Abstract
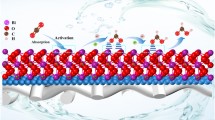
Formic acid is considered one of the most economically viable products for electrocatalytic CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR). However, developing highly active and selective electrocatalysts for effective CO2 conversion remains a grand challenge. Herein, we report that structural modulation of the bismuth oxide nanosheet via Zn2+ cooperation has a profound positive effect on exposure of the active plane, thereby contributing to high electrocatalytic CO2RR performance. The obtained Zn-Bi2O3 catalyst demonstrates superior selectivity towards formate generation in a wide potential range; a high Faradaic efficiency of 95% and a desirable partial current density of around 20 mA·cm−2 are obtained at −0.9 V (vs. reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE)). As proposed by density functional theory calculations, Zn substitution is the most energetically feasible for forming and stabilizing the key OCHO* intermediate among the used metal ions. Moreover, the more negative adsorption energy of OCHO* and the relatively low energy barrier for the desorption of HCOOH* are responsible for the enhanced activity and selectivity.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ager, J. W.; Lapkin, A. A. Chemical storage of renewable energy. Science 2018, 360, 707–708.
Cheng, H. F.; Liu, Y. M.; Wu, J. W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X. G.; Wang, X.; Fan, H. J. Concurrent H2 generation and formate production assisted by CO2 absorption in one electrolyzer. Small Methods 2021, 5, 2100871.
Gong, Q. F.; Ding, P.; Xu, M. Q.; Zhu, X. R.; Wang, M. Y.; Deng, J.; Ma, Q.; Han, N.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, J. et al. Structural defects on converted bismuth oxide nanotubes enable highly active electrocatalysis of carbon dioxide reduction. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2807.
Shen, C. Q.; Wang, P. T.; Li, L. G.; Huang, X. Q.; Shao, Q. Phase and structure modulating of bimetallic Cu/In nanoparticles realizes efficient electrosynthesis of syngas with wide CO/H2 ratios. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 528–534.
Liu, M.; Liu, M. X.; Wang, X. M.; Kozlov, S. M.; Cao, Z.; De Luna, P.; Li, H. M.; Qiu, X. Q.; Liu, K.; Hu, J. H. et al. Quantum-dot-derived catalysts for CO2 reduction reaction. Joule 2019, 3, 1703–1718.
Wang, H. X.; Tzeng, Y. K.; Ji, Y. F.; Li, Y. B.; Li, J.; Zheng, X. L.; Yang, A. K.; Liu, Y. Y.; Gong, Y. J.; Cai, L. L. et al. Synergistic enhancement of electrocatalytic CO2 reduction to C2 oxygenates at nitrogen-doped nanodiamonds/Cu interface. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 131–137.
Wei, Z. N.; Yue, S.; Gao, S. Y.; Cao, M. N.; Cao, R. Synergetic effects of gold-doped copper nanowires with low Au content for enhanced electrocatalytic CO2 reduction to multicarbon products. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 7777–7783.
Fan, L.; Xia, C.; Zhu, P.; Lu, Y. Y.; Wang, H. T. Electrochemical CO2 reduction to high-concentration pure formic acid solutions in an all-solid-state reactor. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3633.
Wang, L.; Nitopi, S.; Wong, A. B.; Snider, J. L.; Nielander, A. C.; Morales-Guio, C. G.; Orazov, M.; Higgins, D. C.; Hahn, C.; Jaramillo, T. F. Electrochemically converting carbon monoxide to liquid fuels by directing selectivity with electrode surface area. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 702–708.
Deng, P. L.; Yang, F.; Wang, Z. T.; Chen, S. H.; Zhou, Y. Z.; Zaman, S.; Xia, B. Y. Metal-organic framework-derived carbon nanorods encapsulating bismuth oxides for rapid and selective CO2 electroreduction to formate. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 10807–10813.
Eppinger, J.; Huang, K. W. Formic acid as a hydrogen energy carrier. ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 188–195.
Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Xia, X. H.; Cai, W.; Chen, Q. G.; Chen, M. H. Metal-CO2 electrochemistry: From CO2 recycling to energy storage. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2100667.
Saha, P.; Amanullah, S.; Dey, A. Selectivity in electrochemical CO2 reduction. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 134–144.
Li, H. X.; Yue, X.; Qiu, Y. S.; Xiao, Z.; Yu, X. B.; Xue, C.; Xiang, J. H. Selective electroreduction of CO2 to formate over the coelectrodeposited Cu/Sn bimetallic catalyst. Mater. Today Energy 2021, 21, 100797.
Ma, M.; Djanashvili, K.; Smith, W. A. Controllable hydrocarbon formation from the electrochemical reduction of CO2 over Cu nanowire arrays. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6680–6684.
Gao, N.; Wang, F. M.; Ding, J. W.; Sendeku, M. G.; Yu, P.; Zhan, X. Y.; Cai, S. F.; Xiao, C. H.; Yang, R.; He, J. et al. Intercalated gold nanoparticle in 2D palladium nanosheet avoiding CO poisoning for formate production under a wide potential window. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 10344–10352.
Xie, J. F.; Wang, X. Y.; Lv, J. Q.; Huang, Y. Y.; Wu, M. X.; Wang, Y. B.; Yao, J. N. Reversible aqueous zinc-CO2 batteries based on CO2–HCOOH interconversion. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 16996–17001.
Chen, Z.; Fan, T. T.; Zhang, Y. Q.; Xiao, J.; Gao, M. R.; Duan, N. Q.; Zhang, J. W.; Li, J. H.; Liu, Q. X.; Yi, X. D. et al. Wavy SnO2 catalyzed simultaneous reinforcement of carbon dioxide adsorption and activation towards electrochemical conversion of CO2 to HCOOH. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2020, 261, 118243.
Liu, S. B.; Xiao, J.; Lu, X. F.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Lou, X. W. Efficient electrochemical reduction of CO2 to HCOOH over sub-2 nm SnO2 quantum wires with exposed grain boundaries. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 8499–8503.
Yang, Z. N.; Oropeza, F. E.; Zhang, K. H. L. P-block metal-based (Sn, In, Bi, Pb) electrocatalysts for selective reduction of CO2 to formate. APL Mater. 2020, 8, 060901.
Greeley, J.; Jaramillo, T. F.; Bonde, J.; Chorkendorff, I.; Nørskov, J. K. Computational high-throughput screening of electrocatalytic materials for hydrogen evolution. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 909–913.
Li, N. H.; Yan, P.; Tang, Y. H.; Wang, J. H.; Yu, X. Y.; Wu, H. B. In-situ formation of ligand-stabilized bismuth nanosheets for efficient CO2 conversion. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2021, 297, 120481.
Yang, H.; Han, N.; Deng, J.; Wu, J. H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y. P.; Ding, P.; Li, Y. F.; Li, Y. G.; Lu, J. Selective CO2 reduction on 2D mesoporous Bi nanosheets. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1801536.
Koh, J. H.; Won, D. H.; Eom, T.; Kim, N. K.; Jung, K. D.; Kim, H.; Hwang, Y. J.; Min, B. K. Facile CO2 electro-reduction to formate via oxygen bidentate intermediate stabilized by high-index planes of Bi dendrite catalyst. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 5071–5077.
Deng, P. L.; Wang, H. M.; Qi, R. J.; Zhu, J. X.; Chen, S. H.; Yang, F.; Zhou, L.; Qi, K.; Liu, H. F.; Xia, B. Y. Bismuth oxides with enhanced bismuth-oxygen structure for efficient electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide to formate. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 743–750.
Wu, Z. X.; Wu, H. B.; Cai, W. Q.; Wen, Z. H.; Jia, B. H.; Wang, L.; Jin, W.; Ma, T. Y. Engineering bismuth–tin interface in bimetallic aerogel with a 3D porous structure for highly selective electrocatalytic CO2 reduction to HCOOH. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 12554–12559.
Zhang, Z.; Wen, G. B.; Luo, D.; Ren, B. H.; Zhu, Y. F.; Gao, R.; Dou, H. Z.; Sun, G. R.; Feng, M.; Bai, Z. Y. et al. “Two ships in a bottle” design for Zn-Ag-O catalyst enabling selective and long-lasting CO2 electroreduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 6855–6864.
Han, N.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Deng, J.; Wu, J. H.; Li, Y. F.; Li, Y. G. Ultrathin bismuth nanosheets from in situ topotactic transformation for selective electrocatalytic CO2 reduction to formate. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1320.
Ren, J. J.; Zheng, L. C.; Su, Y. M.; Meng, P. P.; Zhou, Q. Y.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, T.; Yu, H. J. Competitive adsorption of Cd(II), Pb(II) and Cu(II) ions from acid mine drainage with zero-valent iron/phosphoric titanium dioxide: XPS qualitative analyses and DFT quantitative calculations. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 445, 136778.
Liu, S.; Cao, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, H. L.; Zhang, B. S.; Zhang, Y. M.; Zhang, L. H.; Zhang, S.; Sun, J. Efficient electrochemical reduction of CO2 promoted by the electrospun Cu1.96S/Cu tandem catalyst. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 16986–16994.
Li, M. L.; Li, W. B.; Song, W. T.; Wang, C.; Yao, Y. F.; Wu, C. P.; Luo, W. J.; Zou, Z. G. Do Cu substrates participate in Bi electrocatalytic CO2 reduction? ChemNanoMat 2021, 7, 128–133.
Yan, S.; Peng, C.; Yang, C.; Chen, Y. S.; Zhang, J. B.; Guan, A. X.; Lv, X. M.; Wang, H. Z.; Wang, Z. Q.; Sham, T. K. et al. Electron localization and lattice strain induced by surface lithium doping enable ampere-level electrosynthesis of formate from CO2. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 25741–25745.
Zheng, X. B.; Yang, J. R.; Xu, Z. F.; Wang, Q. S.; Wu, J. B.; Zhang, E. H.; Dou, S. X.; Sun, W. P.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Ru–Co pair sites catalyst boosts the energetics for the oxygen evolution reaction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202205946.
Li, L.; Cai, F. F.; Qi, F. X. Y.; Ma, D. K. Cu nanowire bridged Bi nanosheet arrays for efficient electrochemical CO2 reduction toward formate. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 841, 155789.
Liu, G. B.; Li, Z. H.; Shi, J. J.; Sun, K.; Ji, Y. J.; Wang, Z. G.; Qiu, Y. F.; Liu, Y. Y.; Wang, Z. J.; Hu, P. A. Black reduced porous SnO2 nanosheets for CO2 electroreduction with high formate selectivity and low overpotential. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2020, 260, 118134.
Yang, G.; Liang, Y. J.; Wang, K.; Yang, J.; Zeng, Z. K.; Xu, R.; Xie, X. J. Simultaneous introduction of 0D Bi nanodots and oxygen vacancies onto 1D Bi6Mo2O15 sub-microwires for synergistically enhanced photocatalysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 128098.
Chen, Z. P.; Mou, K. W.; Wang, X. H.; Liu, L. C. Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots enhance the activity of Bi2O3 nanosheets for electrochemical reduction of CO2 in a wide negative potential region. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 12790–12794.
Lee, C. W.; Hong, J. S.; Yang, K. D.; Jin, K.; Lee, J. H.; Ahn, H. Y.; Seo, H.; Sung, N. E.; Nam, K. T. Selective electrochemical production of formate from carbon dioxide with bismuth-based catalysts in an aqueous electrolyte. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 931–937.
Ma, M.; Kim, S.; Chorkendorff, I.; Seger, B. Role of ion-selective membranes in the carbon balance for CO2 electroreduction via gas diffusion electrode reactor designs. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 8854–8861.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Singapore Ministry of Education Academic Research Fund Tier 1 (Nos. RG 85/20 and 125/21), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U20A200201), China Postdoctoral Science Fund, No.3 Special Funding (Pre-Station) (No. 2021TQ007), and natural science program on basic research project of Shaanxi province (No. 2023-JC-QN-0155). The supercomputing facilities provided by Hefei Advanced Computing Center are appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2023_5824_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Active plane modulation of Bi2O3 nanosheets via Zn substitution for efficient electrocatalytic CO2 reduction to formic acid
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Wu, T., Cheng, H. et al. Active plane modulation of Bi2O3 nanosheets via Zn substitution for efficient electrocatalytic CO2 reduction to formic acid. Nano Res. 16, 10803–10809 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5824-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5824-6