Abstract
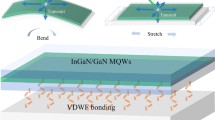
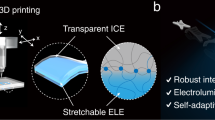
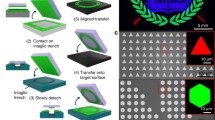
Computer vision techniques are real-time, immersive, and perceptual human-computer interaction technology. Excellent display effect, dynamic surface flexibility, and safe bio-adhesion are essential for various human–computer interaction applications, such as metaverse interfaces, skin-like sensors, and optoelectronic medical devices. However, realizing the flexible matching of inorganic optoelectronic devices and organisms remains a grand challenge for current display technologies. Here, we proposed a novel strategy by combining the optoelectronic advantages of inorganic micro light emitting diode (micro-LED) display and the extraordinary mechanical/biological compatibility of organic materials to overcome this challenge. A highly elastic (greater than 2000% strain), highly transparent (94% visible light transmittance), biocompatible conductive hydrogel composite electrode layer was fabricated. For the first time, we realized the on-chip electrical interconnection of 4900 LED units to form a blue-green light display patch with high resolution (264 PPI), low power consumption (4.4 mW) and adaptive surface attachment. This work demonstrates an integrated scheme and potential applications of flexible high-resolution microdisplays, such as wearable full-color micro-LED smart curved display devices and conformable biomedical monitoring systems.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jang, B.; Won, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Oh, M.; Lee, H. J.; Kim, J. H. Auxetic meta-display: Stretchable display without image distortion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2113299.
Zhang, Z. T.; Wang, W. C.; Jiang, Y. W.; Wang, Y. X.; Wu, Y. L.; Lai, J. C.; Niu, S. M.; Xu, C. Y.; Shih, C. C.; Wang, C. et al. High-brightness all-polymer stretchable LED with charge-trapping dilution. Nature 2022, 603, 624–630.
Lee, Y.; Chung, J. W.; Lee, G. H.; Kang, H.; Kim, J. Y.; Bae, C.; Yoo, H.; Jeong, S.; Cho, H.; Kang, S. G. et al. Standalone real-time health monitoring patch based on a stretchable organic optoelectronic system. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg9180.
Kim, D. H.; Lu, N. S.; Ma, R.; Kim, Y. S.; Kim, R. H.; Wang, S. D.; Wu, J.; Won, S. M.; Tao, H.; Islam, A. et al. Epidermal electronics. Science 2011, 333, 838–843.
Tee, B. C. K.; Wang, C.; Allen, R.; Bao, Z. N. An electrically and mechanically self-healing composite with pressure- and flexion-sensitive properties for electronic skin applications. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 825–832.
Park, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, S. Y.; Cheong, W. H.; Jang, J.; Park, Y. G.; Na, K.; Kim, Y. T.; Heo, J. H.; Lee, C. Y. et al. Soft, smart contact lenses with integrations of wireless circuits, glucose sensors, and displays. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaap9841.
Chortos, A.; Liu, J.; Bao, Z. A. Pursuing prosthetic electronic skin. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 937–950.
Wang, Z. W.; Cong, Y.; Fu, J. Stretchable and tough conductive hydrogels for flexible pressure and strain sensors. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 3437–3459.
Wagner, S.; Bauer, S. Materials for stretchable electronics. MRS Bull. 2012, 37, 207–213.
Yao, S. S.; Zhu, Y. Nanomaterial-enabled stretchable conductors: Strategies, materials and devices. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1480–1511.
Yan, C. Y.; Lee, P. S. Stretchable energy storage and conversion devices. Small 2014, 10, 3443–3460.
Park, S. I.; Xiong, Y. J.; Kim, R. H.; Elvikis, P.; Meitl, M.; Kim, D. H.; Wu, J.; Yoon, J.; Yu, C. J.; Liu, Z. J. et al. Printed assemblies of inorganic light-emitting diodes for deformable and semitransparent displays. Science 2009, 325, 977–981.
Kim, R. H.; Bae, M. H.; Kim, D. G.; Cheng, H. Y.; Kim, B. H.; Kim, D. H.; Li, M.; Wu, J.; Du, F.; Kim, H. S. et al. Stretchable, transparent graphene interconnects for arrays of microscale inorganic light emitting diodes on rubber substrates. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 3881–3886.
Kim, K.; Vöröslakos, M.; Seymour, J. P.; Wise, K. D.; Buzsáki, G.; Yoon, E. Artifact-free and high-temporal-resolution in vivo opto-electrophysiology with microLED optoelectrodes. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2063.
McCall, J. G.; Kim, T. I.; Shin, G.; Huang, X.; Jung, Y. H.; Al-Hasani, R.; Omenetto, F. G.; Bruchas, M. R.; Rogers, J. A. Fabrication and application of flexible, multimodal light-emitting devices for wireless optogenetics. Nat. Protocols 2013, 8, 2413–2428.
Lee, H. E.; Choi, J. H.; Lee, S. H.; Jeong, M.; Shin, J. H.; Joe, D. J.; Kim, D. H.; Kim, C. W.; Park, J. H.; Lee, J. H. et al. Monolithic flexible vertical GaN light-emitting diodes for a transparent wireless brain optical stimulator. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800649.
Guo, Z. V.; Li, N.; Huber, D.; Ophir, E.; Gutnisky, D.; Ting, J. T.; Feng, G. P.; Svoboda, K. Flow of cortical activity underlying a tactile decision in mice. Neuron 2014, 81, 179–194.
Packer, A. M.; Russell, L. E.; Dalgleish, H. W. P.; Hausser, M. Simultaneous all-optical manipulation and recording of neural circuit activity with cellular resolution in vivo. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 140–146.
Zeng, W.; Shu, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, F.; Tao, X. M. Fiber-based wearable electronics: A review of materials, fabrication, devices, and applications. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5310–5336.
Kim, S. H.; Jung, S.; Yoon, I. S.; Lee, C.; Oh, Y.; Hong, J. M. Ultrastretchable conductor fabricated on skin-like hydrogel-elastomer hybrid substrates for skin electronics. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800109.
Liu, Q. H.; Nian, G. D.; Yang, C. H.; Qu, S. X.; Suo, Z. G. Bonding dissimilar polymer networks in various manufacturing processes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 846.
Gan, D. L.; Xing, W. S.; Jiang, L. L.; Fang, J.; Zhao, C. C.; Ren, F. Z.; Fang, L. M.; Wang, K. F.; Lu, X. Plant-inspired adhesive and tough hydrogel based on Ag-Lignin nanoparticles-triggered dynamic redox catechol chemistry. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1487.
Yuk, H.; Zhang, T.; Lin, S. T.; Parada, G. A.; Zhao, X. H. Tough bonding of hydrogels to diverse non-porous surfaces. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 190–196.
Gan, D. L.; Huang, Z. Q.; Wang, X.; Jiang, L. L.; Wang, C. M.; Zhu, M. Y.; Ren, F. Z.; Fang, L. M.; Wang, K. F.; Xie, C. M. et al. Graphene oxide-templated conductive and redox-active nanosheets incorporated hydrogels for adhesive bioelectronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1907678.
Keplinger, C.; Sun, J. Y.; Foo, C. C.; Rothemund, P.; Whitesides, G. M.; Suo, Z. G. Stretchable, transparent, ionic conductors. Science 2011, 341, 984–987.
Shi, L.; Zhu, T. X.; Gao, G. X.; Zhang, X. Y.; Wei, W.; Liu, W. F.; Ding, S. J. Highly stretchable and transparent ionic conducting elastomers. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2630.
Qi, L. H.; Zhang, X.; Chong, W. C.; Li, P. A.; Lau, K. M. 848 ppi high-brightness active-matrix micro-LED micro-display using GaN-on-Si epi-wafers towards mass production. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 10580–10591.
Sha, W.; Hua, Q. L.; Wang, J. W.; Cong, Z. F.; Cui, X.; Ji, K. Y.; Dai, X. H.; Wang, B. J.; Guo, W. B.; Hu, W. G. Enhanced photoluminescence of flexible InGaN/GaN multiple quantum wells on fabric by piezo-phototronic effect. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 3000–3007.
Chen, J. W.; Wang, J. W.; Ji, K. Y.; Jiang, B.; Cui, X.; Sha, W.; Wang, B. J.; Dai, X. H.; Hua, Q. L.; Wan, L. Y. et al. Flexible, stretchable, and transparent InGaN/GaN multiple quantum wells/polyacrylamide hydrogel-based light emitting diodes. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 5492–5499.
Lin, S. T.; Yuk, H.; Zhang, T.; Parada, G. A.; Koo, H.; Yu, C. J.; Zhao, X. H. Stretchable hydrogel electronics and devices. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4497–4505.
Liu, K. L.; Zhang, Z. X.; Li, J. Supramolecular hydrogels based on cyclodextrin-polymer polypseudorotaxanes: Materials design and hydrogel properties. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 11290–11297.
Katsuno, C.; Konda, A.; Urayama, K.; Takigawa, T.; Kidowaki, M.; Ito, K. Pressure-responsive polymer membranes of slide-ring gels with movable cross-links. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 4636–640.
Tan, S.; Ladewig, K.; Fu, Q.; Blencowe, A.; Qiao, G. G. Cyclodextrin-based supramolecular assemblies and hydrogels: Recent advances and future perspectives. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2014, 35, 1166–1184.
Ito, K. Slide-ring materials using cyclodextrin. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 65, 326–329.
Mähler, J.; Persson, I. A study of the hydration of the alkali metal ions in aqueous solution. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 425–438.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank for the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 52173298, 61904012, and 52192611), the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2021YFA1201603), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Niu, J., Sha, W. et al. Flexible high-resolution micro-LED display device with integrations of transparent, conductive, and highly elastic hydrogel. Nano Res. 16, 11893–11899 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5731-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5731-x