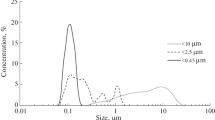
Abstract
Dust particles emitted from smelters can be hazardous to ecosystems and humans, as they are often enriched in metallic compounds. Here, we combined multi-method mineralogical analysis with a sophisticated size sorting approach for copper smelting dust to study the nanosize-effect on heavy metal distribution, which has hitherto been underestimated. Three types of dust were collected from a copper flash smelter and then size-sorted using a Dekati low-pressure impactor. Results showed that all three samples could easily sort out nanoscale dust particles (< 1 µm, grades 10–2) and even those smaller than 100 nm (grades 5–2). Especially for electrostatic precipitators dust, the mass fraction of nanoscale dust (< 1 µm) could reach 10.71%. The presence of heavy metals (Pb, Zn, Cu, and As) and their mineral species in dust was examined at various particle sizes. It was discovered that different heavy metals are enriched on nanoparticles in specific sizes. In micron-sized particles, heavy metals are generally found in discrete phases (e.g., CuSO4, PbSO4, and As2O3). In nanoscale particles, the dominant phase is Fe3O4, while heavy metals are mostly found in lattice substitution (e.g., CuFe2O4 and ZnFe2O4). Two distinct nano-dust morphologies were found: One with irregular mesh or chain structures consisting of particles of a few nanometers, and the other with polygonal crystals in larger sizes of hundreds of nanometers. The enrichment of heavy metals in the latter morphology is more pronounced, possibly because lattice substitution of heavy metals is more likely to occur when polycrystalline particles are formed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rabha, S.; Subramanyam, K. S. V.; Sawant, S. S.; Saikia, B. K. Rare-earth elements and heavy metals in atmospheric particulate matter in an urban area. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2022, 6, 1725–1732.
Liu, B.; Ma, Y. R.; Zhao, D. Y.; Xu, L. H.; Liu, F. S.; Zhou, W.; Guo, L. Effects of morphology and concentration of CuS nanoparticles on alignment and electro-optic properties of nematic liquid crystal. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 618–625.
Zhang, J. W.; Sun, X. H.; Deng, J. G.; Li, G. L.; Li, Z. J.; Jiang, J. K.; Wu, Q. R.; Duan, L. Emission characteristics of heavy metals from a typical copper smelting plant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127311.
Fang, W. X.; Yang, Y. C.; Xu, Z. M. PM10 and PM2.5 and health risk assessment for heavy metals in a typical factory for cathode ray tube television recycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 12469–12476.
Han, J. K.; Yu, D. X.; Wu, J. Q.; Yu, X.; Liu, F. Q.; Wang, J. H.; Xu, M. H. Fine ash formation and slagging deposition during combustion of silicon-rich biomasses and their blends with a low-rank coal. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 5875–5882.
Kong, S. F.; Lu, B.; Ji, Y. Q.; Zhao, X. Y.; Bai, Z. P.; Xu, Y. H.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, H. Risk assessment of heavy metals in road and soil dusts within PM2.5, PM10 and PM100 fractions in Dongying city, Shandong Province, China. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 791–803.
Wen, C.; Gao, X. P.; Yu, Y.; Wu, J. Q.; Xu, M. H.; Wu, H. W. Emission of inorganic PM10 from included mineral matter during the combustion of pulverized coals of various ranks. Fuel 2015, 140, 526–530.
Selivanov, E. N.; Tyushnyakov, S. N.; Pankratov, A. A. Forms of zinc occurrence in blast-furnace dust. Metallrrgist 2018, 22, 225–230.
Bi, X. Y.; Feng, X. B.; Yang, Y. G.; Qiu, G. L.; Li, G. H.; Li, F. L.; Liu, T. Z.; Fu, Z. Y.; Jin, Z. S. Environmental contamination of heavy metals from zinc smelting areas in Hezhang County, western Guizhou, China. Environment International 2006, 32, 883–890.
Meza-Figueroa, D.; Barboza-Flores, M.; Romero, F. M.; Acosta-Elias, M.; Hernández-Mendiola, E.; Maldonado-Escalante, F.; Pérez-Segura, E.; González-Grijalva, B.; Meza-Montenegro, M.; García-Rico, L. et al. Metal bioaccessibility, particle size distribution and polydispersity of playground dust in synthetic lysosomal fluids. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136481.
Zhou, S. L.; Wei, W. D.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z. K.; Liu, Z. H.; Wang, Y.; Kong, J. Y.; Li, J. S. Impact of a coal-fired power plant shutdown campaign on heavy metal emissions in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 14063–14069.
Gao, P.; Hu, J.; Song, J.; Chen, X.; Ou, C. Y.; Wang, H.; Sha, C. Y.; Hang, J.; Xing, B. S. Inhalation bioaccessibility of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in heavy PM25 pollution days: Implications for public health risk assessment in northern China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113296.
Trinkel, V.; Mallow, O.; Aschenbrenner, P.; Rechberger, H.; Fellner, J. Characterization of blast furnace sludge with respect to heavy metal distribution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 5590–5597.
Sui, Z.; Zhang, Y. S.; Peng, Y.; Norris, P.; Cao, Y.; Pan, W. P. Fine particulate matter emission and size distribution characteristics in an ultra-low emission power plant. Fuel 2016, 185, 863–871.
Zhang, W. J.; Che, J. Y.; Xia, L.; Wen, P. C.; Chen, J.; Ma, B. Z.; Wang, C. Y. Efficient removal and recovery of arsenic from copper smelting flue dust by a roasting method: Process optimization, phase transformation and mechanism investigation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125232.
Singh, N.; Tiwari, E.; Khandelwal, N.; Darbha, G. K. Understanding the stability of nanoplastics in aqueous environments: Effect of ionic strength, temperature, dissolved organic matter, clay, and heavy metals. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 2968–2976.
Miao, A. J.; Zhang, X. Y.; Luo, Z. P.; Chen, C. S.; Chin, W. C.; Santschi, P. H.; Quigg, A. Zinc oxide-engineered nanoparticles: Dissolution and toxicity to marine phytoplankton. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 29, 2814–2822.
Martín, M. I.; López-Delgado, A.; López, F. A.; Coedo, A. G.; Dorado, M. T.; Alguacil, F. J. Treatment of copper converter flue dust for the separation of metallic/non-metallic copper by hydrometallurgical processing. J. Chem. Eng. Japan 2003, 36, 1498–1502.
Frenklach, M.; Wang, H. Detailed modeling of soot particle nucleation and growth. Symp. (Int.) Combust. 1991, 23, 1559–1566.
Yli-Penttilä, J. T.; Peuraniemi, E. J.; Jokilaakso, A.; Riihilahti, K. M. Dust formation in flash oxidation of copper matte particles. Min. Metall. Explor. 1998, 15, 41–47.
Sobanska, S.; Ricq, N.; Laboudigue, A.; Guillermo, R.; Brémard, C.; Laureyns, J.; Merlin, J. C.; Wignacourt, J. P. Microchemical investigations of dust emitted by a lead smelter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1334–1339.
Barakat, M. A. The pyrometallurgical processing of galvanizing zinc ash and flue dust. JOM 2003, 55, 26–29.
Okanigbe, D. O.; Popoola, A. P. I.; Adeleke, A. A. Thermal analysis and kinetics of the oxidative roasting process of a copper smelter dust. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 94, 2393–2400.
Selivanov, G. N.; Skopov, G. V.; Gulyaeva, R. I.; Matveev, A. V. Material composition of the dust from the electrostatic precipitators of a Vanyukov furnace at the Middle Ural Copper Smelter. Metallurgist 2014, 58, 431–435.
Wen, C.; Fan, B.; Wang, W. Y.; Zeng, X. P.; Yu, G.; Lv, W. Z.; Xu, M. H. Preliminary research on the effects of coal devolatilization and char combustion processes on the emission of particulate matter during lignite combustion under air and oxy-fuel conditions. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 224–230.
Conway, J. R.; Adeleye, A. S.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.; Keller, A. A. Aggregation, dissolution, and transformation of copper nanoparticles in natural waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 2749–2756.
Okanigbe, D. O.; Popoola, A. P. I.; Adeleke, A. A. Hydrometallurgical processing of copper smelter dust for copper recovery as nano-particles: A review. In Proceedings of the Energy Technology 2017, Cham, 2017, pp 205–226.
Zhong, W. H.; Zhang, X. Y.; Zeng, Y. X.; Lin, D. J.; Wu, J. Recent applications and strategies in nanotechnology for lung diseases. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 2067–2089.
Shen, L. Z.; Qiao, Y. S.; Guo, Y.; Tan, J. R. Preparation of nanometer-sized black iron oxide pigment by recycling of blast furnace flue dust. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 495–500.
Mu, L.; Peng, L.; Liu, X. F.; Bai, H. L.; Song, C. F.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z. Emission characteristics of heavy metals and their behavior during coking processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6425–6430.
Silva, L. F. O.; Moreno, T.; Querol, X. An introductory TEM study of Fe-nanominerals within coal fly ash. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 4972–4974.
Duarte-Ruiz, C. A.; Pérez-Tello, M.; Parra-Sánchez, V. R.; Sohn, H. Y. The role of expansion and fragmentation phenomena on the generation and chemical composition of dust particles in a flash converting reactor. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2016, 47, 3115–3125.
Chen, Y. J.; Zhao, Z. W.; Taskinen, P.; Liang, Y. J.; Ouyang, H. C.; Peng, B.; Jokilaakso, A.; Zhou, S. L.; Chen, T.; Peng, N. et al. Characterization of copper smelting flue dusts from a bottom-blowing bath smelting furnace and a flash smelting furnace. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2020, 51, 2596–2608.
Zhou, H. H.; Liu, G. J.; Zhang, L. Q.; Zhou, C. C. Formation mechanism of arsenic-containing dust in the flue gas cleaning process of flash copper pyrometallurgy: A quantitative identification of arsenic speciation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 423, 130193.
Zhang, R. Y.; Khalizov, A.; Wang, L.; Hu, M.; Xu, W. Nucleation and growth of nanoparticles in the atmosphere. Chem. Rev. 2011, 112, 1957–2011.
Simonyan, L. M.; Govorova, N. M. Features of dust formation in the oxygen-blowing of melts and possible uses of captured dust. Metallurgist 2011, 55, 450–458.
Guo, Y. Q.; Zhang, J. Y.; Zhao, Y. C.; Wang, S. L.; Jiang, C.; Zheng, C. G. Chemical agglomeration of fine particles in coal combustion flue gas: Experimental evaluation. Fuel 2017, 203, 557–569.
Liu, X. W.; Xu, M. H.; Yao, H.; Yu, D. X.; Gao, X. P.; Cao, Q.; Cai, Y. M. Effect of combustion parameters on the emission and chemical composition of particulate matter during coal combustion. Energy Fuels 2007, 21, 157–162.
Zhou, K.; Xu, M. H.; Yu, D. X.; Liu, X. W.; Wen, C.; Zhan, Z. H.; Yao, H. Formation and control of fine potassium-enriched particulates during coal combustion. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 6266–6274.
Fu, B.; Liu, G. J.; Mian, M. M.; Sun, M.; Wu, D. Characteristics and speciation of heavy metals in fly ash and FGD gypsum from Chinese coal-fired power plants. Fuel 2019, 251, 593–602.
Wiseman, C. L. S.; Zereini, F. Characterizing metal(loid) solubility in airborne PM10, PM2.5 and PM1 in Frankfurt, Germany using simulated lung fluids. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 89, 282–289.
Sutto, T. E. Magnetite fine particle and nanoparticle environmental contamination from industrial uses of coal. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 528–533.
Wu, J. Y.; Tou, F.; Yang, Y.; Liu, C.; Hower, J. C.; Baalousha, M.; Wang, G. H.; Liu, M.; Hochella, M. F. Jr. Metal-containing nanoparticles in low-rank coal-derived fly ash from China: Characterization and implications toward human lung toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 6644–6654.
Ermolin, M. S.; Fedotov, P. S.; Ivaneev, A. I.; Karandashev, V. K.; Burmistrov, A. A.; Tatsy, Y. G. Assessment of elemental composition and properties of copper smelter-affected dust and its nano- and micron size fractions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 23781–23790.
Huang, Q.; Li, S. Q.; Shao, Y. C.; Zhao, Y. Q.; Yao, Q. Dynamic evolution of impaction and sticking behaviors of fly ash particle in pulverized coal combustion. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2019, 37, 4419–4426.
Tian, S. L.; Yu, M. J.; Wang, W.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Z. Y. Investigating the speciation of copper in secondary fly ash by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 9084–9088.
Gogos, A.; Thalmann, B.; Voegelin, A.; Kaegi, R. Sulfidation kinetics of copper oxide nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 1733–1741.
Assa, F.; Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H.; Ajamein, H.; Anarjan, N.; Vaghari, H.; Sayyar, Z.; Berenjian, A. A biotechnological perspective on the application of iron oxide nanoparticles. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 2203–2225.
Orac, D.; Laubertova, M.; Piroskova, J.; Klein, D.; Bures, R.; Klimko, J. Characterization of dusts from secondary copper production. J. Min. Metall. B: Metall. 2020, 56, 221–228.
Wang, G.; Ma, Z. Z.; Deng, J. G.; Li, Z.; Duan, L.; Zhang, Q.; Hao, J. M.; Jiang, J. K. Characteristics of particulate matter from four coal-fired power plants with low-low temperature electrostatic precipitator in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 455–461.
Liu, W. Z.; Weng, C. Z.; Zheng, J. Y.; Peng, X. Q.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Z. Emerging investigator series: Treatment and recycling of heavy metals from nanosludge. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 1657–1673.
Lastra-Quintero, R.; Rowlands, N.; Rao, S. R.; Finch, J. A. Characterization and separation of a copper smelter dust residue. Can. Metall. Quart. 1987, 26, 85–90.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Foundation for Innovative Research Groups of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52121004), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 22276218 and 52022111), and Major program Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province of China (No. 2021JC0001), and Science and Technology Innovation Program of Hunan Province (No. 2021RC3013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2023_5926_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Nanosize-effect on the distribution of heavy metals in copper smelting dust: Based on sophisticated dust sorting approach
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, K., Liao, Z., Ye, H. et al. Nanosize-effect on the distribution of heavy metals in copper smelting dust: Based on sophisticated dust sorting approach. Nano Res. 17, 312–320 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5926-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5926-1