Abstract
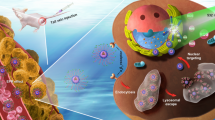
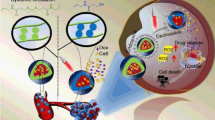
Although anti-cancer nanotherapeutics have made breakthroughs, many remain clinically unsatisfactory due to limited delivery efficiency and complicated biological barriers. Here, we prepared charge-reversible crosslinked nanoparticles (PDC NPs) by supramolecular self-assembly of pro-apoptotic peptides and photosensitizers, followed by crosslinking the self-assemblies with polyethylene glycol to impart tumor microenvironment responsiveness and charge-reversibility. The resultant PDC NPs have a high drug loading of 68.3%, substantially exceeding that of 10%–15% in conventional drug delivery systems. PDC NPs can overcome the delivery hurdles to significantly improve the tumor accumulation and endocytosis of payloads by surface charge reversal and responsive crosslinking strategy. Pro-apoptotic peptides target the mitochondrial membranes and block the respiratory effect to reduce local oxygen consumption, which extensively augments oxygen-dependent photodynamic therapy (PDT). The photosensitizers around mitochondria increased along with the peptides, allowing PDT to work with pro-apoptotic peptides synergistically to induce tumor cell death by mitochondria-dependent apoptotic pathways. Our strategy would provide a valuable reference for improving the delivery efficiency of hydrophilic peptides and developing mitochondrial-targeting cancer therapies.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acar, H.; Ting, J. M.; Srivastava, S.; LaBelle, J. L.; Tirrell, M. V. Molecular engineering solutions for therapeutic peptide delivery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 6553–6569.
Niu, Z. G.; Conejos-Sánchez, I.; Griffin, B. T.; O’Driscoll, C. M.; Alonso, M. J. Lipid-based nanocarriers for oral peptide delivery. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2016, 106, 337–354.
Stuart, M. A. C.; Huck, W. T. S.; Genzer, J.; Müller, M.; Ober, C.; Stamm, M.; Sukhorukov, G. B.; Szleifer, I.; Tsukruk, V. V.; Urban, M. et al. Emerging applications of stimuli-responsive polymer materials. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 101–113.
Peer, D.; Karp, J. M.; Hong, S.; Farokhzad, O. C.; Margalit, R.; Langer, R. Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 751–760.
Zhang, M. J.; Shao, W. X.; Yang, T. R.; Liu, H. L.; Guo, S.; Zhao, D. Y.; Weng, Y. H.; Liang, X. J.; Huang, Y. Y. Conscription of immune cells by light-activatable silencing NK-derived exosome (LASNEO) for synergetic tumor eradication. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2201135.
Sun, Q. H.; Zhou, Z. X.; Qiu, N. S.; Shen, Y. Q. Rational design of cancer nanomedicine: Nanoproperty integration and synchronization. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606628.
Ding, Y. Y.; Wang, Y. X.; Hu, Q. Y. Recent advances in overcoming barriers to cell-based delivery systems for cancer immunotherapy. Exploration 2022, 2, 20210106.
Moghimi, S. M.; Szebeni, J. Stealth liposomes and long circulating nanoparticles: Critical issues in pharmacokinetics, opsonization and protein-binding properties. Prog. Lipid Res. 2003, 42, 463–478.
Owens III, D. E.; Peppas, N. A. Opsonization, biodistribution, and pharmacokinetics of polymeric nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 307, 93–102.
Guan, X. W.; Guo, Z. P.; Lin, L.; Chen, J.; Tian, H. Y.; Chen, X. S. Ultrasensitive pH triggered charge/size dual-rebound gene delivery system. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 6823–6831.
Li, L. M.; Lindstrom, A. R.; Birkeland, A. C.; Tang, M. H.; Lin, T. Y.; Zhou, Y. K.; Xiang, B.; Xue, X. D.; Li, Y. P. Deep tumor-penetrating nano-delivery strategy to improve diagnosis and therapy in patient-derived xenograft (PDX) oral cancer model and patient tissue. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 2927–2937.
Xue, X. D.; Huang, Y.; Bo, R. N.; Jia, B.; Wu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Z. L.; Ma, Z.; Jing, D.; Xu, X. B. et al. Trojan Horse nanotheranostics with dual transformability and multifunctionality for highly effective cancer treatment. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3653.
Xue, X. D.; Qu, H. J.; Bo, R. N.; Zhang, D. L.; Zhu, Z.; Xiang, B.; Li, L. M.; Ricci, M.; Pan, C. X.; Lin, T. Y. et al. A transformable nanoplatform with multiple therapeutic and immunostimulatory properties for treatment of advanced cancers. Biomaterials 2023, 299, 122145.
Chen, S.; Rong, L.; Lei, Q.; Cao, P. X.; Qin, S. Y.; Zheng, D. W.; Jia, H. Z.; Zhu, J. Y.; Cheng, S. X.; Zhuo, R. X. et al. A surface charge-switchable and folate modified system for co-delivery of proapoptosis peptide and p53 plasmid in cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2016, 77, 149–163.
Muttenthaler, M.; King, G. F.; Adams, D. J.; Alewood, P. F. Trends in peptide drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2021, 20, 309–325.
Zhu, W. J.; Yang, Y.; Jin, Q. T.; Chao, Y.; Tian, L. L.; Liu, J. J.; Dong, Z. L.; Liu, Z. Two-dimensional metal-organic-framework as a unique theranostic nano-platform for nuclear imaging and chemo-photodynamic cancer therapy. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 1307–1312.
Dolmans, D. E. J. G. J.; Fukumura, D.; Jain, R. K. Photodynamic therapy for cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 380–387.
Ellerby, H. M.; Arap, W.; Ellerby, L. M.; Kain, R.; Andrusiak, R.; Del Rio, G.; Krajewski, S.; Lombardo, C. R.; Rao, R.; Ruoslahti, E. et al. Anti-cancer activity of targeted pro-apoptotic peptides. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 1032–1038.
Javadpour, M. M.; Juban, M. M.; Lo, W. C. J.; Bishop, S. M.; Alberty, J. B.; Cowell, S. M.; Becker, C. L.; McLaughlin, M. L. De novo antimicrobial peptides with low mammalian cell toxicity. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 3107–3113.
Yan, J. Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, N.; Yang, Y. D.; Zhu, W. W.; Li, L.; He, B. Mitochondria-targeted tetrahedral DNA nanostructures for doxorubicin delivery and enhancement of apoptosis. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 492–503.
Wang, D. M.; Chen, L.; Wang, M. Y.; Cui, M. Y.; Huang, L. L.; Xia, W.; Guan, X. G. Delivering proapoptotic peptide by HSP nanocage for cancer therapy. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2020, 221, 2000003.
An, H. W.; Mamuti, M.; Wang, X. F.; Yao, H. D.; Wang, M. D.; Zhao, L. N.; Li, L. L. Rationally designed modular drug delivery platform based on intracellular peptide self-assembly. Exploration 2021, 1, 20210153.
Levin, A.; Hakala, T. A.; Schnaider, L.; Bernardes, G. J. L.; Gazit, E.; Knowles, T. P. J. Biomimetic peptide self-assembly for functional materials. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2020, 4, 615–634.
Xue, X. D.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X. S.; Wang, Z. L.; Carney, R. P.; Li, X. C.; Yuan, Y.; He, Y. X.; Lin, T. Y.; Li, Y. P. Self-indicating, fully ]active pharmaceutical ingredients nanoparticles (FAPIN) for multimodal imaging guided trimodality cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2018, 161, 203–215.
Xue, X. D.; Zhao, Y. Y.; Dai, L. R.; Zhang, X.; Hao, X. H.; Zhang, C. Q.; Huo, S. D.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Kumar, A. et al. Spatiotemporal drug release visualized through a drug delivery system with tunable aggregation-induced emission. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 712–717.
Liang, Y. S.; Zhi, S.; Qiao, Z. X.; Meng, F. C. Predicting blood-brain barrier permeation of erlotinib and JCN037 by molecular simulation. J. Membr. Biol. 2023, 256, 147–157.
Xue, X. D.; Qu, H. J.; Li, Y. P. Stimuli-responsive crosslinked nanomedicine for cancer treatment. Exploration 2022, 2, 20210134.
Qu, H. J.; Chen, H.; Cheng, W.; Wang, Y. J.; Xia, Y. Y.; Zhang, L. H.; Ma, B. Y.; Hu, R.; Xue, X. D. A supramolecular assembly strategy for hydrophilic drug delivery towards synergistic cancer treatment. Acta Biomater. 2023, 164, 407–421.
Zhang, X. L.; Zhang, C. N.; Cheng, M. B.; Zhang, Y. H.; Wang, W.; Yuan, Z. Dual pH-responsive “charge-reversal like” gold nanoparticles to enhance tumor retention for chemo-radiotherapy. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 2815–2826.
Lu, M.; Xing, H. N.; Shao, W. X.; Wu, P. F.; Fan, Y. C.; He, H. N.; Barth, S.; Zheng, A. P.; Liang, X. J.; Huang, Y. Y. Antitumor synergism between PAK4 silencing and immunogenic phototherapy of engineered extracellular vesicles. Acta Pharm. Sin. B, in press, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2023.03.020.
Lu, M.; Xing, H. N.; Shao, W. X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, M. J.; Wang, Y. C.; Li, F. Z.; Weng, Y. H.; Zheng, A. P.; Huang, Y. Y. et al. Photoactivatable silencing extracellular vesicle (PASEV) sensitizes cancer immunotherapy. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2204765.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 82172084 and 81803002) and STI2030-Major Projects (No. 2022ZD0212500). Scheme is created with BioRender.com.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
12274_2023_5912_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Charge-reversible crosslinked nanoparticle for pro-apoptotic peptide delivery and synergistic photodynamic cancer therapy
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, H., Chen, H., Cheng, W. et al. Charge-reversible crosslinked nanoparticle for pro-apoptotic peptide delivery and synergistic photodynamic cancer therapy. Nano Res. 16, 13267–13282 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5912-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5912-7