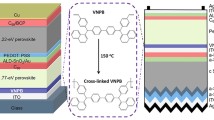
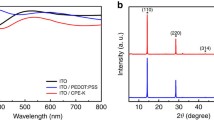
Abstract
Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) have attracted much attention due to their rapidly increased power conversion efficiencies, however, their inherent poor long-term stability hinders their commercialization. The degradation of PSCs first comes from the degradation of hole transport materials (HTMs). Here, we report the construction of periodic π-columnar arrays and ionic interfaces over the skeletons by introducing cationic covalent organic frameworks (C-COFs) to the HTM. Periodic π-columnar arrays can optimize the charge transport ability and energy levels of the hole transport layer and suppress the degradation of HTM, and ionic interfaces over the skeletons can produce stronger electric dipole and electrostatic interactions, as well as higher charge densities. The C-COFs were designed and synthesized via Schiff base reaction by using 1,3,5-triformylphloroglucinol as a neutral knot and dimidium bromide as cationic linker. The neutral COFs (N-COFs) were also synthesized as a reference by using 3,8-diamino-6-phenylphenanthridine as neutral linker. PSCs with cationic COF exhibit the highest efficiency of 23.4% with excellent humidity and thermal stability. To the best of our knowledge, this is the highest efficiency among the meso-structured PSCs fabricated by a sequential process.

Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
08 November 2023
An Erratum to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6250-5
References
Kojima, A.; Teshima, K.; Shirai, Y.; Miyasaka, T. Organometal halide perovskites as visible-light sensitizers for photovoltaic cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6050–6051.
Kim, H. S.; Lee, C. R.; Im, J. H.; Lee, K. B.; Moehl, T.; Marchioro, A.; Moon, S. J.; Humphry-Baker, R.; Yum, J. H.; Moser, J. E. et al. Lead iodide perovskite sensitized all-solid-state submicron thin film mesoscopic solar cell with efficiency exceeding 9%. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 591.
Lee, M. M.; Teuscher, J.; Miyasaka, T.; Murakami, T. N.; Snaith, H. J. Efficient hybrid solar cells based on meso-superstructured organometal halide perovskites. Science 2012, 338, 643–647.
Zhou, H. P.; Chen, Q.; Li, G.; Luo, S.; Song, T. B.; Duan, H. S.; Hong, Z. R.; You, J. B.; Liu, Y. S.; Yang, Y. Interface engineering of highly efficient perovskite solar cells. Science 2014, 345, 542–546.
Yang, W. S.; Noh, J. H.; Jeon, N. J.; Kim, Y. C.; Ryu, S.; Seo, J.; Seok, S. I. High-performance photovoltaic perovskite layers fabricated through intramolecular exchange. Science 2015, 348, 1234–1237.
Yang, W. S.; Park, B. W.; Jung, E. H.; Jeon, N. J.; Kim, Y. C.; Lee, D. U.; Shin, S. S.; Seo, J.; Kim, E. K.; Noh, J. H. et al. Iodide management in formamidinium-lead-halide-based perovskite layers for efficient solar cells. Science 2017, 356, 1376–1379.
Jiang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X. W.; Yang, X. L.; Chen, Y.; Chu, Z. M.; Ye, Q. F.; Li, X. X.; Yin, Z. G.; You, J. B. Surface passivation of perovskite film for efficient solar cells. Nat. Photonics 2019, 13, 460–466.
Jeong, M.; Choi, I. W.; Go, E. M.; Cho, Y.; Kim, M.; Lee, B.; Jeong, S.; Jo, Y.; Choi, H. W.; Lee, J. et al. Stable perovskite solar cells with efficiency exceeding 24.8% and 0.3-V voltage loss. Science 2020, 369, 1615–1620.
Yoo, J. J.; Seo, G.; Chua, M. R.; Park, T. G.; Lu, Y. L.; Rotermund, F.; Kim, Y. K.; Moon, C. S.; Jeon, N. J.; Correa-Baena, J. P. et al. Efficient perovskite solar cells via improved carrier management. Nature 2021, 590, 587–593.
Min, H.; Lee, D. Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, G.; Lee, K. S.; Kim, J.; Paik, M. J.; Kim, Y. K.; Kim, K. S.; Kim, M. G. et al. Perovskite solar cells with atomically coherent interlayers on SnO2 electrodes. Nature 2021, 598, 444–450.
NREL. Best research cell efficiencies. https://www.nrel.gov/pv/assets/pdfs/best-research-cell-efficiencies.pdf. (accessed November 6, 2022).
Chen, J. Z.; Park, N. G. Causes and solutions of recombination in perovskite solar cells. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1803019.
Zhang, J. D.; Guo, S. S.; Zhu, M. Q.; Li, C.; Chen, J. G.; Liu, L. Z.; Xiang, S. C.; Zhang, Z. J. Simultaneous defect passivation and hole mobility enhancement of perovskite solar cells by incorporating anionic metal-organic framework into hole transport materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 408, 127328.
Luo, J. S.; Xia, J. X.; Yang, H.; Chen, L. L.; Wan, Z. Q.; Han, F.; Malik, H. A.; Zhu, X. H.; Jia, C. Y. Toward high-efficiency, hysteresis-less, stable perovskite solar cells: Unusual doping of a hole-transporting material using a fluorine-containing hydrophobic Lewis acid. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 2035–2045.
Jung, E. H.; Jeon, N. J.; Park, E. Y.; Moon, C. S.; Shin, T. J.; Yang, T. Y.; Noh, J. H.; Seo, J. Efficient, stable and scalable perovskite solar cells using poly(3-hexylthiophene). Nature 2019, 567, 511–515.
Lou, Q.; Li, H. L.; Huang, Q. S.; Shen, Z. T.; Li, F. M.; Du, Q.; Jin, M. Q.; Chen, C. Multifunctional CNT:TiO2 additives in spiro-OMeTAD layer for highly efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. EcoMat 2021, 3, e12099.
Ye, S. Y.; Rao, H. X.; Yan, W. B.; Li, Y. L.; Sun, W. H.; Peng, H. T.; Liu, Z. W.; Bian, Z. Q.; Li, Y. F.; Huang, C. H. A strategy to simplify the preparation process of perovskite solar cells by co-deposition of a hole-conductor and a perovskite layer. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 9648–9654.
Chen, C.; Li, C. X.; Li, F. M.; Wu, F.; Tan, F. R.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, W. F. Efficient perovskite solar cells based on low-temperature solution-processed (CH3NH3)PbI3 perovskite/CuInS2 planar heterojunctions. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 457.
Liu, G. L.; Liu, L.; Niu, X. X.; Zhou, H. P.; Chen, Q. Effects of iodine doping on carrier behavior at the interface of perovskite crystals: Efficiency and stability. Crystals 2018, 8, 185.
Wang, S.; Huang, Z. H.; Wang, X. F.; Li, Y. M.; Günther, M.; Valenzuela, S.; Parikh, P.; Cabreros, A.; Xiong, W.; Meng, Y. S. Unveiling the role of tBP-LiTFSI complexes in perovskite solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 16720–16730.
Wang, S.; Sina, M.; Parikh, P.; Uekert, T.; Shahbazian, B.; Devaraj, A.; Meng, Y. S. Role of 4-tert-butylpyridine as a hole transport layer morphological controller in perovskite solar cells. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 5594–5600.
Lou, Q.; Lou, G.; Guo, H. L.; Sun, T.; Wang, C. Y.; Chai, G. D.; Chen, X.; Yang, G. S.; Guo, Y. Z.; Zhou, H. Enhanced efficiency and stability of n-i-p perovskite solar cells by incorporation of fluorinated graphene in the spiro-OMeTAD hole transport layer. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2201344.
Zhao, X. M.; Zhang, F.; Yi, C. Y.; Bi, D. Q.; Bi, X. D.; Wei, P.; Luo, J. S.; Liu, X. C.; Wang, S. R.; Li, X. G. et al. A novel one-step synthesized and dopant-free hole transport material for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 16330–16334.
Lee, I.; Yun, J. H.; Son, H. J.; Kim, T. S. Accelerated degradation due to weakened adhesion from Li-TFSI additives in perovskite solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 7029–7035.
Yang, K.; Liao, Q. G.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Z. L.; Su, M. Y.; Chen, Z. C.; Wu, Z. A.; Wang, D.; Lai, Z. W.; Woo, H. Y. et al. Intramolecular noncovalent interaction-enabled dopant-free hole-transporting materials for high-performance inverted perovskite solar cells. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202113749.
You, G. F.; Li, L. H.; Wang, S. Q.; Cao, J. B.; Yao, L.; Cai, W. Z.; Zhou, Z. G.; Li, K.; Lin, Z. H.; Zhen, H. Y. et al. Donor—acceptor type polymer bearing carbazole side chain for efficient dopant-free perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 12, 2102697.
Ullah, A.; Park, K. H.; Nguyen, H. D.; Siddique, Y.; Shah, S. F. A.; Tran, H.; Park, S.; Lee, S. I.; Lee, K. K.; Han, C. H. et al. Novel phenothiazine-based self-assembled monolayer as a hole selective contact for highly efficient and stable p-i-n perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2103175.
Waller, P. J.; Gándara, F.; Yaghi, O. M. Chemistry of covalent organic frameworks. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 3053–3063.
Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z. W.; Tang, L.; Zeng, G. M.; Xu, P.; Chen, M.; Xiong, T.; Zhou, C. Y.; Li, X. Y. et al. Covalent organic framework photocatalysts: Structures and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 4135–4165.
Geng, K. Y.; He, T.; Liu, R. Y.; Dalapati, S.; Tan, K. T.; Li, Z. P.; Tao, S. S.; Gong, Y. F.; Jiang, Q. H.; Jiang, D. L. Covalent organic frameworks: Design, synthesis, and functions. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 8814–8933.
Li, Y. S.; Chen, W. B.; Xing, G. L.; Jiang, D. L.; Chen, L. New synthetic strategies toward covalent organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 2852–2868.
Ding, S. Y.; Wang, W. Covalent organic frameworks (COFs): From design to applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 548–568.
Zhang, T. Y.; Gregoriou, V. G.; Gasparini, N.; Chochos, C. L. Porous organic polymers in solar cells. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 4465–4483.
Li, Z. P.; Geng, K. Y.; He, T.; Tan, K. T.; Huang, N.; Jiang, Q. H.; Nagao, Y.; Jiang, D. L. Editing light emission with stable crystalline covalent organic frameworks via wall surface perturbation. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 19419–19427.
Ma, H. P.; Liu, B. L.; Li, B.; Zhang, L. M.; Li, Y. G.; Tan, H. Q.; Zang, H. Y.; Zhu, G. S. Cationic covalent organic frameworks: A simple platform of anionic exchange for porosity tuning and proton conduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 5897–5903.
Mi, Z.; Yang, P.; Wang, R.; Unruangsri, J.; Yang, W. L.; Wang, C. C.; Guo, J. Stable radical cation-containing covalent organic frameworks exhibiting remarkable structure-enhanced photothermal conversion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 14433–14442.
Wang, H.; Qian, C.; Liu, J.; Zeng, Y. F.; Wang, D. D.; Zhou, W. Q.; Gu, L.; Wu, H. W.; Liu, G. F.; Zhao, Y. L. Integrating suitable linkage of covalent organic frameworks into covalently bridged inorganic/organic hybrids toward efficient photocatalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 4862–4871.
She, P. F.; Qin, Y. Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q. C. Recent progress in external-stimulus-responsive 2D covalent organic frameworks. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2101175.
Liang, R. R.; Jiang, S. Y.; A, R. H.; Zhao, X. Two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks with hierarchical porosity. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 3920–3951.
Li, J.; Jing, X. C.; Li, Q. Q.; Li, S. W.; Gao, X.; Feng, X.; Wang, B. Bulk COFs and COF nanosheets for electrochemical energy storage and conversion. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 3565–3604.
Yu, F.; Liu, W. B.; Ke, S. W.; Kurmoo, M.; Zuo, J. L.; Zhang, Q. C. Electrochromic two-dimensional covalent organic framework with a reversible dark-to-transparent switch. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5534.
Segura, J. L.; Mancheno, M. J.; Zamora, F. Covalent organic frameworks based on Schiff-base chemistry: Synthesis, properties and potential applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5635–5671.
Zhao, J. W.; Ren, J. Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, Z. Q.; Liu, S. Y.; Zhang, W. D.; Chen, L. Donor—acceptor type covalent organic frameworks. Chemistry 2021, 27, 10781–10797.
Xu, S. Q.; Sun, H. J.; Addicoat, M.; Biswal, B. P.; He, F.; Park, S.; Paasch, S.; Zhang, T.; Sheng, W. B.; Brunner, E. et al. Thiophene-bridged donor—acceptor sp2-carbon-linked 2D conjugated polymers as photocathodes for water reduction. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006274.
Wu, C. Y.; Liu, Y. M.; Liu, H.; Duan, C. H.; Pan, Q. Y.; Zhu, J.; Hu, F.; Ma, X. Y.; Jiu, T.; Li, Z. B. et al. Highly conjugated three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks based on spirobifluorene for perovskite solar cell enhancement. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 10016–10024.
Li, Z. P.; Zhang, Z. W.; Nie, R. M.; Li, C. Z.; Sun, Q. K.; Shi, W.; Chu, W. C.; Long, Y. Y.; Li, H.; Liu, X. M. Construction of stable donor—acceptor type covalent organic frameworks as functional platform for effective perovskite solar cell enhancement. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2112553.
He, J.; Liu, H. L.; Zhang, F.; Li, X. G.; Wang, S. R. In situ synthesized 2D covalent organic framework nanosheets induce growth of high-quality perovskite film for efficient and stable solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2110030.
Li, Y. S.; Chen, Q.; Xu, T. T.; Xie, Z.; Liu, J. J.; Yu, X.; Ma, S. Q.; Qin, T. S.; Chen, L. De novo design and facile synthesis of 2D covalent organic frameworks: A two-in-one strategy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 13822–13828.
Mohamed, M. G.; Lee, C. C.; El-Mahdy, A. F. M.; Lüder, J.; Yu, M. H.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Z. L.; Chueh, C. C.; Kuo, S. W. Exploitation of two-dimensional conjugated covalent organic frameworks based on tetraphenylethylene with bicarbazole and pyrene units and applications in perovskite solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 11448–11459.
Dogru, M.; Handloser, M.; Auras, F.; Kunz, T.; Medina, D.; Hartschuh, A.; Knochel, P.; Bein, T. A photoconductive thienothiophene-based covalent organic framework showing charge transfer towards included fullerene. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 2920–2924.
Li, Z. P.; Zhi, Y. F.; Feng, X.; Ding, X. S.; Zou, Y. C.; Liu, X. M.; Mu, Y. An azine-linked covalent organic framework: Synthesis, characterization and efficient gas storage. Chem.—Eur. J. 2015, 21, 12079–12084.
Zheng, K. H.; Ge, J. F.; Liu, C.; Lou, Q.; Chen, X.; Meng, Y. Y.; Yin, X.; Bu, S. X.; Liu, C. R.; Ge, Z. Y. Improved phase stability of CsPbI2Br perovskite by released microstrain toward highly efficient and stable solar cells. InfoMat 2021, 3, 1431–1444.
Nie, R. M.; Deng, X. Y.; Feng, L.; Hu, G. G.; Wang, Y. Y.; Yu, G.; Xu, J. B. Highly sensitive and broadband organic photodetectors with fast speed gain and large linear dynamic range at low forward bias. Small 2017, 13, 1603260.
Zheng, L. P.; Zhou, Q. M.; Deng, X. Y.; Yuan, M.; Yu, G.; Cao, Y. Methanofullerenes used as electron acceptors in polymer photovoltaic devices. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 11921–11926.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52203359), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. NS2022092), National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2019YFA0705400), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20212008), the Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Mechanics and Control of Mechanical Structures (Nos. MCMS-I-0421K01 and MCMS-I-0422K01), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. NJ2022002), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 52073119 and 21774040), and A Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nie, R., Chen, X., Li, Z. et al. Efficient and stable perovskite solar cells by build-in π-columns and ionic interfaces in covalent organic frameworks. Nano Res. 16, 9387–9397 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5603-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5603-4