisted formation and stability of mustard oil in water nanoemulsion: Effect of process parameters and their optimization. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 35, 422–430.
Manickam, S.; Sivakumar, K.; Pang, C. H. Investigations on the generation of oil-in-water (O/W) nanoemulsions through the combination of ultrasound and microchannel. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 69, 105258.
Bader, H.; Ringsdorf, H.; Schmidt, B. Watersoluble polymers in medicine. Die Angew. Makromol. Chem. 1984, 123, 457–485.
Hari, S. K.; Gauba, A.; Shrivastava, N.; Tripathi, R. M.; Jain, S. K.; Pandey, A. K. Polymeric micelles and cancer therapy: An ingenious multimodal tumor-targeted drug delivery system. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2023, 13, 135–163.
Van Strien, J.; Escalona-Rayo, O.; Jiskoot, W.; Slütter, B.; Kros, A. Elastin-like polypeptide-based micelles as a promising platform in nanomedicine. J. Control. Release 2023, 353, 713–726.
Pokharkar, V.; Suryawanshi, S.; Dhapte-Pawar, V. Exploring micellar-based polymeric systems for effective nose-to-brain drug delivery as potential neurotherapeutics. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 1019–1031.
Lu, Y.; Zhang, E. S.; Yang, J. H.; Cao, Z. Q. Strategies to improve micelle stability for drug delivery. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 4985–4998.
Zhou, Q. Y.; Zhao, T. C.; Liu, M. L.; Yin, D. R.; Liu, M. C.; Elzatahry, A. A.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, D. Y.; Li, X. M. Highly stable hybrid single-micelle: A universal nanocarrier for hydrophobic bioimaging agents. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 4582–4589.
Kamegawa, R.; Naito, M.; Miyata, K. Functionalization of silica nanoparticles for nucleic acid delivery. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 5219–5239.
Yu, C. C.; Li, K.; Xu, L.; Li, B.; Li, C. H.; Guo, S.; Li, Z. Y.; Zhang, Y. Q.; Hussain, A.; Tan, H. et al. siRNA-functionalized lanthanide nanoparticle enables efficient endosomal escape and cancer treatment. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 9160–9168.
Yi, X. Q.; Zeng, W. J.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, L. Y.; Zhu, X. L.; Ke, Y. Q.; He, X. Y.; Kuang, Y.; Huang, Q. T. A step-by-step multiple stimuli-responsive metal-phenolic network prodrug nanoparticles for chemotherapy. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 1205–1212.
Jeong, S. H.; Jang, J. H.; Cho, H. Y.; Lee, Y. B. Soft- and hard-lipid nanoparticles: A novel approach to lymphatic drug delivery. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2018, 41, 797–814.
Anderluzzi, G.; Lou, G.; Su, Y.; Perrie, Y. Scalable manufacturing processes for solid lipid nanoparticles. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2019, 7, 444–459.
Nasirizadeh, S.; Malaekeh-Nikouei, B. Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers in oral cancer drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 101458.
De Oliveira Junior, E. R.; Truzzi, E.; Ferraro, L.; Fogagnolo, M.; Pavan, B.; Beggiato, S.; Rustichelli, C.; Maretti, E.; Lima, E. M.; Leo, E. et al. Nasal administration of nanoencapsulated geraniol/ursodeoxycholic acid conjugate: Towards a new approach for the management of Parkinson’s disease. J. Control. Release 2020, 321, 540–552.
Hasan, N.; Imran, M.; Kesharwani, P.; Khanna, K.; Karwasra, R.; Sharma, N.; Rawat, S.; Sharma, D.; Ahmad, F. J.; Jain, G. K. et al. Intranasal delivery of naloxone-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles as a promising simple and non-invasive approach for the management of opioid overdose. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 599, 120428.
Uppuluri, C. T.; Ravi, P. R.; Dalvi, A. V. Design, optimization and pharmacokinetic evaluation of piribedil loaded solid lipid nanoparticles dispersed in nasal in situ gelling system for effective management of Parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 606, 120881.
Akel, H.; Ismail, R.; Csóka, I. Progress and perspectives of brain-targeting lipid-based nanosystems via the nasal route in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 148, 38–53.
Correia, A. C.; Monteiro, A. R.; Silva, R.; Moreira, J. N.; Lobo, J. M. S.; Silva, A. C. Lipid nanoparticles strategies to modify pharmacokinetics of central nervous system targeting drugs: Crossing or circumventing the blood-brain barrier (BBB) to manage neurological disorders. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 189, 114485.
Costa, C.; Moreira, J. N.; Amaral, M. H.; Lobo, J. M. S.; Silva, A. C. Nose-to-brain delivery of lipid-based nanosystems for epileptic seizures and anxiety crisis. J. Control. Release 2019, 295, 187–200.
Keck, C. M.; Specht, D.; Brüßler, J. Influence of lipid matrix composition on biopharmaceutical properties of lipid nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2021, 338, 149–163.
Kovačević, A. B.; Müller, R. H.; Keck, C. M. Formulation development of lipid nanoparticles: Improved lipid screening and development of tacrolimus loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC). Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 576, 118918.
Dana, P.; Yostawonkul, J.; Chonniyom, W.; Unger, O.; Sakulwech, S.; Sathornsumetee, S.; Saengkrit, N. Nanostructured lipid base carrier for specific delivery of garlic oil through blood brain barrier against aggressiveness of glioma. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 64, 102651.
Agbo, C. P.; Ugwuanyi, T. C.; Ugwuoke, W. I.; McConville, C.; Attama, A. A.; Ofokansi, K. C. Intranasal artesunate-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers: A convenient alternative to parenteral formulations for the treatment of severe and cerebral malaria. J. Control. Release 2021, 334, 224–236.
Nguyen, T. T. L.; Maeng, H. J. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of intranasal solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers for nose-to-brain delivery. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 572.
Hong, S. S.; Oh, K. T.; Choi, H. G.; Lim, S. J. Liposomal formulations for nose-to-brain delivery: Recent advances and future perspectives. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 540.
Ahmad, E.; Feng, Y. H.; Qi, J. P.; Fan, W. F.; Ma, Y. H.; He, H. S.; Xia, F.; Dong, X. C.; Zhao, W. L.; Lu, Y. et al. Evidence of nose-to-brain delivery of nanoemulsions: Cargoes but not vehicles. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 1174–1183.
Le, M. Q.; Carpentier, R.; Lantier, I.; Ducournau, C.; Dimier-Poisson, I.; Betbeder, D. Residence time and uptake of porous and cationic maltodextrin-based nanoparticles in the nasal mucosa: Comparison with anionic and cationic nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 550, 316–324.
Guo, T. W.; Guo, Y. Y.; Gong, Y. H.; Ji, J. G.; Hao, S. L.; Deng, J.; Wang, B. C. An enhanced charge-driven intranasal delivery of nicardipine attenuates brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 566, 46–56.
Suk, J. S.; Xu, Q. G.; Kim, N.; Hanes, J.; Ensign, L. M. PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 99, 28–51.
Chaudhury, S. S.; Nandi, M.; Kumar, K.; Ruidas, B.; Sur, T. K.; Prasad, P.; Chakrabarti, S.; De, P.; Sil, J.; Das Mukhopadhyay, C. Rodent model preclinical assessment of PEGylated block copolymer targeting cognition and oxidative stress insults of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 2036–2050.
Goel, H.; Kalra, V.; Verma, S. K.; Dubey, S. K.; Tiwary, A. K. Convolutions in the rendition of nose to brain therapeutics from bench to bedside: Feats & fallacies. J. Control. Release 2022, 341, 782–811.
Schlachet, I.; Sosnik, A. Mixed mucoadhesive amphiphilic polymeric nanoparticles cross a model of nasal septum epithelium in vitro. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 21360–21371.
Guimaraes, M. E. N.; Lopez-Blanco, R.; Correa, J.; Fernandez-Villamarin, M.; Bistué, M. B.; Martino-Adami, P.; Morelli, L.; Kumar, V.; Wempe, M. F.; Cuello, A. C. et al. Liver X receptor activation with an intranasal polymer therapeutic prevents cognitive decline without altering lipid levels. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 4678–4687.
Law, L. H.; Huang, J. P.; Xiao, P.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z. L.; Lai, J. H. C.; Han, X. Q.; Cheng, G. W. Y.; Tse, K. H.; Chan, K. W. Y. Multiple CEST contrast imaging of nose-to-brain drug delivery using Iohexol liposomes at 3T MRI. J. Control. Release 2023, 354, 208–220.
Teo, S. L. Y.; Rennick, J. J.; Yuen, D.; Al-Wassiti, H.; Johnston, A. P. R.; Pouton, C. W. Unravelling cytosolic delivery of cell penetrating peptides with a quantitative endosomal escape assay. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3721.
Zorko, M.; Jones, S.; Langel, Ü. Cell-penetrating peptides in protein mimicry and cancer therapeutics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 180, 114044.
Tian, Y.; Zhou, S. B. Advances in cell penetrating peptides and their functionalization of polymeric nanoplatforms for drug delivery. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 13, e1668.
Xu, J. K.; Khan, A. R.; Fu, M. F.; Wang, R. J.; Ji, J. B.; Zhai, G. X. Cell-penetrating peptide: A means of breaking through the physiological barriers of different tissues and organs. J. Control. Release 2019, 309, 106–124.
Yoo, D. Y.; Barros, S. A.; Brown, G. C.; Rabot, C.; Bar-Sagi, D.; Arora, P. S. Macropinocytosis as a key determinant of peptidomimetic uptake in cancer cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 14461–14471.
Patel, S. G.; Sayers, E. J.; He, L.; Narayan, R.; Williams, T. L.; Mills, E. M.; Allemann, R. K.; Luk, L. Y. P.; Jones, A. T.; Tsai, Y. H. Cell-penetrating peptide sequence and modification dependent uptake and subcellular distribution of green florescent protein in different cell lines. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6298.
Liu, Y. K.; Zhao, Z. H.; Li, M. Overcoming the cellular barriers and beyond: Recent progress on cell penetrating peptide modified nanomedicine in combating physiological and pathological barriers. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 17, 523–543.
Akita, T.; Oda, Y.; Kimura, R.; Nagai, M.; Tezuka, A.; Shimamura, M.; Washizu, K.; Oka, J. I.; Yamashita, C. Involvement of trigeminal axons in nose-to-brain delivery of glucagon-like peptide-2 derivative. J. Control. Release 2022, 351, 573–580.
Akita, T.; Kimura, R.; Akaguma, S.; Nagai, M.; Nakao, Y.; Tsugane, M.; Suzuki, H.; Oka, J. I.; Yamashita, C. Usefulness of cell-penetrating peptides and penetration accelerating sequence for nose-to-brain delivery of glucagon-like peptide-2. J. Control. Release 2021, 335, 575–583.
Lin, T. T.; Liu, E. G.; He, H. N.; Shin, M. C.; Moon, C.; Yang, V. C.; Huang, Y. Z. Nose-to-brain delivery of macromolecules mediated by cell-penetrating peptides. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 352–358.
Hou, Q. H.; Wang, L. L.; Xiao, F.; Wang, L.; Liu, X. Y.; Zhu, L. N.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, W. F.; Jiang, X. Y. Dual targeting nanoparticles for epilepsy therapy. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 12913–12920.
Copolovici, D. M.; Langel, K.; Eriste, E.; Langel, Ü. Cell-penetrating peptides: Design, synthesis, and applications. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 1972–1994.
Chen, K. Y.; Pei, D. H. Engineering cell-permeable proteins through insertion of cell-penetrating motifs into surface loops. ACS Chem. Biol. 2020, 15, 2568–2576.
Kanazawa, T.; Taki, H.; Okada, H. Nose-to-brain drug delivery system with ligand/cell-penetrating peptide-modified polymeric nano-micelles for intracerebral gliomas. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 152, 85–94.
Van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228.
Wu, J.; Ma, L.; Sun, D. N.; Zhang, X. R.; Cui, J. W.; Du, Y. J.; Guo, Y. M.; Wang, X.; Di, L. Q.; Wang, R. N. Bioengineering extracellular vesicles as novel nanocarriers towards brain disorders. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 2635–2659.
Maeki, M.; Kimura, N.; Sato, Y.; Harashima, H.; Tokeshi, M. Advances in microfluidics for lipid nanoparticles and extracellular vesicles and applications in drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 128, 84–100.
Ke, W. N.; Afonin, K. A. Exosomes as natural delivery carriers for programmable therapeutic nucleic acid nanoparticles (NANPs). Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 176, 113835.
Jiang, X. C.; Zhang, T. Y.; Gao, J. Q. The in vivo fate and targeting engineering of crossover vesicle-based gene delivery system. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 187, 114324.
Li, Y. S.; Wu, H. H.; Jiang, X. C.; Dong, Y. F.; Zheng, J. J.; Gao, J. Q. New idea to promote the clinical applications of stem cells or their extracellular vesicles in central nervous system disorders: Combining with intranasal delivery. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 3215–3232.
Herman, S.; Fishel, I.; Offen, D. Intranasal delivery of mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles for the treatment of neurological diseases. Stem Cells 2021, 39, 1589–1600.
Liu, B.; Kong, Y. F.; Shi, W.; Kuss, M.; Liao, K.; Hu, G. K.; Xiao, P.; Sankarasubramanian, J.; Guda, C.; Wang, X. L. et al. Exosomes derived from differentiated human ADMSC with the Schwann cell phenotype modulate peripheral nerve-related cellular functions. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 14, 61–75.
Labusek, N.; Mouloud, Y.; Köster, C.; Diesterbeck, E.; Tertel, T.; Wiek, C.; Hanenberg, H.; Horn, P. A.; Felderhoff-Müser, U.; Bendix, I. et al. Extracellular vesicles from immortalized mesenchymal stromal cells protect against neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Inflamm. Regen. 2023, 43, 24.
Peng, H.; Li, Y.; Ji, W. H.; Zhao, R. C.; Lu, Z. G.; Shen, J.; Wu, Y. Y.; Wang, J. Z.; Hao, Q. L.; Wang, J. W. et al. Intranasal administration of self-oriented nanocarriers based on therapeutic exosomes for synergistic treatment of Parkinson’s disease. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 869–884.
Raguraman, R.; Bhavsar, D.; Kim, D.; Ren, X. Y.; Sikavitsas, V.; Munshi, A.; Ramesh, R. Tumor-targeted exosomes for delivery of anticancer drugs. Cancer Lett. 2023, 558, 216093.
Dasgupta, A.; Sun, T.; Palomba, R.; Rama, E.; Zhang, Y. Z.; Power, C.; Moeckel, D.; Liu, M. J.; Sarode, A.; Weiler, M. et al. Nonspherical ultrasound microbubbles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2218847120.
Gorick, C. M.; Breza, V. R.; Nowak, K. M.; Cheng, V. W. T.; Fisher, D. G.; Debski, A. C.; Hoch, M. R.; Demir, Z. E. F.; Tran, N. M.; Schwartz, M. R. et al. Applications of focused ultrasound-mediated blood-brain barrier opening. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 191, 114583.
Ye, D. Z.; Luan, J. Y.; Pang, H.; Yang, Y. H.; Nazeri, A.; Rubin, J. B.; Chen, H. Characterization of focused ultrasound-mediated brainstem delivery of intranasally administered agents. J. Control. Release 2020, 328, 276–285.
Chen, H.; Chen, C. C.; Acosta, C.; Wu, S. Y.; Sun, T.; Konofagou, E. E. A new brain drug delivery strategy: Focused ultrasound-enhanced intranasal drug delivery. PLoS One 2014, 9, e108880.
Ye, D. Z.; Zhang, X. H.; Yue, Y. M.; Raliya, R.; Biswas, P.; Taylor, S.; Tai, Y. C.; Rubin, J. B.; Liu, Y. J.; Chen, H. Focused ultrasound combined with microbubble-mediated intranasal delivery of gold nanoclusters to the brain. J. Control. Release 2018, 286, 145–153.
Ye, D. Z.; Yuan, J. Y.; Yang, Y. H.; Yue, Y. M.; Hu, Z. T.; Fadera, S.; Chen, H. Incisionless targeted adeno-associated viral vector delivery to the brain by focused ultrasound-mediated intranasal administration. eBioMedicine 2022, 84, 104277.
Ye, D. Z.; Sultan, D.; Zhang, X. H.; Yue, Y. M.; Heo, G. S.; Kothapalli, S. V. V. N.; Luehmann, H.; Tai, Y. C.; Rubin, J. B.; Liu, Y. et al. Focused ultrasound-enabled delivery of radiolabeled nanoclusters to the pons. J. Control. Release 2018, 283, 143–150.
Dimatteo, R.; Darling, N. J.; Segura, T. In situ forming injectable hydrogels for drug delivery and wound repair. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 127, 167–184.
Shah, S.; Rangaraj, N.; Laxmikeshav, K.; Sampathi, S. “Nanogels as drug carriers—Introduction, chemical aspects, release mechanisms and potential applications”. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 581, 119268.
Ayoubi-Joshaghani, M. H.; Seidi, K.; Azizi, M.; Jaymand, M.; Javaheri, T.; Jahanban-Esfahlan, R.; Hamblin, M. R. Potential applications of advanced nano/hydrogels in biomedicine: Static, dynamic, multi-stage, and bioinspired. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2004098.
Kandil, R.; Merkel, O. M. Recent progress of polymeric nanogels for gene delivery. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 39, 11–23.
Salatin, S.; Barar, J.; Barzegar-Jalali, M.; Adibkia, K.; Milani, M. A.; Jelvehgari, M. Hydrogel nanoparticles and nanocomposites for nasal drug/vaccine delivery. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2016, 39, 1181–1192.
Kim, Y. S.; Sung, D. K.; Kim, H.; Kong, W. H.; Kim, Y. E.; Hahn, S. K. Nose-to-brain delivery of hyaluronate—FG loop peptide conjugate for non-invasive hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy therapy. J. Control. Release 2019, 307, 76–89.
Majcher, M. J.; Babar, A.; Lofts, A.; Leung, A.; Li, X. Y.; Abu-Hijleh, F.; Smeets, N. M. B.; Mishra, R. K.; Hoare, T. In situ-gelling starch nanoparticle (SNP)/O-carboxymethyl chitosan (CMCh) nanoparticle network hydrogels for the intranasal delivery of an antipsychotic peptide. J. Control. Release 2021, 330, 738–752.
Li, X. M.; Tsibouklis, J.; Weng, T. T.; Zhang, B. N.; Yin, G. Q.; Feng, G. Z.; Cui, Y. D.; Savina, I. N.; Mikhalovska, L. I.; Sandeman, S. R. et al. Nano carriers for drug transport across the blood-brain barrier. J. Drug Target. 2017, 25, 17–28.
Khatri, D. K.; Preeti, K.; Tonape, S.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Patel, M.; Shah, S.; Singh, P. K.; Srivastava, S.; Gugulothu, D.; Vora, L. et al. Nanotechnological advances for nose to brain delivery of therapeutics to improve the Parkinson therapy. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2023, 21, 493–516.
Kumar, A.; Pandey, A. N.; Jain, S. K. Nasal-nanotechnology: Revolution for efficient therapeutics delivery. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 671–683.
Hu, Y.; Jiang, K.; Wang, D. L.; Yao, S. Y.; Lu, L. W.; Wang, H.; Song, J.; Zhou, J. F.; Fan, X. Y.; Wang, Y. et al. Core–shell lipoplexes inducing active macropinocytosis promote intranasal delivery of c-Myc siRNA for treatment of glioblastoma. Acta Biomater. 2022, 138, 478–490.
Tian, Y.; Zheng, Z. Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, S. Z.; Gu, L. W.; Mu, J.; Zheng, X. J.; Li, Y. J.; Shen, S. Establishment and evaluation of glucose-modified nanocomposite liposomes for the treatment of cerebral malaria. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 318.
Gadhave, D.; Tupe, S.; Tagalpallewar, A.; Gorain, B.; Choudhury, H.; Kokare, C. Nose-to-brain delivery of amisulpride-loaded lipid-based poloxamer-gellan gum nanoemulgel: In vitro and in vivo pharmacological studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 607, 121050.
Shen, X.; Cui, Z. X.; Wei, Y. D.; Huo, Y. N.; Yu, D.; Zhang, X.; Mao, S. R. Exploring the potential to enhance drug distribution in the brain subregion via intranasal delivery of nanoemulsion in combination with borneol as a guider. Asian J. Pharm. Sci., in press, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajps.2023.100778.
Lee, Y.; Ha, J.; Kim, M.; Kang, S. B.; Kang, M. J.; Lee, M. Antisense-oligonucleotide co-micelles with tumor targeting peptides elicit therapeutic effects by inhibiting microRNA-21 in the glioblastoma animal models. J. Adv. Res., in press, https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JARE.2023.01.005.
Saini, S.; Sharma, T.; Jain, A.; Kaur, H.; Katare, O. P.; Singh, B. Systematically designed chitosan-coated solid lipid nanoparticles of ferulic acid for effective management of Alzheimer’s disease: A preclinical evidence. Colloids Surf. B: Biointerf. 2021, 205, 111838.
Zhou, C.; Sun, P.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y. A.; Huang, Y. X.; Hamblin, M. H.; Foley, L.; Hitchens, T. K.; Li, S.; Yin, K. J. Genetic deficiency of microRNA-15a/16-1 confers resistance to neuropathologicaldamage and cognitive dysfunction in experimental vascular cognitive impairment and dementia. Adv. Sci. (Weinh.) 2022, 9, 2104986.
Zhuang, X. Y.; Teng, Y.; Samykutty, A.; Mu, J. Y.; Deng, Z. B.; Zhang, L. F.; Cao, P. X.; Rong, Y.; Yan, J.; Miller, D. et al. Grapefruit-derived nanovectors delivering therapeutic miR17 through an intranasal route inhibit brain tumor progression. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 96–105.
Khan, A.; Aqil, M.; Imam, S. S.; Ahad, A.; Sultana, Y.; Ali, A.; Khan, K. Temozolomide loaded nano lipid based chitosan hydrogel for nose to brain delivery: Characterization, nasal absorption, histopathology and cell line study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 1260–1267.
Guo, S. W.; Perets, N.; Betzer, O.; Ben-Shaul, S.; Sheinin, A.; Michaelevski, I.; Popovtzer, R.; Offen, D.; Levenberg, S. Intranasal delivery of mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes loaded with phosphatase and tensin homolog sirna repairs complete spinal cord injury. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 10015–10028.
Abdelmonem, R.; El-Enin, H. A. A.; Abdelkader, G.; Abdel-Hakeem, M. Formulation and characterization of lamotrigine nasal insert targeted brain for enhanced epilepsy treatment. Drug Deliv. 2023, 30, 2163321.
Singh, S. K.; Hidau, M. K.; Gautam, S.; Gupta, K.; Singh, K. P.; Singh, S. K.; Singh, S. Glycol chitosan functionalized asenapine nanostructured lipid carriers for targeted brain delivery: Pharmacokinetic and teratogenic assessment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 1092–1100.
Zafar, A.; Alsaidan, O. A.; Alruwaili, N. K.; Imam, S. S.; Yasir, M.; Alharbi, K. S.; Singh, L.; Ahmed, M. M. Formulation of intranasal surface engineered nanostructured lipid carriers of rotigotine: Full factorial design optimization, in vitro characterization, and pharmacokinetic evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 627, 122232.
Noorulla, K. M.; Yasir, M.; Muzaffar, F.; Roshan, S.; Ghoneim, M. M.; Almurshedi, A. S.; Tura, A. J.; Alshehri, S.; Gebissa, T.; Mekit, S. et al. Intranasal delivery of chitosan decorated nanostructured lipid carriers of Buspirone for brain targeting: Formulation development, optimization and in-vivo preclinical evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 67, 102939.
See, G. L.; Arce, F.; Dahlizar, S.; Okada, A.; Fadli, M. F. B. M.; Hijikuro, I.; Itakura, S.; Katakura, M.; Todo, H.; Sugibayashi, K. Enhanced nose-to-brain delivery of tranilast using liquid crystal formulations. J. Control. Release 2020, 325, 1–9.
García-Pardo, J.; Novio, F.; Nador, F.; Cavaliere, I.; Suárez-García, S.; Lope-Piedrafita, S.; Candiota, A. P.; Romero-Gimenez, J.; Rodríguez-Galván, B.; Bové, J. et al. Bioinspired theranostic coordination polymer nanoparticles for intranasal dopamine replacement in Parkinson’s disease. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 8592–8609.
Gadhave, D.; Rasal, N.; Sonawane, R.; Sekar, M.; Kokare, C. Nose-to-brain delivery of teriflunomide-loaded lipid-based carbopol-gellan gum nanogel for glioma: Pharmacological and in vitro cytotoxicity studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 906–920.
Gieszinger, P.; Csaba, N. S.; Garcia-Fuentes, M.; Prasanna, M.; Gáspár, R.; Sztojkov-Ivanov, A.; Ducza, E.; Márki, Á.; Janáky, T.; Kecskeméti, G. et al. Preparation and characterization of lamotrigine containing nanocapsules for nasal administration. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 153, 177–186.
Bhattamisra, S. K.; Shak, A. T.; Xi, L. W.; Safian, N. H.; Choudhury, H.; Lim, W. M.; Shahzad, N.; Alhakamy, N. A.; Anwer, M. K.; Radhakrishnan, A. K. et al. Nose to brain delivery of rotigotine loaded chitosan nanoparticles in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells and animal model of Parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 579, 119148.
Nakao, Y.; Horiguchi, M.; Nakamura, R.; Sasaki-Hamada, S.; Ozawa, C.; Funane, T.; Ozawa, R.; Oka, J. I.; Yamashita, C. LARETH-25 and β-CD improve central transitivity and central pharmacological effect of the GLP-2 peptide. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 515, 37–45.
Al-Suhaimi, E. A.; Nawaz, M.; Khan, F. A.; Aljafary, M. A.; Baykal, A.; Homeida, A. M. Emerging trends in the delivery of nanoformulated oxytocin across blood-brain barrier. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 609, 121141.
Borrajo, M. L.; Alonso, M. J. Using nanotechnology to deliver biomolecules from nose to brain—peptides, proteins, monoclonal antibodies and RNA. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 862–880.
Sharma, M.; Waghela, S.; Mhatre, R.; Saraogi, G. K. A recent update on intranasal delivery of high molecular weight proteins, peptides, and hormones. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 4279–4299.
González, L. F.; Acuña, E.; Arellano, G.; Morales, P.; Sotomayor, P.; Oyarzun-Ampuero, F.; Naves, R. Intranasal delivery of interferon-β-loaded nanoparticles induces control of neuroinflammation in a preclinical model of multiple sclerosis: A promising simple, effective, non-invasive, and low-cost therapy. J. Control. Release 2021, 331, 443–459.
Zhao, Y. Z.; Lin, M.; Lin, Q.; Yang, W.; Yu, X. C.; Tian, F. R.; Mao, K. L.; Yang, J. J.; Lu, C. T.; Wong, H. L. Intranasal delivery of bFGF with nanoliposomes enhances in vivo neuroprotection and neural injury recovery in a rodent stroke model. J. Control. Release 2016, 224, 165–175.
Zhou, X.; Deng, X. H.; Liu, M. F.; He, M. T.; Long, W. H.; Xu, Z. B.; Zhang, K.; Liu, T.; So, K. F.; Fu, Q. L. et al. Intranasal delivery of BDNF-loaded small extracellular vesicles for cerebral ischemia therapy. J. Control. Release 2023, 357, 1–19.
Bernocchi, B.; Carpentier, R.; Lantier, I.; Ducournau, C.; Dimier-Poisson, I.; Betbeder, D. Mechanisms allowing protein delivery in nasal mucosa using NPL nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2016, 232, 42–50.
Henninger, N.; Mayasi, Y. Nucleic acid therapies for ischemic stroke. Neurotherapeutics 2019, 16, 299–313.
Shah, P.; Lalan, M.; Barve, K. Intranasal delivery: An attractive route for the administration of nucleic acid based therapeutics for CNS disorders. Front Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 974666.
Rupaimoole, R.; Slack, F. J. MicroRNA therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 203–222.
Zheng, T.; Wang, W. T.; Mohammadniaei, M.; Ashley, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, N. L.; Shen, J.; Sun, Y. Anti-microRNA-21 oligonucleotide loaded spermine-modified acetalated dextran nanoparticles for B1 receptor-targeted gene therapy and antiangiogenesis therapy. Adv. Sci. (Weinh.) 2022, 9, 2103812.
Lee, Y.; Kim, M.; Ha, J.; Lee, M. Brain-targeted exosome-mimetic cell membrane nanovesicles with therapeutic oligonucleotides elicit anti-tumor effects in glioblastoma animal models. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2022, 8, e10426.
Ha, J.; Kim, M.; Lee, Y.; Lee, M. Intranasal delivery of self-assembled nanoparticles of therapeutic peptides and antagomirs elicits anti-tumor effects in an intracranial glioblastoma model. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 14745–14759.
Kim, M.; Lee, Y.; Lee, M. Hypoxia-specific anti-RAGE exosomes for nose-to-brain delivery of anti-miR-181a oligonucleotide in an ischemic stroke model. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 14166–14178.
Dong, Y. Z.; Siegwart, D. J.; Anderson, D. G. Strategies, design, and chemistry in siRNA delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 144, 133–147.
Whitehead, K. A.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D. G. Knocking down barriers: Advances in siRNA delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 129–138.
Tang, L.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y. S.; Zhang, X. Y.; Yang, Y. L.; Zhao, B. Y.; Yang, L. A simple self-assembly nanomicelle based on brain tumor-targeting peptide-mediated siRNA delivery for glioma immunotherapy via intranasal administration. Acta Biomater. 2023, 155, 521–537.
Yang, Y. L.; Zhang, X. Y.; Wu, S. W.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, B. L.; Zhang, X. Y.; Tang, L.; Tian, Y. M.; Men, K.; Yang, L. Enhanced nose-to-brain delivery of siRNA using hyaluronan-enveloped nanomicelles for glioma therapy. J. Control. Release 2022, 342, 66–80.
Yang, X. T.; Yang, W. Q.; Xia, X.; Lei, T.; Yang, Z. H.; Jia, W. F.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, G.; Gao, H. L. Intranasal delivery of BACE1 siRNA and rapamycin by dual targets modified nanoparticles for Alzheimer’s disease therapy. Small 2022, 18, 2203182.
Aly, A. E. E.; Harmon, B. T.; Padegimas, L.; Sesenoglu-Laird, O.; Cooper, M. J.; Waszczak, B. L. Intranasal delivery of pGDNF DNA nanoparticles provides neuroprotection in the rat 6-hydroxydopamine model of Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 688–701.
Aly, A. E. E.; Harmon, B.; Padegimas, L.; Sesenoglu-Laird, O.; Cooper, M. J.; Yurek, D. M.; Waszczak, B. L. Intranasal delivery of hGDNF plasmid DNA nanoparticles results in long-term and widespread transfection of perivascular cells in rat brain. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2019, 16, 20–33.
Shin, H.; Park, S. J.; Yim, Y.; Kim, J.; Choi, C.; Won, C.; Min, D. H. Recent advances in RNA therapeutics and RNA delivery systems based on nanoparticles. Adv. Therap. 2018, 1, 1800065.
Xiao, X. R.; Li, H.; Zhao, L. J.; Zhang, Y. F.; Liu, Z. C. Oligonucleotide aptamers: Recent advances in their screening, molecular conformation and therapeutic applications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 143, 112232.
Bukari, B.; Samarasinghe, R. M.; Noibanchong, J.; Shigdar, S. L. Non-invasive delivery of therapeutics into the brain: The potential of aptamers for targeted delivery. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 120.
Elnaggar, Y. S. R.; Etman, S. M.; Abdelmonsif, D. A.; Abdallah, O. Y. Intranasal piperine-loaded chitosan nanoparticles as brain-targeted therapy in Alzheimer’s disease: Optimization, biological efficacy, and potential toxicity. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 3544–3556.
Don, T. M.; Chang, W. J.; Jheng, P. R.; Huang, Y. C.; Chuang, E. Y. Curcumin-laden dual-targeting fucoidan/chitosan nanocarriers for inhibiting brain inflammation via intranasal delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 181, 835–846.
Tang, S. N.; Wang, A. P.; Yan, X. J.; Chu, L. X.; Yang, X. C.; Song, Y. N.; Sun, K. X.; Yu, X.; Liu, R. X.; Wu, Z. M. et al. Brain-targeted intranasal delivery of dopamine with borneol and lactoferrin co-modified nanoparticles for treating Parkinson’s disease. Drug Deliv. 2019, 26, 700–707.
Rassu, G.; Porcu, E. P.; Fancello, S.; Obinu, A.; Senes, N.; Galleri, G.; Migheli, R.; Gavini, E.; Giunchedi, P. Intranasal delivery of genistein-loaded nanoparticles as a potential preventive system against neurodegenerative disorders. Pharmaceutics 2018, 11, 8.
Fonseca-Santos, B.; Chorilli, M. The uses of resveratrol for neurological diseases treatment and insights for nanotechnology based-drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 589, 119832.
Wang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, M. N.; Peng, C.; Shi, S. J. Ginsenosides emerging as both bifunctional drugs and nanocarriers for enhanced antitumor therapies. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 322.
Karthika, C.; Appu, A. P.; Akter, R.; Rahman, M. H.; Tagde, P.; Ashraf, G. M.; Abdel-Daim, M. M.; Ul Hassan, S. S.; Abid, A.; Bungau, S. Potential innovation against Alzheimer’s disorder: A tricomponent combination of natural antioxidants (vitamin E, quercetin, and basil oil) and the development of its intranasal delivery. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 10950–10965.
Bandiwadekar, A.; Jose, J.; Khayatkashani, M.; Habtemariam, S.; Kashani, H. R. K.; Nabavi, S. M. Emerging novel approaches for the enhanced delivery of natural products for the management of neurodegenerative diseases. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 72, 653–676.
Xu, D.; Lu, Y. R.; Kou, N.; Hu, M. J.; Wang, Q. S.; Cui, Y. L. Intranasal delivery of icariin via a nanogel-thermoresponsive hydrogel compound system to improve its antidepressant-like activity. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 586, 119550.
Xu, D.; Qiao, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q. S.; Cui, Y. L. Alginate nanogels-based thermosensitive hydrogel to improve antidepressant-like effects of albiflorin via intranasal delivery. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 2137–2149.
Qizilbash, F. F.; Ashhar, M. U.; Zafar, A.; Qamar, Z.; Annu; Ali, J.; Baboota, S.; Ghoneim, M. M.; Alshehri, S.; Ali, A. Thymoquinone-enriched naringenin-loaded nanostructured lipid carrier for brain delivery via nasal route: In vitro prospect and in vivo therapeutic efficacy for the treatment of depression. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 656.
Dou, Y.; Zhao, D. J.; Yang, F.; Tang, Y. Q.; Chang, J. Natural phyto-antioxidant albumin nanoagents to treat advanced Alzheimer’s disease. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 30373–30382.
Wang, L. T.; Xu, L.; Du, J. F.; Zhao, X.; Liu, M.; Feng, J. F.; Hu, K. L. Nose-to-brain delivery of borneol modified tanshinone IIA nanoparticles in prevention of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 1363–1375.
Ali, J.; Ali, M.; Baboota, S.; Sahni, J. K.; Ramassamy, C.; Dao, L.; Bhavna. Potential of nanoparticulate drug delivery systems by intranasal administration. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 1644–1653.
Shahi, S. R.; Pardeshi, C. V. Chapter 21—A technology overview on advanced drug administration devices for effective nose-to-brain delivery. In Direct Nose-to-Brain Drug Delivery. Pardeshi, C. V.; Souto, E. B., Eds.; Academic Press, 2021; pp 417–427.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the STI 2030-Major Projects (No. 2021ZD0201602).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Y., Pan, X., Yu, T. et al. Intranasal administration nanosystems for brain-targeted drug delivery. Nano Res. 16, 13077–13099 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6026-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6026-y